Pound Sterling falls further as UK scraps tax raise plans
- The Pound Sterling underperforms against its peers as the UK government might avoid tax hike plans.
- Weak US economic data has prompted BoE dovish bets.
- US BLS confirms that it will publish economic data soon.
The Pound Sterling (GBP) continues to underperform its peers on Friday. The British currency trades lower against its peers as United Kingdom (UK) fiscal risks have escalated, following reports from the Financial Times (FT) signaling that Prime Minister Keir Starmer and Chancellor of the Exchequer Rachel Reeves might scrap their plans of raising basic and higher tax bands in the upcoming Autumn Budget on November 26.
The FT reported earlier in the day that the UK government could avoid raising the burden on individuals and look for other non-direct revenues to cover the £30billion fiscal gap.
A few weeks back, Chancellor Reeves stated that the administration might need to ditch their election manifesto’s promise of not hiking households’ taxes to fund the stopgap bill.
The absence of fresh tax hikes would prompt fiscal debt risks, a scenario that would increase interest obligations on public borrowings for the government. At the time of writing, 10-year UK gilt yields trade 0.8% higher to near 4.40%.
Daily digest market movers: Pound Sterling weakens against US Dollar
- The Pound Sterling trades 0.4% lower to near 1.3130 against the US Dollar (USD) during the European trading session on Friday. The GBP/USD pair slumps as the Pound Sterling remains on the back foot. Meanwhile, the US Dollar is also under pressure as investors turn cautious ahead of key United States (US) economic data releases, which were halted due to the government shutdown.
- At the time of writing, the US Dollar Index (DXY), which tracks the Greenback’s value against six major currencies, edges lower to near 99.15. The USD Index remains close to its two-week low of 99.00 posted on Thursday.
- The US Bureau of Labour Statistics (BLS) dropped a statement on its website stating that it will publish the updated schedule on its website soon. The release of the US economic data would significantly influence market expectations for the Federal Reserve’s (Fed) monetary policy outlook.
- On Thursday, White House Economic Council Director Kevin Hassett said in an appearance on Fox News that the upcoming labour data release won’t include the Unemployment data.
- Meanwhile, traders have trimmed Fed dovish bets for the October policy meeting as a slew of policymakers have warned of upside inflation risks.
- “The Fed needs to proceed with caution now, and continue to lean against inflation," St. Louis Fed President Alberto Musalem said at the Economic Impact & Policy Forum hosted by the University of Evansville, in Indiana, on Thursday.
- In the UK, intensifying expectations of an interest rate cut by the Bank of England (BoE) for the December policy meeting are also being a drag on the Pound Sterling. BoE dovish bets have accelerated following weak employment data for three months ending September and the flash Q3 Gross Domestic Product (GDP) data.
- This week, the Office for National Statistics (ONS) reported that the ILO Unemployment Rate jumped to 5%, and the economy expanded at a moderate pace of 0.1%.
- Going forward, investors will focus on the UK Consumer Price Index (CPI) data for October, which will be released on Wednesday.
Technical Analysis: Pound Sterling slides to near 1.3130
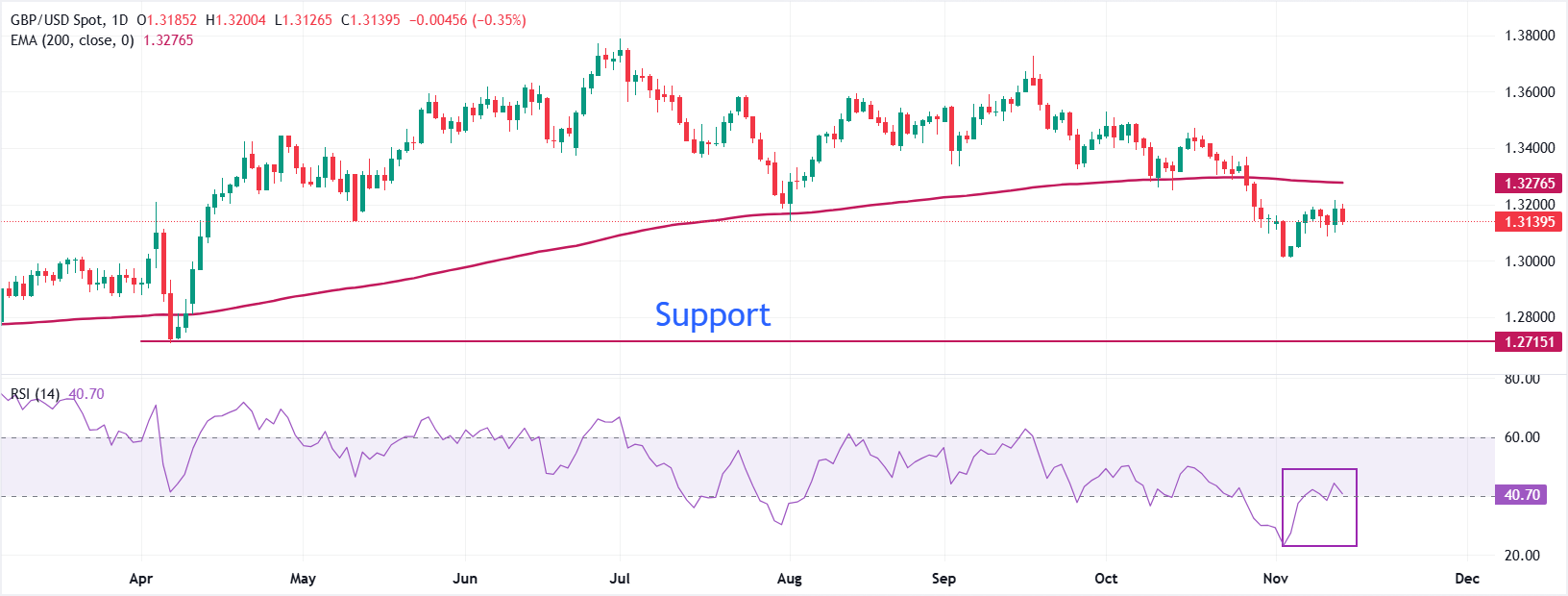
The Pound Sterling declines to near 1.3130 against the US Dollar on Friday. The overall trend of the pair remains bearish as it trades below the 200-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA), which is around 1.3276.
The 14-day Relative Strength Index (RSI) struggles to return above 40.00. A fresh bearish momentum would emerge if the RSI resumes its downside journey.
Looking down, the April low near 1.2700 will act as a key support zone. On the upside, the October 28 high around 1.3370 will act as a key barrier.
Pound Sterling FAQs
The Pound Sterling (GBP) is the oldest currency in the world (886 AD) and the official currency of the United Kingdom. It is the fourth most traded unit for foreign exchange (FX) in the world, accounting for 12% of all transactions, averaging $630 billion a day, according to 2022 data. Its key trading pairs are GBP/USD, also known as ‘Cable’, which accounts for 11% of FX, GBP/JPY, or the ‘Dragon’ as it is known by traders (3%), and EUR/GBP (2%). The Pound Sterling is issued by the Bank of England (BoE).
The single most important factor influencing the value of the Pound Sterling is monetary policy decided by the Bank of England. The BoE bases its decisions on whether it has achieved its primary goal of “price stability” – a steady inflation rate of around 2%. Its primary tool for achieving this is the adjustment of interest rates. When inflation is too high, the BoE will try to rein it in by raising interest rates, making it more expensive for people and businesses to access credit. This is generally positive for GBP, as higher interest rates make the UK a more attractive place for global investors to park their money. When inflation falls too low it is a sign economic growth is slowing. In this scenario, the BoE will consider lowering interest rates to cheapen credit so businesses will borrow more to invest in growth-generating projects.
Data releases gauge the health of the economy and can impact the value of the Pound Sterling. Indicators such as GDP, Manufacturing and Services PMIs, and employment can all influence the direction of the GBP. A strong economy is good for Sterling. Not only does it attract more foreign investment but it may encourage the BoE to put up interest rates, which will directly strengthen GBP. Otherwise, if economic data is weak, the Pound Sterling is likely to fall.
Another significant data release for the Pound Sterling is the Trade Balance. This indicator measures the difference between what a country earns from its exports and what it spends on imports over a given period. If a country produces highly sought-after exports, its currency will benefit purely from the extra demand created from foreign buyers seeking to purchase these goods. Therefore, a positive net Trade Balance strengthens a currency and vice versa for a negative balance.
