Canadian Dollar falls once again as Loonie support withers
- The Canadian Dollar fell another 0.15% on Wednesday.
- The Loonie continues to decline against the Greenback.
- Fed rate cut bets continue to ride high, while economic fears weigh on CAD.
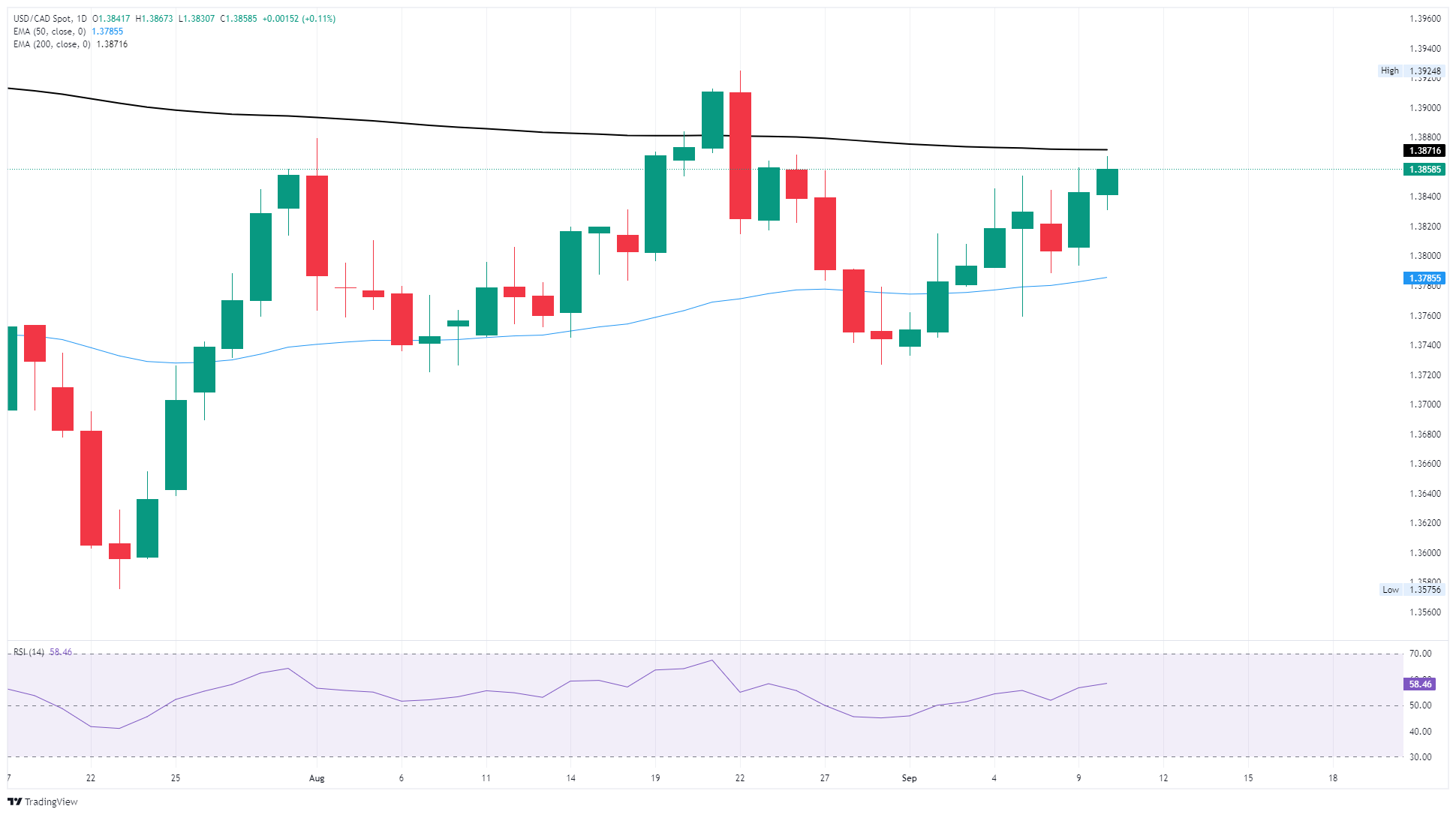
The Canadian Dollar eased further on Wednesday, declining around one-sixth of one percent and putting the USD/CAD pair on track to challenge its key 200-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA). Key US Producer Price Index (PPI) inflation data eased back in August, bolstering bets that the Federal Reserve (Fed) will get pushed into an economy-stabilizing rate-cutting cycle.
The Bank of Canada (BoC) is also broadly expected to begin cutting interest rates once again, but the Canadian economy is facing significant contraction as Canada and the US continue to quietly go to loggerheads on trade. The Canadian data docket remains restricted this week, leaving CAD traders to grapple with Thursday’s US Consumer Price Index (CPI) inflation print and next week’s key Fed interest rate decision.
Daily digest market movers: Canadian Dollar extends near-term declines
- The Canadian Dollar fell another 0.15% on Wednesday, pushing the USD/CAD pair into 1.3860.
- USD/CAD is now on pace to retest the 200-day EMA near 1.3870 for the second time inside of a month.
- The Loonie has lost ground against the Greenback for all but one of the last eight straight trading sessions.
- US PPI inflation eased in August, a welcome reprieve from inflationary pressure concerns and giving the Fed further leeway to deliver an interest rate cut next week.
- Key US inflation metrics still loom large on Thursday: CPI inflation, which has greater exposure to tariff impacts than PPI, is expected to tick higher once again in August.
Canadian Dollar price forecast
The Canadian Dollar is continuing its trend of shedding weight against the US Dollar. USD/CAD has risen a little over one percent bottom-to-top after hitting a swing low of 1.3726 at the tail end of August, and the pair is now heading into a technical consolidation zone near the 200-day EMA at 1.3871.
USD/CAD daily chart
Canadian Dollar FAQs
The key factors driving the Canadian Dollar (CAD) are the level of interest rates set by the Bank of Canada (BoC), the price of Oil, Canada’s largest export, the health of its economy, inflation and the Trade Balance, which is the difference between the value of Canada’s exports versus its imports. Other factors include market sentiment – whether investors are taking on more risky assets (risk-on) or seeking safe-havens (risk-off) – with risk-on being CAD-positive. As its largest trading partner, the health of the US economy is also a key factor influencing the Canadian Dollar.
The Bank of Canada (BoC) has a significant influence on the Canadian Dollar by setting the level of interest rates that banks can lend to one another. This influences the level of interest rates for everyone. The main goal of the BoC is to maintain inflation at 1-3% by adjusting interest rates up or down. Relatively higher interest rates tend to be positive for the CAD. The Bank of Canada can also use quantitative easing and tightening to influence credit conditions, with the former CAD-negative and the latter CAD-positive.
The price of Oil is a key factor impacting the value of the Canadian Dollar. Petroleum is Canada’s biggest export, so Oil price tends to have an immediate impact on the CAD value. Generally, if Oil price rises CAD also goes up, as aggregate demand for the currency increases. The opposite is the case if the price of Oil falls. Higher Oil prices also tend to result in a greater likelihood of a positive Trade Balance, which is also supportive of the CAD.
While inflation had always traditionally been thought of as a negative factor for a currency since it lowers the value of money, the opposite has actually been the case in modern times with the relaxation of cross-border capital controls. Higher inflation tends to lead central banks to put up interest rates which attracts more capital inflows from global investors seeking a lucrative place to keep their money. This increases demand for the local currency, which in Canada’s case is the Canadian Dollar.
Macroeconomic data releases gauge the health of the economy and can have an impact on the Canadian Dollar. Indicators such as GDP, Manufacturing and Services PMIs, employment, and consumer sentiment surveys can all influence the direction of the CAD. A strong economy is good for the Canadian Dollar. Not only does it attract more foreign investment but it may encourage the Bank of Canada to put up interest rates, leading to a stronger currency. If economic data is weak, however, the CAD is likely to fall.

