Dow Jones Industrial Average slips 250 points as markets await Fed and trade updates
- The Dow Jones backslid on Tuesday as investor sentiment gets hamstrung.
- The Fed’s upcoming rate call is expected to keep rates on hold as uncertainty weighs on policymakers.
- Traders await meaningful updates on trade deals the US is allegedly working on and will be announcing at some point.
The Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) followed the broader stock market lower on Tuesday, with equities taking a soft hit ahead of the Federal Reserve’s (Fed) upcoming rate call on Wednesday. Investors are also awaiting any meaningful update from the Trump administration on a slew of trade deals that are allegedly in the works. Still, details remain light to the point of being non-existent.
The Fed is broadly expected to keep rates on hold on Wednesday, but Fed talking points will be taking on added significance for market participants hoping for signs of a pivot into a rate-cutting cycle from Fed policymakers in the coming months. Rate markets are pricing in 100-125 basis points in rate cuts over the next 12 months.
Fed rate cuts and trade deals remain elusive
The Trump administration has also been adamant that the Fed must start cutting rates. However, this position has more to do with a desire to ease US debt financing pressures than supporting the Fed’s mandate of supporting maximum employment and controlling price volatility. Fed officials have thus far appeared to be structurally opposed to trimming interest rates before the appropriate time.
According to the Trump administration, a bundle of possible trade deals is in the pipeline. Specific details, or even what countries these alleged trade deals are being negotiated with, remain a secret. According to key staff within the Trump administration, these trade deals are being negotiated with 17-18 countries. None of those appear to be China, which recently expressed a possible willingness to approach the negotiating table, blowing Donald Trump’s claims that his administration has been negotiating with unnamed Chinese officials for weeks entirely out of the water.
Dow Jones price forecast
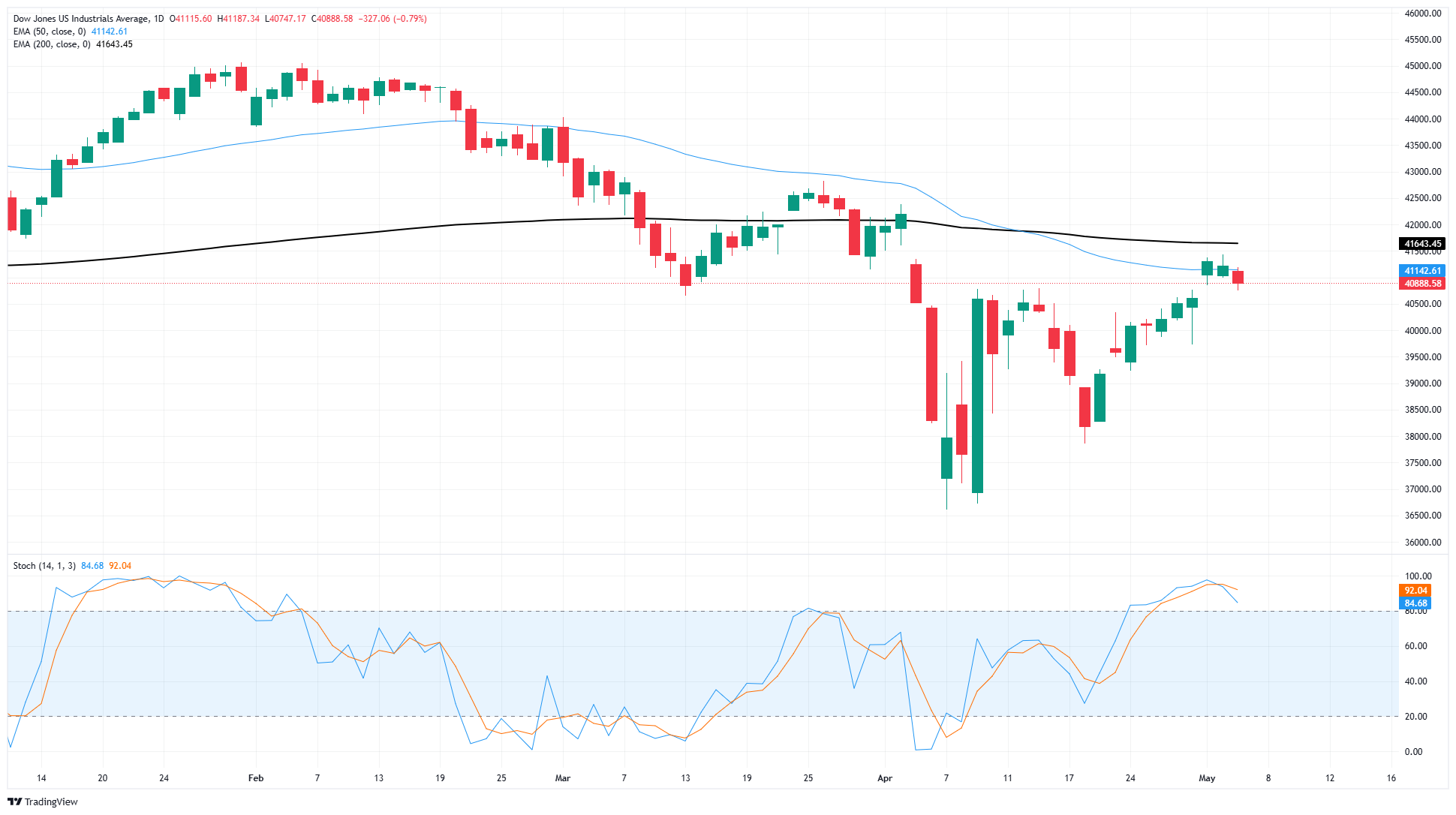
Momentum in the broad recovery for the Dow Jones Industrial Average has hit a rough patch. Price action has gotten hung up on the 50-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA) at 41,144, with bullish momentum drying up just south of the key 200-day EMA at 41,620.
The 41,000 price handle is the new price ceiling for bidders to beat. Technical oscillators remain pinned in overbought territory, implying some buying pressure may need to find a blowoff release before another leg higher can be generated.
Dow Jones daily chart
Dow Jones FAQs
The Dow Jones Industrial Average, one of the oldest stock market indices in the world, is compiled of the 30 most traded stocks in the US. The index is price-weighted rather than weighted by capitalization. It is calculated by summing the prices of the constituent stocks and dividing them by a factor, currently 0.152. The index was founded by Charles Dow, who also founded the Wall Street Journal. In later years it has been criticized for not being broadly representative enough because it only tracks 30 conglomerates, unlike broader indices such as the S&P 500.
Many different factors drive the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA). The aggregate performance of the component companies revealed in quarterly company earnings reports is the main one. US and global macroeconomic data also contributes as it impacts on investor sentiment. The level of interest rates, set by the Federal Reserve (Fed), also influences the DJIA as it affects the cost of credit, on which many corporations are heavily reliant. Therefore, inflation can be a major driver as well as other metrics which impact the Fed decisions.
Dow Theory is a method for identifying the primary trend of the stock market developed by Charles Dow. A key step is to compare the direction of the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) and the Dow Jones Transportation Average (DJTA) and only follow trends where both are moving in the same direction. Volume is a confirmatory criteria. The theory uses elements of peak and trough analysis. Dow’s theory posits three trend phases: accumulation, when smart money starts buying or selling; public participation, when the wider public joins in; and distribution, when the smart money exits.
There are a number of ways to trade the DJIA. One is to use ETFs which allow investors to trade the DJIA as a single security, rather than having to buy shares in all 30 constituent companies. A leading example is the SPDR Dow Jones Industrial Average ETF (DIA). DJIA futures contracts enable traders to speculate on the future value of the index and Options provide the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell the index at a predetermined price in the future. Mutual funds enable investors to buy a share of a diversified portfolio of DJIA stocks thus providing exposure to the overall index.

