Dow Jones Industrial Average slow bleeds as government shutdown looms
- The Dow Jones shed around 150 points on Tuesday as investors brace for a government shutdown.
- Equity market momentum has drained away, but indexes are still heading for a stellar September performance.
- The latest US NFP jobs report could be delayed if the federal government can’t pass a budget.
The Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) saw a slow bleed on Tuesday, shedding around 150 points as investors braced ahead of what is likely to be a federal government shutdown. The US has been unable to successfully push out a spending bill ahead of the deadline, sending the federal government headfirst into a spending furlough.
The latest Nonfarm Payrolls (NFP) jobs report, currently slated to be released on Friday, could be delayed if the US government heads into a shutdown phase. Employment figures have become a hot-button issue for investors as the Federal Reserve (Fed) grapples with using interest rates to both bolster what is now a lagging labor market and keep inflation under control.
NFP release becomes hypothetical
In the span of less than a week, President Donald Trump has rolled over from being hopeful about reaching a budget deal to acknowledging that there will likely be a shuttering of federal government operations. Trump has threatened to “do things during a shutdown that are irreversible”, including cutting benefits and axing federal worker jobs in large numbers.
The US Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) has already warned that a government shutdown will result in a delay or suspension of the latest NFP jobs report. The potential publication suspension comes at a time when US jobs numbers are critically important to investors, who are weighing the likelihood of additional interest rate cuts through the remainder of the year.
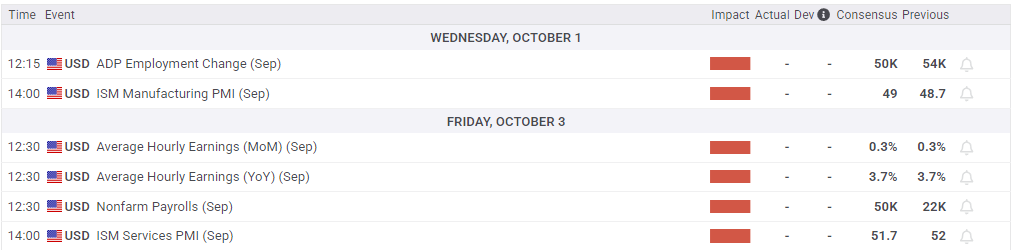
According to the CME’s FedWatch Tool, rate traders are pricing in 95% odds of a follow-up interest rate trim on October 29. However, the jury is still out on a third rate cut: Although rate markets see nearly 75% of a third-straight rate cut in December, many investors are blinking at the prospect and expect the Fed may hold in December before delivering a third cut in January.
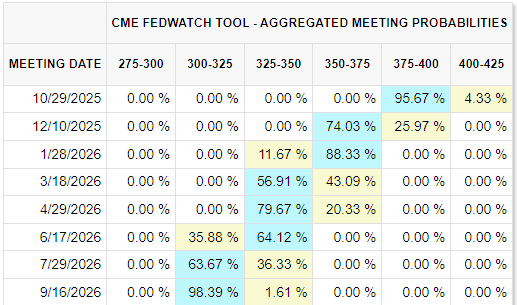
Dow Jones daily chart
Dow Jones FAQs
The Dow Jones Industrial Average, one of the oldest stock market indices in the world, is compiled of the 30 most traded stocks in the US. The index is price-weighted rather than weighted by capitalization. It is calculated by summing the prices of the constituent stocks and dividing them by a factor, currently 0.152. The index was founded by Charles Dow, who also founded the Wall Street Journal. In later years it has been criticized for not being broadly representative enough because it only tracks 30 conglomerates, unlike broader indices such as the S&P 500.
Many different factors drive the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA). The aggregate performance of the component companies revealed in quarterly company earnings reports is the main one. US and global macroeconomic data also contributes as it impacts on investor sentiment. The level of interest rates, set by the Federal Reserve (Fed), also influences the DJIA as it affects the cost of credit, on which many corporations are heavily reliant. Therefore, inflation can be a major driver as well as other metrics which impact the Fed decisions.
Dow Theory is a method for identifying the primary trend of the stock market developed by Charles Dow. A key step is to compare the direction of the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) and the Dow Jones Transportation Average (DJTA) and only follow trends where both are moving in the same direction. Volume is a confirmatory criteria. The theory uses elements of peak and trough analysis. Dow’s theory posits three trend phases: accumulation, when smart money starts buying or selling; public participation, when the wider public joins in; and distribution, when the smart money exits.
There are a number of ways to trade the DJIA. One is to use ETFs which allow investors to trade the DJIA as a single security, rather than having to buy shares in all 30 constituent companies. A leading example is the SPDR Dow Jones Industrial Average ETF (DIA). DJIA futures contracts enable traders to speculate on the future value of the index and Options provide the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell the index at a predetermined price in the future. Mutual funds enable investors to buy a share of a diversified portfolio of DJIA stocks thus providing exposure to the overall index.

