Mexican Peso rallies as hope for 50 bps Fed rate cut rise
- Mexican Peso rises to a three-week peak as US Dollar drops.
- Fed rate cut expectations increase with CME FedWatch Tool showing a 43% chance of a 50 bps cut, pressuring the US Dollar.
- Political concerns in Mexico ease following the approval of the judicial reform, helping the Peso's rally.
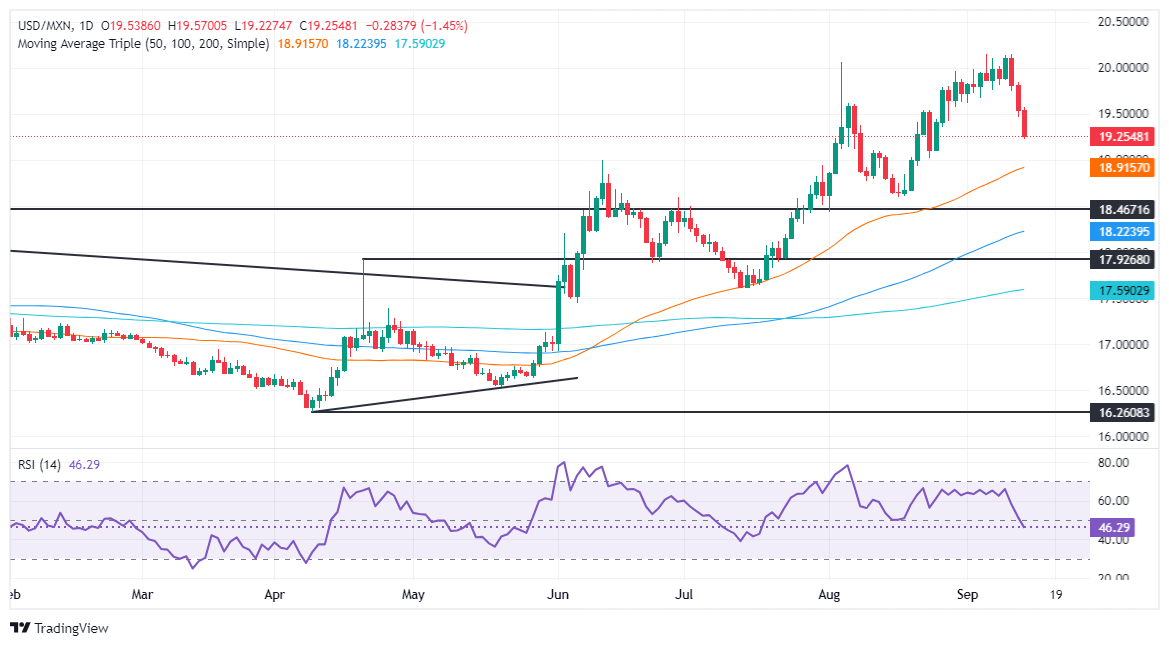
The Mexican Peso rallied for the third straight session against the US Dollar due to overall weakness on the latter. Market participants gaining confidence that the US Federal Reserve (Fed) will lower borrowing costs “aggressively” boosted the Mexican currency, which shrugged off judicial reform fears. The USD/MXN trades at 19.25, down 1.30%.
The Greenback has been the focus during the last two trading sessions. On Thursday, investors seemed confident that the Fed will cut interest rates by 0.25% due to data provided by the CME FedWatch Tool. Nevertheless, a worse-than-expected Initial Jobless Claims report overshadowed an uptick in the Producer Price Index (PPI).
On Thursday, the CME FedWatch Tool showed that the odds for a 50-basis-point Fed cut were 28%. However, at the time of writing, the chances increased to 43%; and for a 25 bps cut, diminished to 53%.
This undermined the buck, which, according to the US Dollar Index (DXY), lost 0.17%, changing hands at 101.06.
The University of Michigan (UoM) revealed that Consumer Sentiment rose to a four-month peak in September, which was helped by an improvement in inflation expectations.
Meanwhile, in Mexico, the political turbulence eased after the approval of the judicial system bill.
Gerardo Carrillo, Regional Director for LATAM at Fitch Ratings, commented on Mexico’s creditworthiness. He said, “The rating outlook is stable, which means that we are seeing a balance between strengths and weaknesses. Before observing a direct downgrade of the sovereign rating, what could be expected from us is a change in the outlook, either from stable to positive or from stable to negative, the latter probably occurring.”
On Thursday, Bank of Mexico (Banxico) Director of Economic Research Alejandrina Salcedo stated that a robust environment in the rule of law can help generate conditions that encourage investment. She added that respecting the rule of law and public safety “would provide greater certainty, boost the flow of investment in all regions, and contribute to capitalizing on the opportunities offered by the relocation process.”
Daily digest market movers: Mexican Peso is bolstered by US Dollar weakness
- USD/MXN would continue to be driven by market mood and expectations for a bigger Fed rate cut.
- Mexico’s economic docket next week will feature Aggregate Demand and Private Spending for the second quarter of 2024.
- Mexico’s Inflation dipped below 5% in August, increasing the chances of additional easing by Banxico.
- September’s Citibanamex Survey showed that Banxico is expected to lower rates to 10.25% in 2024 and to 8.25% in 2025. The USD/MXN exchange rate is forecast to end 2024 at 19.50 and 2025 at 19.85.
- The UoM Consumer Sentiment index rose from 67.9 to 69.0, exceeding estimates of 68.
- Inflation expectations improved from 2.8% to 2.7% for the one-year period. For a longer term, they rose from 3% to 3.1%.
- Greenback remained offered in the US after the US Bureau of Labor Statistics revealed that the August PPI figures were mixed. At the same time, the number of Americans filing for unemployment benefits rose as estimated and cleared the previous week's reading.
- Data from the Chicago Board of Trade suggests the Fed will cut at least 98 basis points this year, down from 108 a day ago, according to the fed funds rate futures contract for December 2024.
USD/MXN technical outlook: Mexican Peso surges as USD/MXN slumps below 19.30
The USD/MXN’s sudden pullback pushed the exotic pair more than 7,000 pips below the 20.00 psychological figure, though key support levels lie ahead. Nonetheless, momentum shifted in the sellers' favor as the Relative Strength Index (RSI) turned bearish.
Hence, in the short term, the USD/MXN is tilted to the downside. The first support would be the August 23 low of 19.02. A breach of the latter will expose the 50-day Simple Moving Average at 18.99, followed by the August 19 cycle low of 18.59.
Conversely, the USD/MXN must clear the psychological 20.00 figure for a bullish continuation. If surpassed, the next ceiling level would be the YTD high at 20.22. On further strength, the pair could challenge the daily high of September 28, 2022, at 20.57. If those two levels are surrendered, the next stop would be the swing high at 20.82 on August 2, 2022, ahead of 21.00.
Mexican Peso FAQs
The Mexican Peso (MXN) is the most traded currency among its Latin American peers. Its value is broadly determined by the performance of the Mexican economy, the country’s central bank’s policy, the amount of foreign investment in the country and even the levels of remittances sent by Mexicans who live abroad, particularly in the United States. Geopolitical trends can also move MXN: for example, the process of nearshoring – or the decision by some firms to relocate manufacturing capacity and supply chains closer to their home countries – is also seen as a catalyst for the Mexican currency as the country is considered a key manufacturing hub in the American continent. Another catalyst for MXN is Oil prices as Mexico is a key exporter of the commodity.
The main objective of Mexico’s central bank, also known as Banxico, is to maintain inflation at low and stable levels (at or close to its target of 3%, the midpoint in a tolerance band of between 2% and 4%). To this end, the bank sets an appropriate level of interest rates. When inflation is too high, Banxico will attempt to tame it by raising interest rates, making it more expensive for households and businesses to borrow money, thus cooling demand and the overall economy. Higher interest rates are generally positive for the Mexican Peso (MXN) as they lead to higher yields, making the country a more attractive place for investors. On the contrary, lower interest rates tend to weaken MXN.
Macroeconomic data releases are key to assess the state of the economy and can have an impact on the Mexican Peso (MXN) valuation. A strong Mexican economy, based on high economic growth, low unemployment and high confidence is good for MXN. Not only does it attract more foreign investment but it may encourage the Bank of Mexico (Banxico) to increase interest rates, particularly if this strength comes together with elevated inflation. However, if economic data is weak, MXN is likely to depreciate.
As an emerging-market currency, the Mexican Peso (MXN) tends to strive during risk-on periods, or when investors perceive that broader market risks are low and thus are eager to engage with investments that carry a higher risk. Conversely, MXN tends to weaken at times of market turbulence or economic uncertainty as investors tend to sell higher-risk assets and flee to the more-stable safe havens.


