Gold price stays firm as traders eye FOMC’s meeting
- Gold sees a modest increase, as investors watch this week's central bank meetings.
- Focus remains on the Federal Reserve, where a hawkish stance could potentially impact Gold prices while bolstering the US Dollar.
- Recent US inflation data and Treasury yield resurgence, weighed on Gold prices.
Gold price registers modest gains on Monday amid a quiet session as investors brace for major central banks monetary policy decisions. Even though the Bank of Japan (BoJ), the Bank of England (BoE), and the Federal Reserve (Fed) would announce their decisions, the spotlight is on the latter. A Fed’s hawkish tilt could drive XAU/USD prices toward the $2,100.00 figure due to market participants' aggressive short positioning on the Greenback. At the time of writing, Gold trades at around $2,160.55, which is up 0.22%.
The price of the yellow metal remains underpinned by previous speculations that the Fed will begin to ease monetary policy sooner than expected. Nevertheless, during the last week, Bullion tumbled close to 1% as inflation in the consumer and the producer side on the United States (US) surprisingly reaccelerated, spurring a jump in US Treasury bond yields. Consequently, the Greenback posted gains of more than 0.69% last week, according to the US Dollar Index (DXY) and Gold’s slumped.
Daily digest market movers: Gold holds to modest gains as US yields rise
- On Monday, the US economic docket will featured housing data on the first two days of the week. Data from the National Association of Home Builders (NAHB) revealed that homebuilders' confidence rose in March to its highest level since July 2023, as mortgage rates dip, on expectations that the Fed might begin to ease policy. The NAHB Market Index came at 51, up from 48 in February.
- The US 10-year Treasury bond yield climbs two and a half basis points, up at 4.334%.
- The latest US economic data witnessed mixed readings in business activity, making it challenging to predict the pace of the economic deceleration in the US. The labor market has shown signs of cooling, though the economy added more people to the workforce than expected while fewer people applied for unemployment benefits.
- Given the backdrop, Fed Chairman Jerome Powell’s words in his testimony at the US Congress, suggesting that they would begin to cut borrowing costs, were justified. However, last week’s inflation figures and retail sales data triggered a repricing of Fed rate cut bets, aligning with the US central bank's view of 75 basis points of easing toward the end of 2024.
- The Fed’s next meeting is scheduled for March 19-20 next week. Given the latest inflation data, speculation is growing that Fed officials could eliminate one rate cut towards the end of the year, signaling they could cut rates twice in 2024.
- According to the CME FedWatch Tool, expectations for a June rate cut stand at 58%, down from 72% a week ago.
Technical analysis: Gold buyers take a breather below $2,170
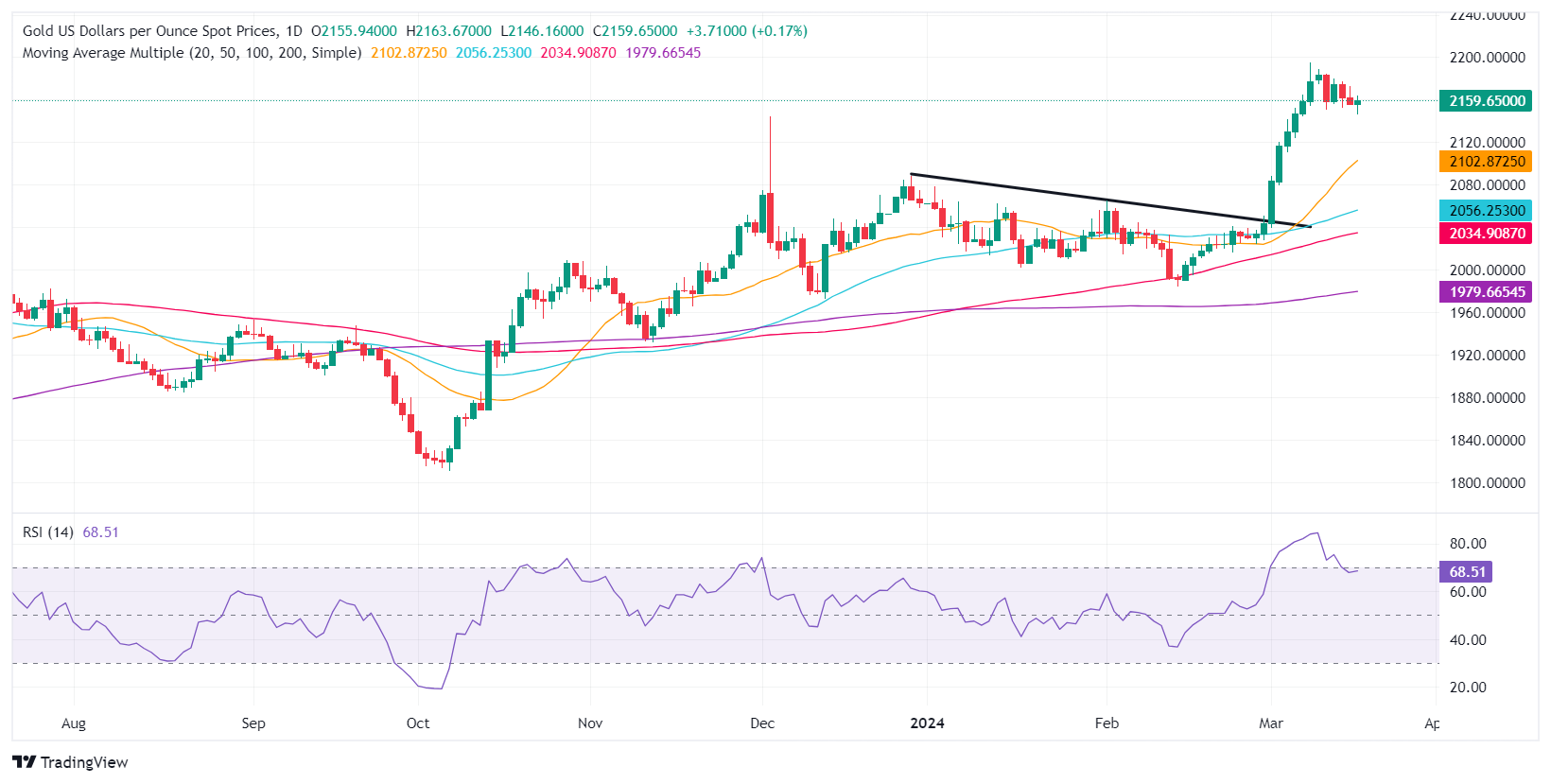
Gold’s uptrend remains in place, though the non-yielding metal remains glued to the $2,160-$2,180 area. Market participants keep the XAU/USD spot price near the bottom of the previously mentioned range, which could suggest that buyers are in charge and could drive prices toward the year-to-date (YTD) high of $2,195.15, ahead of the $2,200.00 mark.
However, the Relative Strength Index (RSI) indicator exiting from overbought conditions suggests that buyers are taking a breather. If sellers stepped in, pulling Gold’s price below $2,160.00, that would pave the way to test the December 4 high of $2,146.79, followed by the March 6 low of $2,123.80, followed by $2,100.00.
Fed FAQs
Monetary policy in the US is shaped by the Federal Reserve (Fed). The Fed has two mandates: to achieve price stability and foster full employment. Its primary tool to achieve these goals is by adjusting interest rates. When prices are rising too quickly and inflation is above the Fed’s 2% target, it raises interest rates, increasing borrowing costs throughout the economy. This results in a stronger US Dollar (USD) as it makes the US a more attractive place for international investors to park their money. When inflation falls below 2% or the Unemployment Rate is too high, the Fed may lower interest rates to encourage borrowing, which weighs on the Greenback.
The Federal Reserve (Fed) holds eight policy meetings a year, where the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) assesses economic conditions and makes monetary policy decisions. The FOMC is attended by twelve Fed officials – the seven members of the Board of Governors, the president of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York, and four of the remaining eleven regional Reserve Bank presidents, who serve one-year terms on a rotating basis.
In extreme situations, the Federal Reserve may resort to a policy named Quantitative Easing (QE). QE is the process by which the Fed substantially increases the flow of credit in a stuck financial system. It is a non-standard policy measure used during crises or when inflation is extremely low. It was the Fed’s weapon of choice during the Great Financial Crisis in 2008. It involves the Fed printing more Dollars and using them to buy high grade bonds from financial institutions. QE usually weakens the US Dollar.
Quantitative tightening (QT) is the reverse process of QE, whereby the Federal Reserve stops buying bonds from financial institutions and does not reinvest the principal from the bonds it holds maturing, to purchase new bonds. It is usually positive for the value of the US Dollar.




