Dow Jones Industrial Average grapples with downside post-PPI on Tuesday
- Dow Jones shied away from gains after PPI printed higher than expected.
- Fed Chair Powell made an appearance to soothe investor nerves after inflation print.
- US CPI inflation and Retail Sales in the barrel for Wednesday.
The Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) stumbled on Tuesday, slipping back to 39,320.00 after US Producer Price Index (PPI) inflation came in higher than expected. Market sentiment recovered and dragged the DJIA back to even. However, a double-header of US Consumer Price Index (CPI) inflation and Retail Sales are still loaded in the barrel for Wednesday.
US PPI inflation rose to 0.5% MoM in April, over and above the forecast 0.3% and rebounding from the previous month’s -0.1% decline (revised down from 0.2%). Core annualized PPI came in at the expected 2.4% YoY, rising from the previous period’s 2.1% which was revised down from 2.4%.
Next up will be the US’ data headliner for the week with Wednesday’s Consumer Price Index (CPI) inflation print. US CPI inflation is expected to hold steady in April at 0.4% MoM, while YoY headline CPI inflation is expected to drop slightly to 3.4% from 3.5%.
US Retail Sales are also due on Wednesday, and investors are forecasting that MoM Retail Sales growth in April will ease to 0.4% from the previous month’s 0.7%.
Dow Jones news
About half of the securities that make up the Dow Jones Industrial Average are in the red on Tuesday. Visa Inc. (V) fell -1.5%, shedding -4.2 points and trading below $276.00 per share, closely followed by Walmart Inc. (WMT) which shed -1.25% and fell below $60.00 per share.
On the high side, Goldman Sachs Group Inc. (GS) gained around 1.6%, climbing seven points to trade above $460.00 per share. Boeing Co. (BA) and Intel Corp. (INTC) are battling for second place, up around 1.3% apiece on Tuesday and trading near $181.00 and $31.00 per share, respectively.
Dow Jones technical outlook
The Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) is mired in intraday technical congestion near 39,400.00 on Tuesday as the major equity index grapples with twisting investor sentiment. The index dumped below 39,320.00 on reaction to inflation data, but the Dow Jones recovered back above the day’s opening bids before treading water.
Downside potential is weighing on the Dow Jones after snapping a winning streak that saw the index gain nearly 5% over seven consecutive trading days. The last bull run on daily candlesticks fell short of crossing all-time highs as the equity index nears the 40,000.00 major handle.
Dow Jones five minute chart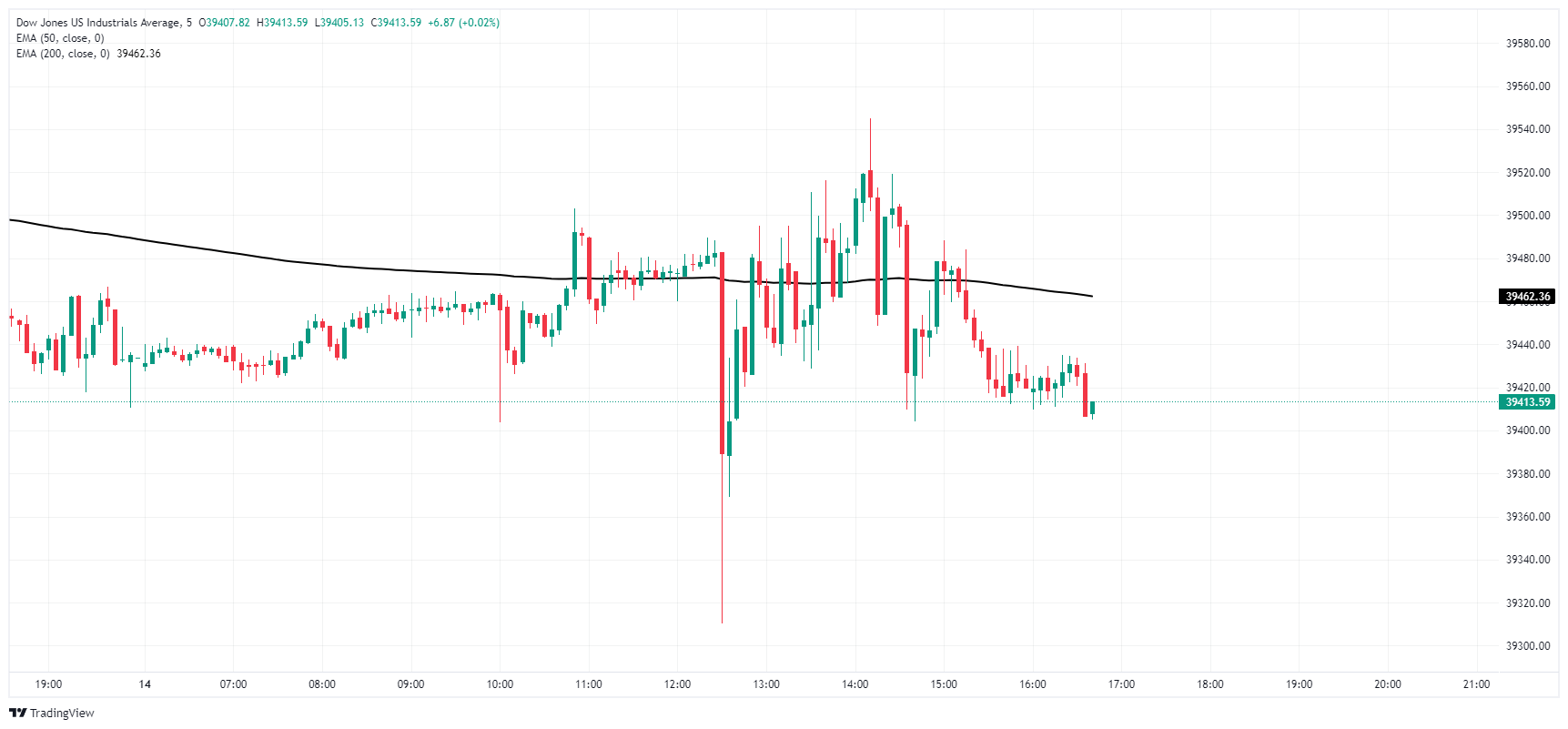
Dow Jones daily chart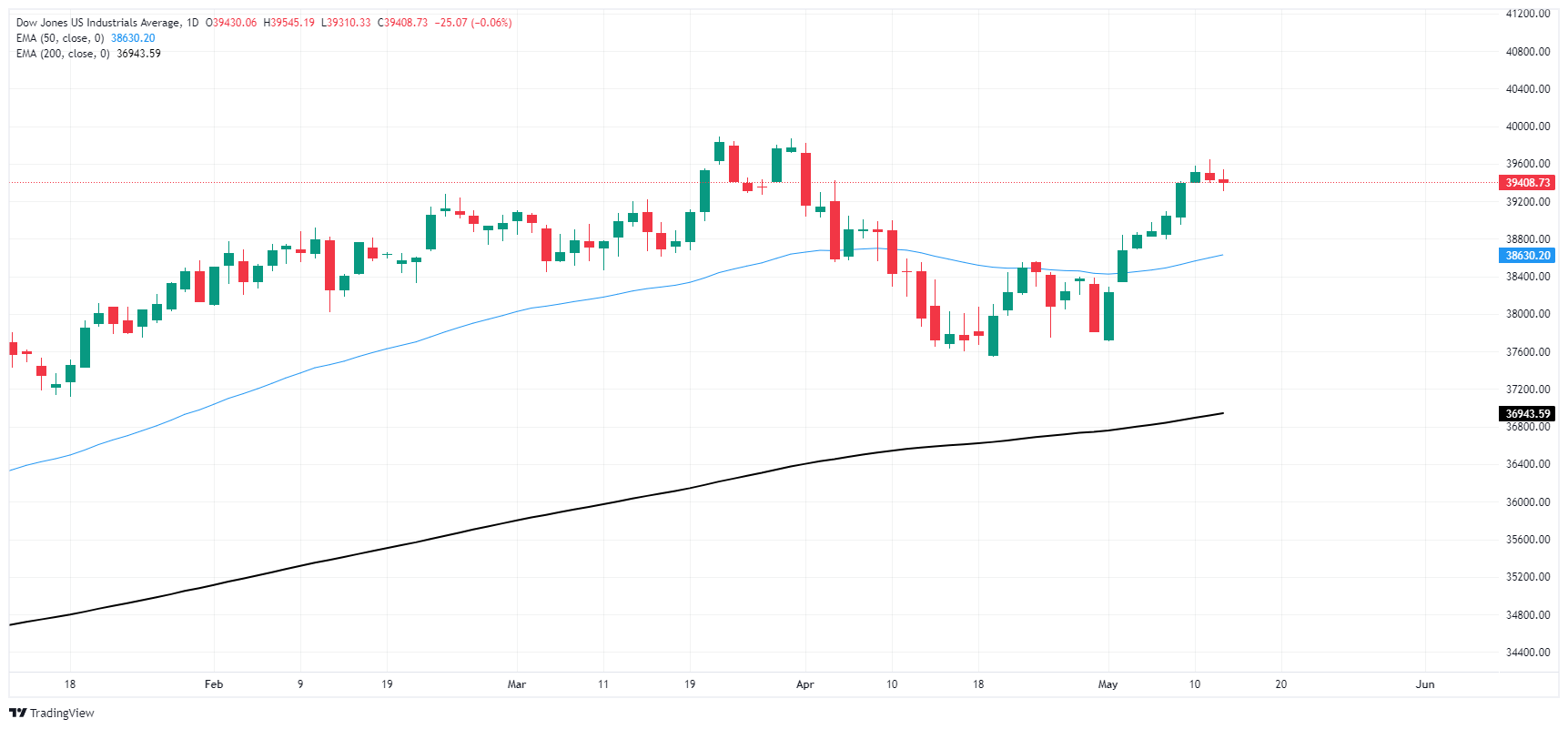
Dow Jones FAQs
The Dow Jones Industrial Average, one of the oldest stock market indices in the world, is compiled of the 30 most traded stocks in the US. The index is price-weighted rather than weighted by capitalization. It is calculated by summing the prices of the constituent stocks and dividing them by a factor, currently 0.152. The index was founded by Charles Dow, who also founded the Wall Street Journal. In later years it has been criticized for not being broadly representative enough because it only tracks 30 conglomerates, unlike broader indices such as the S&P 500.
Many different factors drive the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA). The aggregate performance of the component companies revealed in quarterly company earnings reports is the main one. US and global macroeconomic data also contributes as it impacts on investor sentiment. The level of interest rates, set by the Federal Reserve (Fed), also influences the DJIA as it affects the cost of credit, on which many corporations are heavily reliant. Therefore, inflation can be a major driver as well as other metrics which impact the Fed decisions.
Dow Theory is a method for identifying the primary trend of the stock market developed by Charles Dow. A key step is to compare the direction of the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) and the Dow Jones Transportation Average (DJTA) and only follow trends where both are moving in the same direction. Volume is a confirmatory criteria. The theory uses elements of peak and trough analysis. Dow’s theory posits three trend phases: accumulation, when smart money starts buying or selling; public participation, when the wider public joins in; and distribution, when the smart money exits.
There are a number of ways to trade the DJIA. One is to use ETFs which allow investors to trade the DJIA as a single security, rather than having to buy shares in all 30 constituent companies. A leading example is the SPDR Dow Jones Industrial Average ETF (DIA). DJIA futures contracts enable traders to speculate on the future value of the index and Options provide the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell the index at a predetermined price in the future. Mutual funds enable investors to buy a share of a diversified portfolio of DJIA stocks thus providing exposure to the overall index.


