EUR/USD soars on soft US CPI, closes in on 1.1500
- EUR/USD advances as lower US inflation sparks calls for aggressive Fed rate cuts.
- Trump urges full percentage point cut in Fed funds rate post-CPI.
- ECB policymakers cautious, but inflation outlook hints at further fine-tuning.
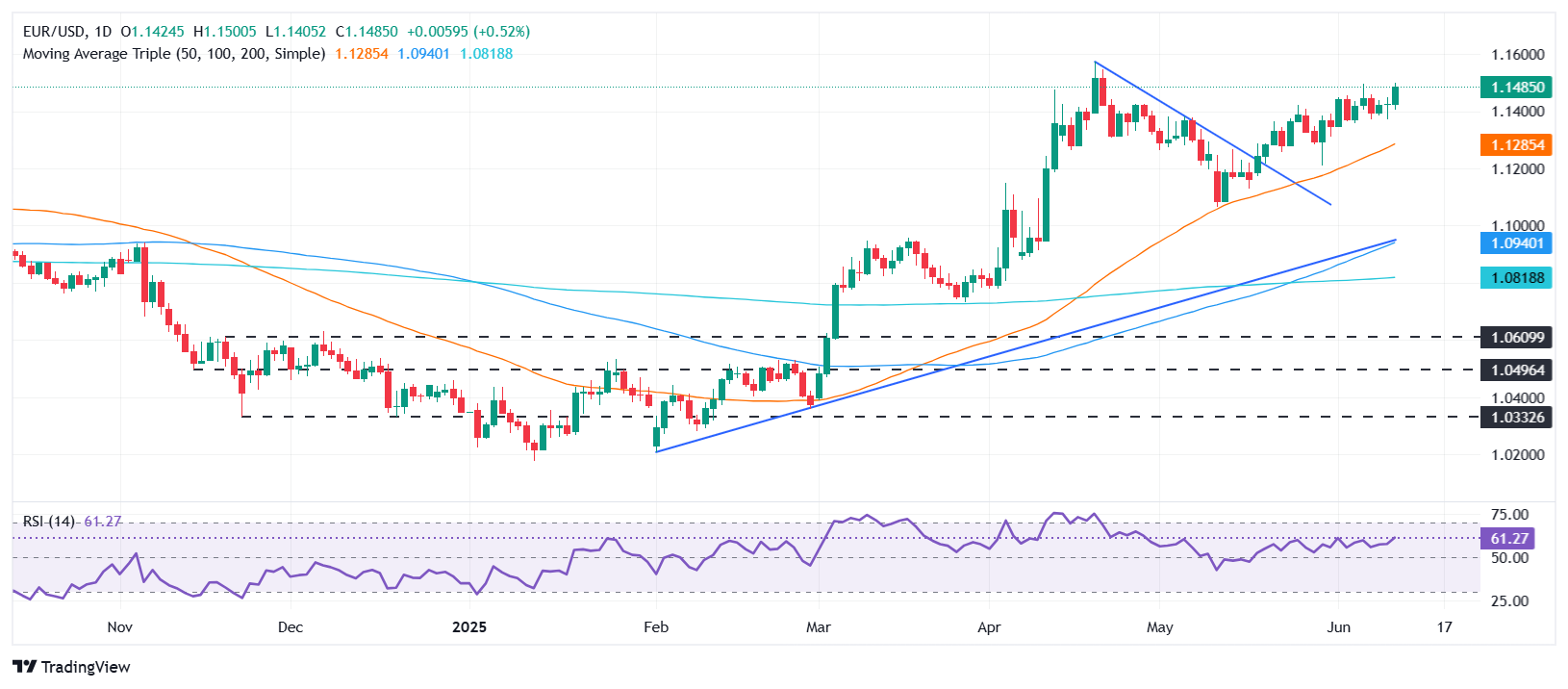
The EUR/USD surged during the North American session but remains shy of clearing the 1.1500 figure, following the release of a softer-than-expected inflation report in the United States (US), which could prompt the Federal Reserve (Fed) to reduce borrowing costs in the near term. At the time of writing, the pair trades at 1.1482, up by over 0.50%.
US data revealed that the Consumer Price Index (CPI) in May fell short of estimates as prices continued to trend lower. Following the data release, US President Donald Trump posted on his social network that the Fed should lower the fed funds rate by one whole percentage point.
Although inflation edged lower, some analysts project that households in the upcoming month will feel the impact of tariffs. Meanwhile, positive trade news regarding negotiations between the US and China emerged, as the Wall Street Journal (WSJ) revealed that China is putting a six-month limit on rare-earth export licenses for US automakers and manufacturers.
Meanwhile, in the Eurozone (EU), European Central Bank (ECB) policymakers made headlines, although they failed to move the EUR/USD pair. The ECB’s Vujcic said that he is looking for more clarity on trade, while Kazaks noted that it is “quite likely that 2% inflation will require some further cuts for fine-tuning,” said via Econostream on X.
The ECB Chief Economist, Philip Lane, added that last week’s rate cut helped clarify the bank’s policy stance to bring inflation toward its target.
Ahead in the week, the EUR/USD is expected to be greatly influenced by the release of the US Producer Price Index (PPI) numbers, along with the Initial Jobless Claims report. Across the pond, the EU’s schedule is scarce on economic data, but ECB officials led by Vice-President Luis de Guindos will cross the wires.
Daily digest market movers: EUR/USD soars past 1.1480 as traders shift toward US PPI data
- EUR/USD appears poised to test the 1.1500 mark in the near term as positive news about US-China talks could increase appetite for riskier assets and weigh on the US Dollar.
- US Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent commented that trade fairness with China could be achieved through reduced exports to the US or by rebalancing the world’s largest economies. He added that the Trump administration is committed to maintaining the US Dollar’s reserve currency status.
- US inflation came in softer than expected in May. Headline CPI rose 2.4% YoY, slightly above April’s 2.3% but below the 2.5% forecast. Core CPI held steady at 2.8% YoY, suggesting underlying inflation remains stable but persistent.
- The PPI for May is projected to increase from 2.4% to 2.6% YoY. Underlying PPI figures are expected to remain at 3.1% higher, unchanged compared to April’s print.
- Financial market players do not expect that the ECB would reduce its Deposit Facility Rate by 25 basis points (bps) at the July monetary policy meeting.
Euro technical outlook: EUR/USD bulls eyes 1.15 and the YTD high
From a technical perspective, the uptrend is expected to continue as buyers target a clear break above the 1.1500 figure. This will expose the year-to-date (YTD) high of 1.1572, ahead of 1.1600. The Relative Strength Index (RSI) is bullish, indicating an upward direction, which suggests that buyers are gaining momentum.
The less likely scenario on the downside is that the EUR/USD needs to clear the 1.1450 area. This would set the pair for a pullback toward the 20-day Simple Moving Average (SMA) at 1.1346 before testing 1.1300.
Euro FAQs
The Euro is the currency for the 19 European Union countries that belong to the Eurozone. It is the second most heavily traded currency in the world behind the US Dollar. In 2022, it accounted for 31% of all foreign exchange transactions, with an average daily turnover of over $2.2 trillion a day. EUR/USD is the most heavily traded currency pair in the world, accounting for an estimated 30% off all transactions, followed by EUR/JPY (4%), EUR/GBP (3%) and EUR/AUD (2%).
The European Central Bank (ECB) in Frankfurt, Germany, is the reserve bank for the Eurozone. The ECB sets interest rates and manages monetary policy. The ECB’s primary mandate is to maintain price stability, which means either controlling inflation or stimulating growth. Its primary tool is the raising or lowering of interest rates. Relatively high interest rates – or the expectation of higher rates – will usually benefit the Euro and vice versa. The ECB Governing Council makes monetary policy decisions at meetings held eight times a year. Decisions are made by heads of the Eurozone national banks and six permanent members, including the President of the ECB, Christine Lagarde.
Eurozone inflation data, measured by the Harmonized Index of Consumer Prices (HICP), is an important econometric for the Euro. If inflation rises more than expected, especially if above the ECB’s 2% target, it obliges the ECB to raise interest rates to bring it back under control. Relatively high interest rates compared to its counterparts will usually benefit the Euro, as it makes the region more attractive as a place for global investors to park their money.
Data releases gauge the health of the economy and can impact on the Euro. Indicators such as GDP, Manufacturing and Services PMIs, employment, and consumer sentiment surveys can all influence the direction of the single currency. A strong economy is good for the Euro. Not only does it attract more foreign investment but it may encourage the ECB to put up interest rates, which will directly strengthen the Euro. Otherwise, if economic data is weak, the Euro is likely to fall. Economic data for the four largest economies in the euro area (Germany, France, Italy and Spain) are especially significant, as they account for 75% of the Eurozone’s economy.
Another significant data release for the Euro is the Trade Balance. This indicator measures the difference between what a country earns from its exports and what it spends on imports over a given period. If a country produces highly sought after exports then its currency will gain in value purely from the extra demand created from foreign buyers seeking to purchase these goods. Therefore, a positive net Trade Balance strengthens a currency and vice versa for a negative balance.

