EUR/USD falls below 1.1600 as Dollar strengthens ahead of US NFP
- EUR/USD retreats to 1.1589 as traders buy Dollar amid expectations the Fed may keep rates unchanged in December.
- US government reopening fuels volatility ahead of NFP and earnings, with AI-bubble fears boosting safe-haven flows.
- ECB’s de Guindos says inflation is converging toward target but warns rising tariffs and sovereign debt remain risks.
The EUR/USD registers loses during the North American session down 030% as the Greenback enjoys a healthy recovery on speculation that the Federal Reserve might hold rates unchanged. The pair trades at 1.1589 after reaching a daily high of 1.1624.
Euro slips 0.30% as rising risk aversion and renewed Fed caution lift the Greenback into the new trading week
Risk aversion keeps the US Dollar bid as the US government reopening unleashes a flood of data, led by the release of the Nonfarm Payrolls report on Thursday. The US Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) will release those figures, and the Real Earnings print on Friday. Meanwhile, investors bought Greenback amid fears of a possible AI bubble, with NVIDIA set to release earnings on Wednesday, which could set markets mood ahead of US crucial data.
The US schedule is light on Monday, except for Federal Reserve officials. Vice-Chai Philip Jeffers was slightly dovish, while Fed Governor Christopher Waller supports the continuation of the easing cycle at the December’s meeting.
Earlier, the New York Fed released the Empire State Manufacturing index for November, improving with current business conditions faring better than expected
European Central Bank Vice President Luis de Guindos expressed confidence that Eurozone inflation is on track to converge toward the ECB’s price-stability target. Still, he warned that rising tariffs and elevated sovereign debt levels pose risks and potentially impact an abrupt shift in market mood.
Daily market movers: Euro slide on broad US Dollar strength
- The US Dollar Index (DXY), which tracks the buck’s value against a basket of six currencies, is up 0.20% at 99.47.
- The New York Fed’s latest survey showed a stronger-than-expected rebound in current manufacturing conditions, with gains in new orders and employment, while prices paid continued to ease. However, the six-month business outlook softened notably, falling to 19.1 from 30.3, signaling a decline in forward-looking confidence.
- The Fed Vice Chair Philip Jefferson said upside risks to inflation have likely diminished, while downside risks to the labor market have increased. He noted that firms remain hesitant to either hire or fire, and characterized current monetary policy as “somewhat restrictive.”
- Fed Governor Chritopher Waller said that a weak labor market justifies a rate cut in the December meeting. He added that once the impact of tariff is excluded, inflation would get closer to the Fed’s 2% target.
- Money markets have shifted toward a more hawkish outlook, with CME FedWatch data showing a 43% probability of a 25-basis-point cut at the December meeting—implying a 57% chance the Fed holds rates steady.
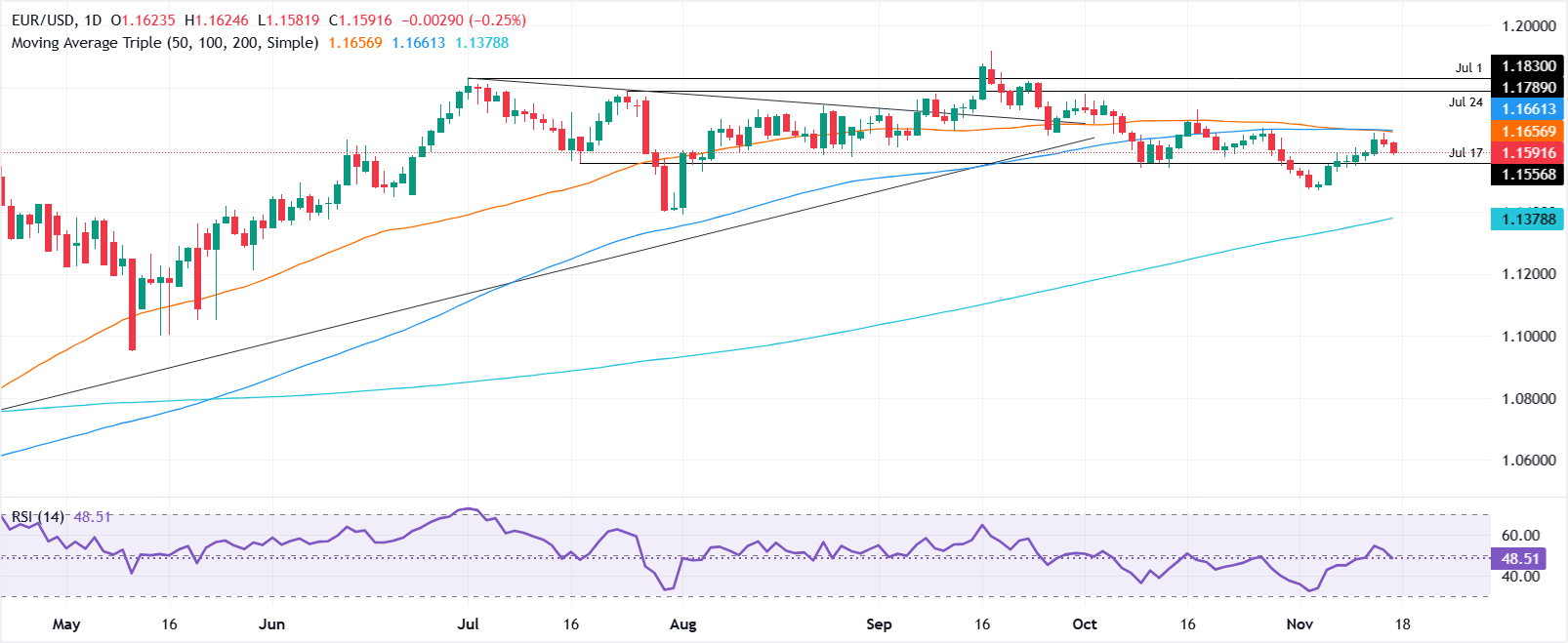
EUR/USD technical outlook: Tumbles below 1.1600, traders eye 1.1550
EUR/USD continues to trade with a bearish tone, with sellers gaining control pushing the exchange rate towards the 50-day Simple Moving Average (SMA) at 1.1581. The Relative Strength Index (RSI) made a U-turn, edging lower, suggesting a pickup in bearish pressure. A clear breach of the 1.1550 would open the door toward the 1.1500 level.
On the upside, the EUR/USD must reclaim 1.1600 if buyers would like to regain the upper hand. Once done, the next stop is the 50-day SMA at 1.1656, followed by the 100-day SMA at 1.1659. On further strength, the next resistance is 1.1700.
Euro FAQs
The Euro is the currency for the 20 European Union countries that belong to the Eurozone. It is the second most heavily traded currency in the world behind the US Dollar. In 2022, it accounted for 31% of all foreign exchange transactions, with an average daily turnover of over $2.2 trillion a day. EUR/USD is the most heavily traded currency pair in the world, accounting for an estimated 30% off all transactions, followed by EUR/JPY (4%), EUR/GBP (3%) and EUR/AUD (2%).
The European Central Bank (ECB) in Frankfurt, Germany, is the reserve bank for the Eurozone. The ECB sets interest rates and manages monetary policy. The ECB’s primary mandate is to maintain price stability, which means either controlling inflation or stimulating growth. Its primary tool is the raising or lowering of interest rates. Relatively high interest rates – or the expectation of higher rates – will usually benefit the Euro and vice versa. The ECB Governing Council makes monetary policy decisions at meetings held eight times a year. Decisions are made by heads of the Eurozone national banks and six permanent members, including the President of the ECB, Christine Lagarde.
Eurozone inflation data, measured by the Harmonized Index of Consumer Prices (HICP), is an important econometric for the Euro. If inflation rises more than expected, especially if above the ECB’s 2% target, it obliges the ECB to raise interest rates to bring it back under control. Relatively high interest rates compared to its counterparts will usually benefit the Euro, as it makes the region more attractive as a place for global investors to park their money.
Data releases gauge the health of the economy and can impact on the Euro. Indicators such as GDP, Manufacturing and Services PMIs, employment, and consumer sentiment surveys can all influence the direction of the single currency. A strong economy is good for the Euro. Not only does it attract more foreign investment but it may encourage the ECB to put up interest rates, which will directly strengthen the Euro. Otherwise, if economic data is weak, the Euro is likely to fall. Economic data for the four largest economies in the euro area (Germany, France, Italy and Spain) are especially significant, as they account for 75% of the Eurozone’s economy.
Another significant data release for the Euro is the Trade Balance. This indicator measures the difference between what a country earns from its exports and what it spends on imports over a given period. If a country produces highly sought after exports then its currency will gain in value purely from the extra demand created from foreign buyers seeking to purchase these goods. Therefore, a positive net Trade Balance strengthens a currency and vice versa for a negative balance.


