USD/INR snaps four-day losing streak as Fed dovish bets recede
- The Indian Rupee opens lower to near 88.80 against the US Dollar ahead of the US NFP data for September.
- Many FOMC members opposed another rate cut in December.
- The RBI is expected to cut the Repo Rate further this year.
The Indian Rupee (INR) opens on a negative note against the US Dollar (USD) on Thursday. The USD/INR pair jumps to near 88.80 as the US Dollar (USD) outperforms its peers, following the release of the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) minutes of the October policy meeting on Wednesday. In the policy meeting, the Fed decided to cut interest rates by 25 basis points (bps) to 3.75%-4.00%.
At the time of writing, the US Dollar Index (DXY), which tracks the Greenback’s value against six major currencies, revisits an over five-month high of around 100.40.
The FOMC minutes showed that few policymakers would have been satisfied even if interest rates were held steady, as the outright rate cut for the second time in a row could stall progress in inflation returning to the central bank’s 2% target.
Over the December policy meeting, officials were divided about reducing interest rates again, citing that further monetary expansion could boost inflation expectations and dampen households’ trust in the central bank’s commitment to bring inflation lower to the 2% target in a timely manner.
Remarks from many Fed officials pointing to a pause in the monetary expansion cycle have resulted in a further reduction in bets supporting an interest rate cut in December. According to the CME FedWatch tool, the probability of the Fed cutting interest rates by 25 basis points (bps) to 3.50%-3.75% in the December meeting has diminished to 32.8% from 50.1% seen a day before the FOMC minutes release.
Daily digest market movers: Investors await US NFP data for fresh cues on current status of labour market
- A strong opening by the USD/INR pair on Thursday is also driven by weakness in the Indian Rupee. The Indian currency has come under pressure as investors turn anxious over the delay in the announcement of a trade deal between the United States (US) and India.
- Top negotiators from both nations have been expressing that they are close to reaching a deal; however, an absence of a concrete announcement has kept investors on edge.
- Meanwhile, growing acceptance among financial market participants that the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) will cut interest rates in its December policy meeting is also keeping the Indian Rupee under pressure.
- RBI dovish bets have accelerated due to cooling inflationary pressures. In October, the retail inflation decelerated at a faster-than-expected pace to 0.25% on an annualized basis, driven by soft food prices and tax cuts in consumer goods announced in the third quarter of the year. This was the second straight month when the inflation data came below the RBI’s tolerance range of 2%-6%.
- Going forward, investors will focus on India’s flash HSBC Purchasing Managers’ Index (PMI) data for November, which will be released on Friday.
- In Thursday’s session, the major trigger for the USD/INR pair will be the US Nonfarm Payrolls (NFP) data for September, which will be published at 13:30 GMT. Investors will pay close attention to the official employment data as it will influence market expectations for the Fed’s monetary policy outlook.
- Economists expect US employers to have created 50K fresh jobs, higher than 22K in August. The Unemployment Rate is seen unchanged at 4.3%. Average Hourly Earnings, a key measure of wage growth, is expected to have grown steadily by 0.3% and 3.7% on a monthly as well as annual basis.
Technical Analysis: USD/INR rises to near 88.80
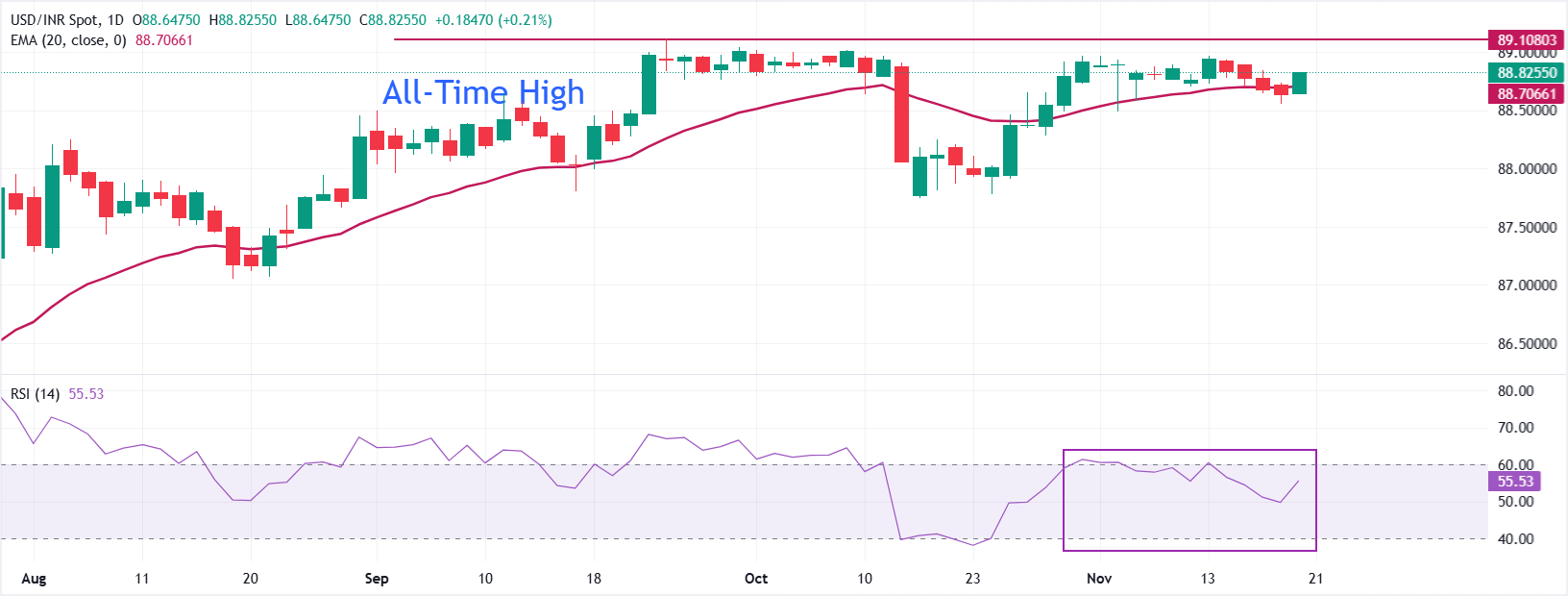
The USD/INR pair jumps to near 88.80 at open on Thursday. The pair snaps a four-day losing streak after attracting bids below the 20-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA), which trades around 88.70.
The 14-day Relative Strength Index (RSI) rebounds towards 60.00. A decisive break by the RSI above that level would trigger a bullish momentum.
Looking down, the August 21 low of 87.07 will act as key support for the pair. On the upside, the all-time high of 89.12 will be a key barrier.
Indian Rupee FAQs
The Indian Rupee (INR) is one of the most sensitive currencies to external factors. The price of Crude Oil (the country is highly dependent on imported Oil), the value of the US Dollar – most trade is conducted in USD – and the level of foreign investment, are all influential. Direct intervention by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) in FX markets to keep the exchange rate stable, as well as the level of interest rates set by the RBI, are further major influencing factors on the Rupee.
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) actively intervenes in forex markets to maintain a stable exchange rate, to help facilitate trade. In addition, the RBI tries to maintain the inflation rate at its 4% target by adjusting interest rates. Higher interest rates usually strengthen the Rupee. This is due to the role of the ‘carry trade’ in which investors borrow in countries with lower interest rates so as to place their money in countries’ offering relatively higher interest rates and profit from the difference.
Macroeconomic factors that influence the value of the Rupee include inflation, interest rates, the economic growth rate (GDP), the balance of trade, and inflows from foreign investment. A higher growth rate can lead to more overseas investment, pushing up demand for the Rupee. A less negative balance of trade will eventually lead to a stronger Rupee. Higher interest rates, especially real rates (interest rates less inflation) are also positive for the Rupee. A risk-on environment can lead to greater inflows of Foreign Direct and Indirect Investment (FDI and FII), which also benefit the Rupee.
Higher inflation, particularly, if it is comparatively higher than India’s peers, is generally negative for the currency as it reflects devaluation through oversupply. Inflation also increases the cost of exports, leading to more Rupees being sold to purchase foreign imports, which is Rupee-negative. At the same time, higher inflation usually leads to the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) raising interest rates and this can be positive for the Rupee, due to increased demand from international investors. The opposite effect is true of lower inflation.



