US Dollar edges higher ahead of top-tier PCE and GDP data releases
- The US Dollar trades slightly higher against most major currencies.
- President Trump lashed out at Fed’s Powell again during a rally in Detroit.
- The US Dollar Index is capped below the 100.00 round level ahead of key US data.
The US Dollar Index (DXY), which tracks the performance of the US Dollar (USD) against six major currencies, edges slightly higher and trades at 99.40 at the time of writing on Wednesday. The Greenback is not really going anywhere as investors stay on the sidelines against key data releases during the American session. United States (US) President Donald Trump signed an executive order to ease the tariff impact on car parts and, during a rally in Detroit, lashed out at Federal Reserve Chairman Jerome Powell again, proclaiming Trump knows more about interest rates than Powell does.
On the economic calendar front, a general rehearsal will take place this Wednesday ahead of the Nonfarm Payrolls release on Friday. The US Gross Domestic Product (GDP) preliminary reading for Q1 will already be a vital element to assess the first impact, if any, of the administration’s tariff policy. The reading could stoke recession fears in case it shows weak growth or even contraction, while it could fire up stock markets if the initial impact of tariffs and Trump’s presidency on growth proves to be rather limited.
Daily digest market movers: Chunky data ahead
- At 12:30 GMT, the preliminary reading of the first quarter for US Gross Domestic Product is to be released. Economists expect the US economy to have grown by a modest annualized rate of 0.4%, much slower than the 2.4% expansion seen in 2024’s fourth quarter.
- In that same time span, the monthly PCE data for March will also be released. The Monthly Core PCE is expected to come in at 0.1%, down from 0.4%. The monthly headline number is expected to fall to 0%, from 0.3% previously.
- Around 13:35 GMT, the Chicago Purchasing Manager’s Index for April is due. Expectations are for a further contraction to 45.5 from 47.6.
- Equities are rather mixed, with overall losses to be reported. In the US, all futures are already pointing to red openings. After the US closing bell, Microsoft (MSFT) and Alphabet (GOOG) will report earnings.
- The CME FedWatch tool shows the chance of an interest rate cut by the Federal Reserve in the May’s meeting stands at 7.6% against a 92.4% probability of no change. The June meeting sees a 65.1% chance of a rate cut.
- The US 10-year yields trade around 4.15%, ticking lower for a second day in a row, with traders slowly but surely buying back into US bonds as rate cut bets are starting to pick up.
US Dollar Index Technical Analysis: Nothing moving
The US Dollar Index (DXY) is starting to pick up from its low levels of 2025. Bulls are slowly starting to take back control of the chart. However, risk elements persist with the uncertainty and possible further deterioration of US data likely to cause the DXY to edge substantially lower.
On the upside, the DXY’s first resistance comes in at 100.22, which supported the DXY back in September 2024, with a break back above the 100.00 round level as a bullish signal. A firm recovery would be a return to 101.90, which acted as a pivotal level throughout December 2023 and again as a base for the inverted head-and-shoulders (H&S) formation during the summer of 2024.
On the other hand, the 97.73 support could quickly be tested on any substantial bearish headline. Further below, a relatively thin technical support comes in at 96.94 before looking at the lower levels of this new price range. These would be at 95.25 and 94.56, meaning fresh lows not seen since 2022.
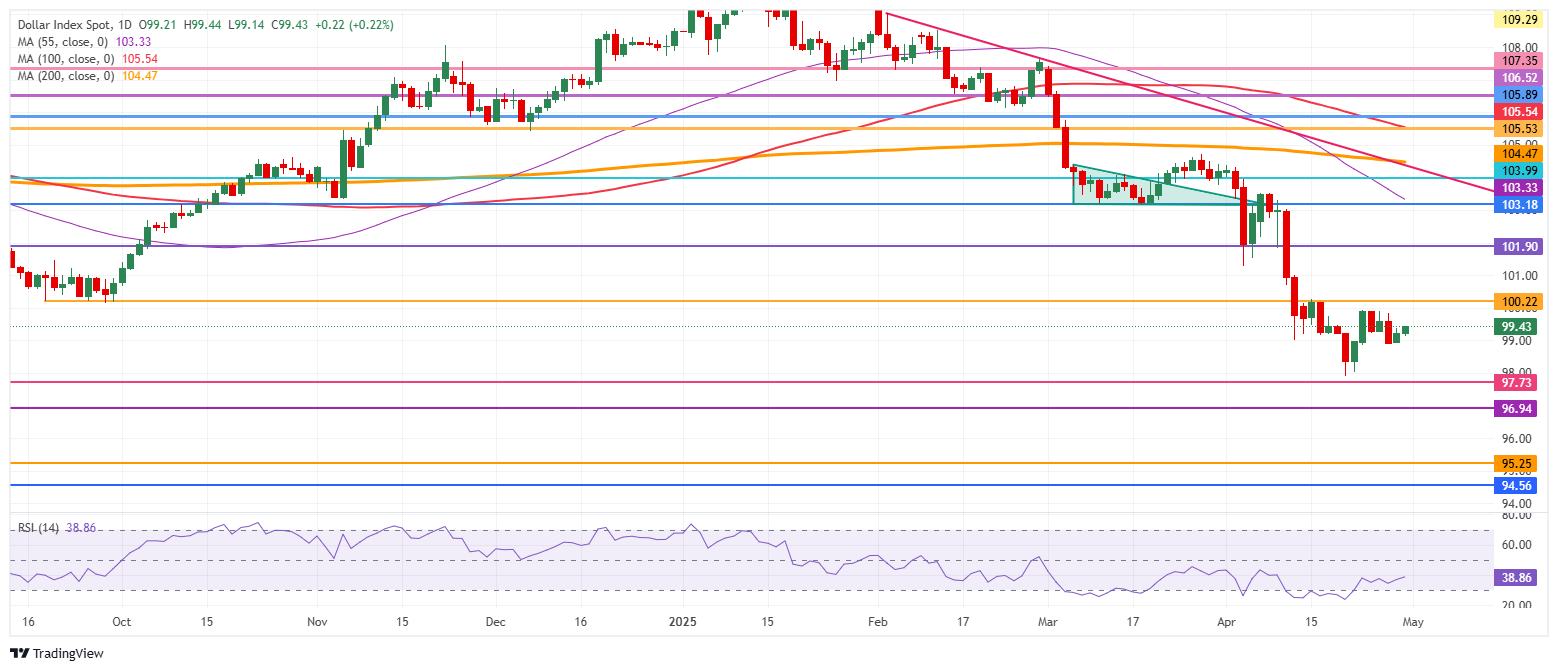
US Dollar Index: Daily Chart
US-China Trade War FAQs
Generally speaking, a trade war is an economic conflict between two or more countries due to extreme protectionism on one end. It implies the creation of trade barriers, such as tariffs, which result in counter-barriers, escalating import costs, and hence the cost of living.
An economic conflict between the United States (US) and China began early in 2018, when President Donald Trump set trade barriers on China, claiming unfair commercial practices and intellectual property theft from the Asian giant. China took retaliatory action, imposing tariffs on multiple US goods, such as automobiles and soybeans. Tensions escalated until the two countries signed the US-China Phase One trade deal in January 2020. The agreement required structural reforms and other changes to China’s economic and trade regime and pretended to restore stability and trust between the two nations. However, the Coronavirus pandemic took the focus out of the conflict. Yet, it is worth mentioning that President Joe Biden, who took office after Trump, kept tariffs in place and even added some additional levies.
The return of Donald Trump to the White House as the 47th US President has sparked a fresh wave of tensions between the two countries. During the 2024 election campaign, Trump pledged to impose 60% tariffs on China once he returned to office, which he did on January 20, 2025. With Trump back, the US-China trade war is meant to resume where it was left, with tit-for-tat policies affecting the global economic landscape amid disruptions in global supply chains, resulting in a reduction in spending, particularly investment, and directly feeding into the Consumer Price Index inflation.

