GBP/USD drops towards 1.3500 as US weighs joining Israel in Iran conflict
- Cable drops to 1.3498 as Trump considers military support for Israel against Iran.
- Safe-haven flows lift US Dollar; DXY climbs to 98.43 despite soft US data.
- Fed and BoE policy decisions eyed; interest rate spread still favors the Greenback.
The GBP/USD tumbled below the 1.3500 figure for the first time in the week, down over 0.39%, as tensions in the Middle East remained high, with news sources revealing that the United States (US) is weighing whether to join Israel in its confrontation with Iran. At the time of writing, the pair traded at 1.3515, having previously reached daily highs of 1.3579.
Sterling slumps over 0.5% amid surging US Dollar demand and growing Middle East tensions
Geopolitical risks are boosting the US dollar, which, according to the US Dollar Index (DXY), which tracks the performance of the Dollar against six currencies, is up 0.31% at 98.43. On Monday, US President Donald Trump recommended Iranians in Tehran to evacuate as he exited abruptly from the G7 meeting in Canada.
According to Politico, US President Donald Trump is evaluating “whether to join Israel’s bombardment of Iran.” The source revealed that “Trump has been consistent that Iran can’t have a nuclear bomb. Given the state of Iran’s air defences there are a lot of options…”
In the meantime, GBP/USD traders are awaiting the monetary policy decisions of the Federal Reserve (Fed) and the Bank of England (BoE). Both are expected to keep rates unchanged, though the interest rate differential favors the US Dollar.
Data-wise, the US docket indicated that Retail Sales contracted in May due to a decline in major vehicle purchases. Sales dropped 0.9% month-over-month, which was below the forecast of 0.7%. In the twelve months leading up to May, sales rose sharply by 3.3%, down from a 5% jump in April.
Industrial Production in the US dived for the second time in three months, missing forecasts of 0.1% expansion, and fell -0.2% MoM.
Across the pond, the docket was empty, though there was progress in the US-UK talks in the G7. US President Donald Trump signed an agreement that lowered some tariffs on imports from Britain as both parties continued to engage toward a formal trade deal.
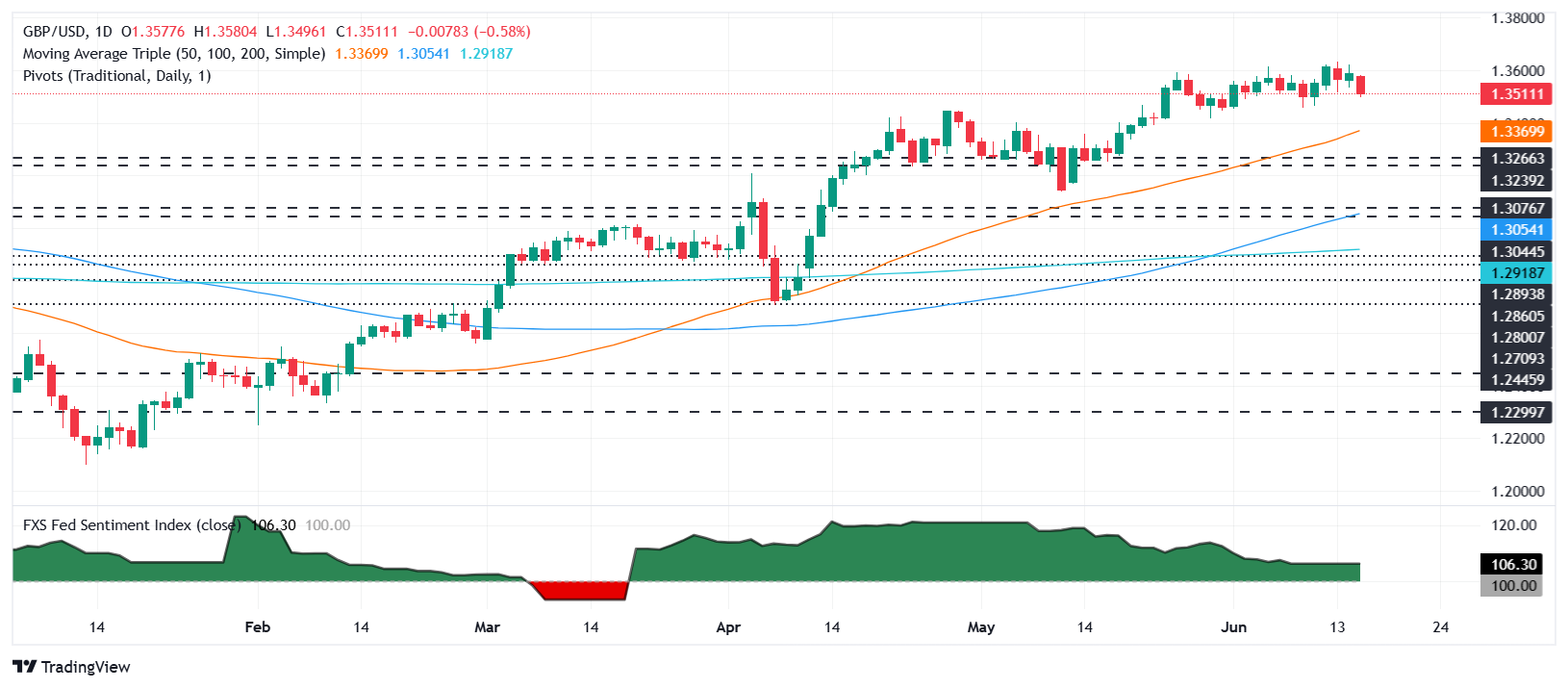
GBP/USD Price Forecast: Technical outlook
With the pair clearing 1.3500, the GBP/USD could be headed for a pullback, opening the door to challenge the May 29 swing low of 1.3414. Once decisively cleared, the next support would be the 50-day Simple Moving Average (SMA) at 1.3365.
Conversely, if GBP/USD reclaims the 20-day SMA at 1.3544, expect a test of 1.3600. A breach of the latter will expose the YTD high at 1.3631.
Pound Sterling FAQs
The Pound Sterling (GBP) is the oldest currency in the world (886 AD) and the official currency of the United Kingdom. It is the fourth most traded unit for foreign exchange (FX) in the world, accounting for 12% of all transactions, averaging $630 billion a day, according to 2022 data. Its key trading pairs are GBP/USD, also known as ‘Cable’, which accounts for 11% of FX, GBP/JPY, or the ‘Dragon’ as it is known by traders (3%), and EUR/GBP (2%). The Pound Sterling is issued by the Bank of England (BoE).
The single most important factor influencing the value of the Pound Sterling is monetary policy decided by the Bank of England. The BoE bases its decisions on whether it has achieved its primary goal of “price stability” – a steady inflation rate of around 2%. Its primary tool for achieving this is the adjustment of interest rates. When inflation is too high, the BoE will try to rein it in by raising interest rates, making it more expensive for people and businesses to access credit. This is generally positive for GBP, as higher interest rates make the UK a more attractive place for global investors to park their money. When inflation falls too low it is a sign economic growth is slowing. In this scenario, the BoE will consider lowering interest rates to cheapen credit so businesses will borrow more to invest in growth-generating projects.
Data releases gauge the health of the economy and can impact the value of the Pound Sterling. Indicators such as GDP, Manufacturing and Services PMIs, and employment can all influence the direction of the GBP. A strong economy is good for Sterling. Not only does it attract more foreign investment but it may encourage the BoE to put up interest rates, which will directly strengthen GBP. Otherwise, if economic data is weak, the Pound Sterling is likely to fall.
Another significant data release for the Pound Sterling is the Trade Balance. This indicator measures the difference between what a country earns from its exports and what it spends on imports over a given period. If a country produces highly sought-after exports, its currency will benefit purely from the extra demand created from foreign buyers seeking to purchase these goods. Therefore, a positive net Trade Balance strengthens a currency and vice versa for a negative balance.




