US Dollar gets beaten up after Fed large rate cut bets are back on the table
- Fed rate futures for September are flip-flopping and price back in a chance for a 50 basis points interest-rate cut by the Federal Reserve.
- Former Fed member Dudley surprised markets by advocating for a bigger rate cut, while a couple of news articles suggest that a big rate cut is still in play.
- The US Dollar Index is crossing back to the lower band at 100.62 after another rejection.
The US Dollar (USD) trades very soft again on Friday, set to close out the week with another loss. The decline comes on comments from former Federal Reserve Bank of New York President William Dudley, who mentioned there is still a possibility for a 50-basis-point interest-rate cut next week from the Fed. These comments came after two news articles published in The Wall Street Journal and the Financial Times suggested that a 50bps move is still on the cards after markets had largely ruled out such a big move.
Dudley pointed to a slowing US labor market, with risks to jobs greater than those from lingering inflation, supported by the comments from Fed Chairman Jerome Powell in his Jackson Hole speech that he did not want to see more weakness in the labor market, Reuters reports.
On the economic data front, the US Import/Export prices are due, together with the University of Michigan Consumer Sentiment data. However, not much movement is expected unless the Michigan Consumer Sentiment number comes in well below estimates, a scenario that could support further the case for a 50-basis-point rate cut.
Daily digest market movers: Dudley pushes back
- At 12:30 GMT, both the Import and Export Price indexes for August will be released:
- Monthly Import Prices are expected to decline by -0.2% after increasing by 0.1% in July. On the year, import prices grew by 1.6% in July, with no forecast pencilled in for August.
- The monthly Export Prices are expected to shrink by 0.1% after the 0.7% advance seen a month earlier. The yearly index was at 1.4%, with no consensus issued.
- The University of Michigan preliminary findings for September are expected at 14:00 GMT:
- The headline Michigan Consumer Sentiment is expected to increase slightly to 68.0 from 67.9.
- The 5-Year inflation expectation, a closely-followed indicator by the Fed, stood at 3% at the end of July. There is no forecast available for August.
- Asian equities have closed off this Friday in the red, while European equities are jumping higher on expectations that the European Central Bank will cut more than previously foreseen. US futures are rather flat.
- The CME Fedwatch Tool shows only a 57.0% chance aof a 25 basis points (bps) interest rate cut by the Fed on September 18, sharply down from the 87% seen a day ago. Meanwhile, markets have increased the chances of a 50 bps cut to 43.0% on the back of Fed’s Dudley comments and the news articles. For the meeting on November 7, another 25 bps cut (if September is a 25 bps cut) is expected by 24.9%, while there is a 51.4% chance that rates will be 75 bps (25 bps + 50 bps) and a 23.7% probability of rates being 100 (25 bps + 75 bps) basis points lower.
- The US 10-year benchmark rate trades at 3.63%, very close to the 15-month low at 3.60%.
US Dollar Index Technical Analysis: Breakout for another day
The US Dollar Index (DXY) came close to snapping the upper band at 101.90 for a breakout on Thursday. That was until Fed Dudley came along and placed the possibility for a 50-basis-point rate cut back in the mind of traders. The DXY is now back down, at a loss for this week, and could be seen testing that lower band at 100.62 for possibly a break lower.
The first resistance at 101.90 is getting ready for a third test after its rejection last week and earlier this week. Further up, a steep 1.2% uprising would be needed to get the index to 103.18. The next tranche up is a very misty one, with the 55-day Simple Moving Average (SMA) at 103.40, followed by the 200-day SMA at 103.89, just ahead of the big 104.00 round level.
On the downside, 100.62 (the low from December 28) holds strong and has already made the DXY rebound four times in recent weeks. Should it break, the low from July 14, 2023, at 99.58, will be the ultimate level to look out for. Once that level gives way, early levels from 2023 are coming in near 97.73.
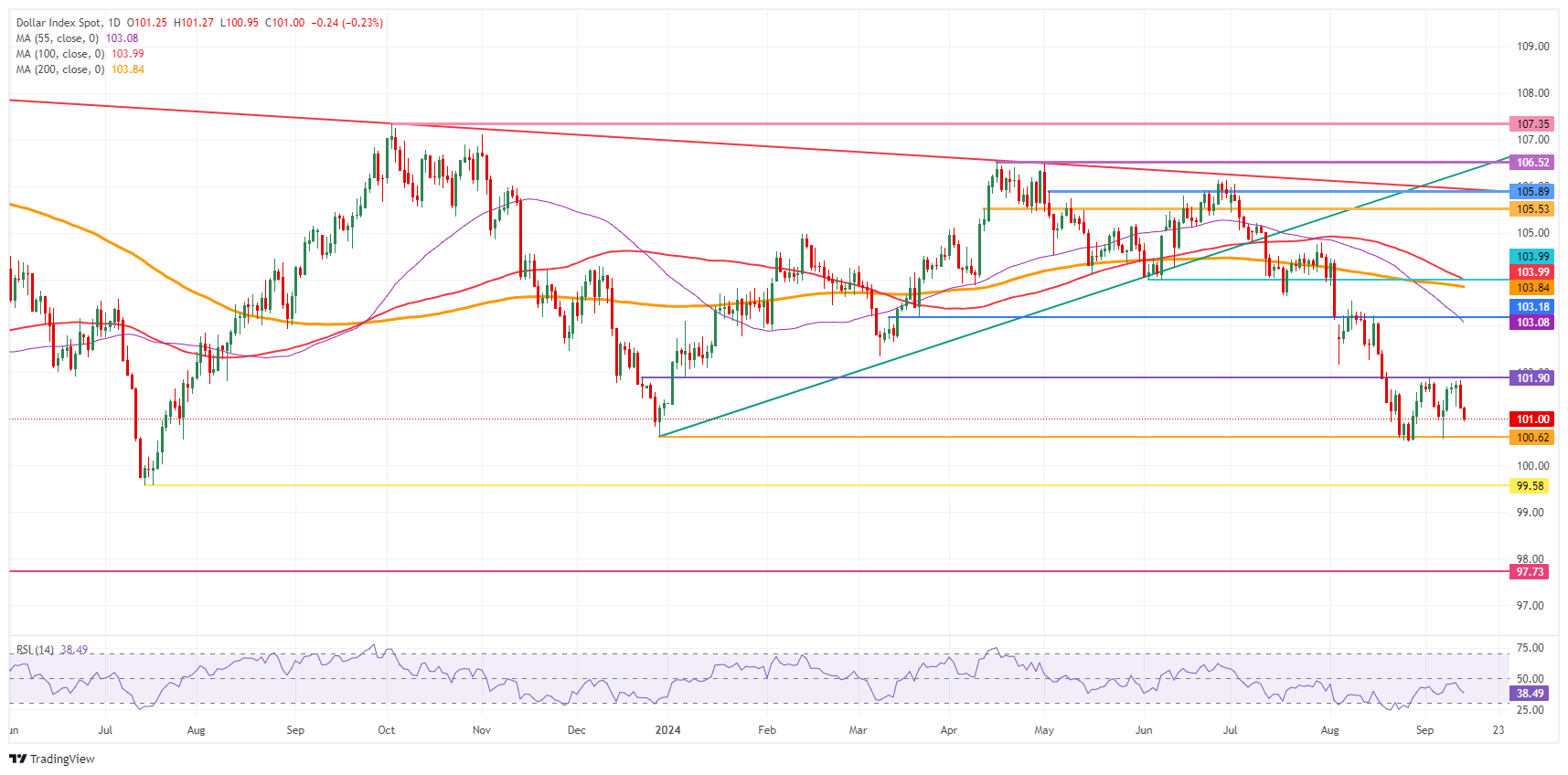
US Dollar Index: Daily Chart
US Dollar FAQs
The US Dollar (USD) is the official currency of the United States of America, and the ‘de facto’ currency of a significant number of other countries where it is found in circulation alongside local notes. It is the most heavily traded currency in the world, accounting for over 88% of all global foreign exchange turnover, or an average of $6.6 trillion in transactions per day, according to data from 2022. Following the second world war, the USD took over from the British Pound as the world’s reserve currency. For most of its history, the US Dollar was backed by Gold, until the Bretton Woods Agreement in 1971 when the Gold Standard went away.
The most important single factor impacting on the value of the US Dollar is monetary policy, which is shaped by the Federal Reserve (Fed). The Fed has two mandates: to achieve price stability (control inflation) and foster full employment. Its primary tool to achieve these two goals is by adjusting interest rates. When prices are rising too quickly and inflation is above the Fed’s 2% target, the Fed will raise rates, which helps the USD value. When inflation falls below 2% or the Unemployment Rate is too high, the Fed may lower interest rates, which weighs on the Greenback.
In extreme situations, the Federal Reserve can also print more Dollars and enact quantitative easing (QE). QE is the process by which the Fed substantially increases the flow of credit in a stuck financial system. It is a non-standard policy measure used when credit has dried up because banks will not lend to each other (out of the fear of counterparty default). It is a last resort when simply lowering interest rates is unlikely to achieve the necessary result. It was the Fed’s weapon of choice to combat the credit crunch that occurred during the Great Financial Crisis in 2008. It involves the Fed printing more Dollars and using them to buy US government bonds predominantly from financial institutions. QE usually leads to a weaker US Dollar.
Quantitative tightening (QT) is the reverse process whereby the Federal Reserve stops buying bonds from financial institutions and does not reinvest the principal from the bonds it holds maturing in new purchases. It is usually positive for the US Dollar.


