USD/INR sees more downside on hopes of US-India trade deal
- The Indian Rupee aims to extend its winning streak against the US Dollar on hopes that the US and India will announce a deal soon.
- India’s Commerce and Industry Minister Goyal stated that the deal will be announced once it is fair.
- The impact of the US NFP data will be significant on the US Dollar and the Fed’s monetary policy expectations.
The Indian Rupee (INR) extends its winning streak against the US Dollar (USD) for the fourth trading day on Wednesday. The USD/INR falls to near 88.60 as the Indian currency remains broadly firm amid growing expectations that the United States (US) and India could announce a trade deal soon.
The US-India trade deal hopes intensified last week after President Donald Trump stated that he will reduce tariffs on imports from New Delhi “at some point”, adding that India has agreed on halting Oil imports from Russia.
This week, expectations for the US-India trade pact accelerated further after India’s Commerce Secretary Rajesh Agarwal stated that the first part of the bilateral trade deal with the US is “nearly closure”, which addresses 50% tariffs and market access to the US, and the finalized deal will be announced on a mutually decided date, PTI reported.
Meanwhile, India’s Commerce and Industry Minister Piyush Goyal stated on Tuesday that the bilateral deal will be announced when negotiations from both sides have confidence that the agreement is “fair, equitable and balanced”. “When the deal will become fair, equitable, and balanced, you will hear good news," Goyal said at the Indo-US Economic Summit.
Daily digest market movers: Investors await the US NFP data for September
- The USD/INR pair struggles to gain ground as the US Dollar is expected to trade sideways, with investors awaiting the United States (US) Nonfarm Payrolls (NFP) data for September releasing on Thursday.
- At the time of writing, the US Dollar Index (DXY), which tracks the Greenback’s value against six major currencies, trades calmly near the weekly high around 99.70.
- Investors will closely monitor the US NFP data to get cues on the Federal Reserve’s (Fed) monetary policy outlook, as it will be the first economic release since the federal reopening. Additionally, almost all Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) members have been warning of weak labor demand amid increasing Artificial Intelligence (AI) adaptability.
- The US NFP report is expected to show that the economy added 50K fresh workers, higher than 22K in August. The Unemployment Rate is seen unchanged at 4.3%. Average Hourly Earnings, a key measure of wage growth, is expected to have grown steadily by 0.3% and 3.7% on a monthly as well as annual basis.
- Signs of a weak job trend from the US official employment data would prompt expectations of an interest rate cut by the Fed for its December policy meeting. On the contrary, better-than-projected figures would weaken the same.
- Currently, the CME FedWatch tool shows that the probability of the Fed cutting interest rates by 25 basis points (bps) to 3.50%-3.75% in the December meeting has diminished to 48.9% from 66.9% seen a week ago. Traders have trimmed Fed dovish bets as FOMC members have also warned of upside inflation risks, and have stressed the need to exercise caution on loosening monetary conditions further.
- Meanwhile, US President Donald Trump said to reporters on Tuesday that he has made the choice for the replacement of Fed Chair Jerome Powell, but didn’t mention the name. “I have started interviews for Fed chair, and I think I already know the choice,” Trump said. He added that he would “love to get Fed Chair Powell out right now”, but people are “holding me back”.
Technical Analysis: USD/INR corrects to near 20-day EMA
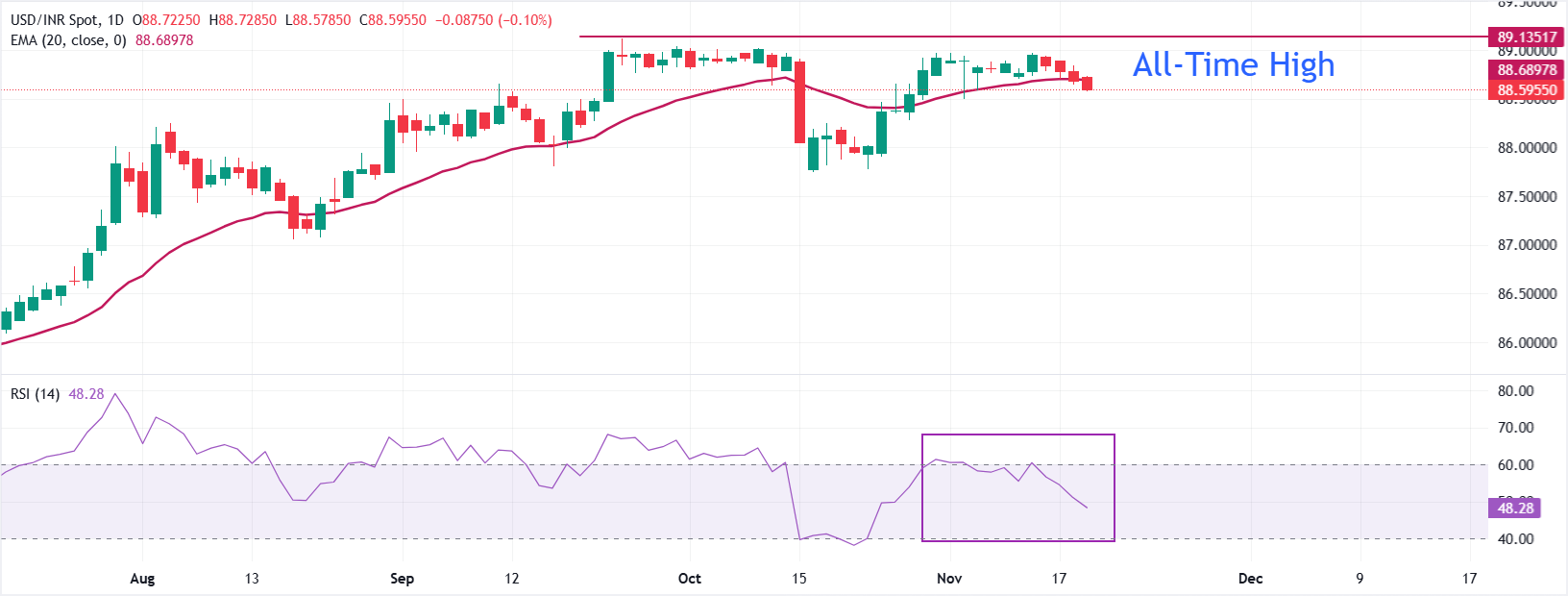
The USD/INR pair falls to near 88.60 at open on Wednesday. The pair extends correction to near the 20-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA), which trades around 88.70.
The 14-day Relative Strength Index (RSI) falls into the 40.00-60.00 range from the 60.00-80.00 zone. The range shift suggests that the overall momentum is not bullish anymore.
Looking down, the August 21 low of 87.07 will act as key support for the pair. On the upside, the all-time high of 89.12 will be a key barrier.
Indian Rupee FAQs
The Indian Rupee (INR) is one of the most sensitive currencies to external factors. The price of Crude Oil (the country is highly dependent on imported Oil), the value of the US Dollar – most trade is conducted in USD – and the level of foreign investment, are all influential. Direct intervention by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) in FX markets to keep the exchange rate stable, as well as the level of interest rates set by the RBI, are further major influencing factors on the Rupee.
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) actively intervenes in forex markets to maintain a stable exchange rate, to help facilitate trade. In addition, the RBI tries to maintain the inflation rate at its 4% target by adjusting interest rates. Higher interest rates usually strengthen the Rupee. This is due to the role of the ‘carry trade’ in which investors borrow in countries with lower interest rates so as to place their money in countries’ offering relatively higher interest rates and profit from the difference.
Macroeconomic factors that influence the value of the Rupee include inflation, interest rates, the economic growth rate (GDP), the balance of trade, and inflows from foreign investment. A higher growth rate can lead to more overseas investment, pushing up demand for the Rupee. A less negative balance of trade will eventually lead to a stronger Rupee. Higher interest rates, especially real rates (interest rates less inflation) are also positive for the Rupee. A risk-on environment can lead to greater inflows of Foreign Direct and Indirect Investment (FDI and FII), which also benefit the Rupee.
Higher inflation, particularly, if it is comparatively higher than India’s peers, is generally negative for the currency as it reflects devaluation through oversupply. Inflation also increases the cost of exports, leading to more Rupees being sold to purchase foreign imports, which is Rupee-negative. At the same time, higher inflation usually leads to the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) raising interest rates and this can be positive for the Rupee, due to increased demand from international investors. The opposite effect is true of lower inflation.
