Gold declines after strong US data offsets Fed rate cut
- XAU/USD retreats from $3,673 high to $3,643 as profit-taking follows solid US labor and manufacturing data.
- Fed delivered 25 bps cut Wednesday; dissent from Miran favored 50 bps, keeping easing path open for 2025.
- Gold demand outlook supported by Fed easing cycle and surge in Swiss exports to China, up 254% in August.
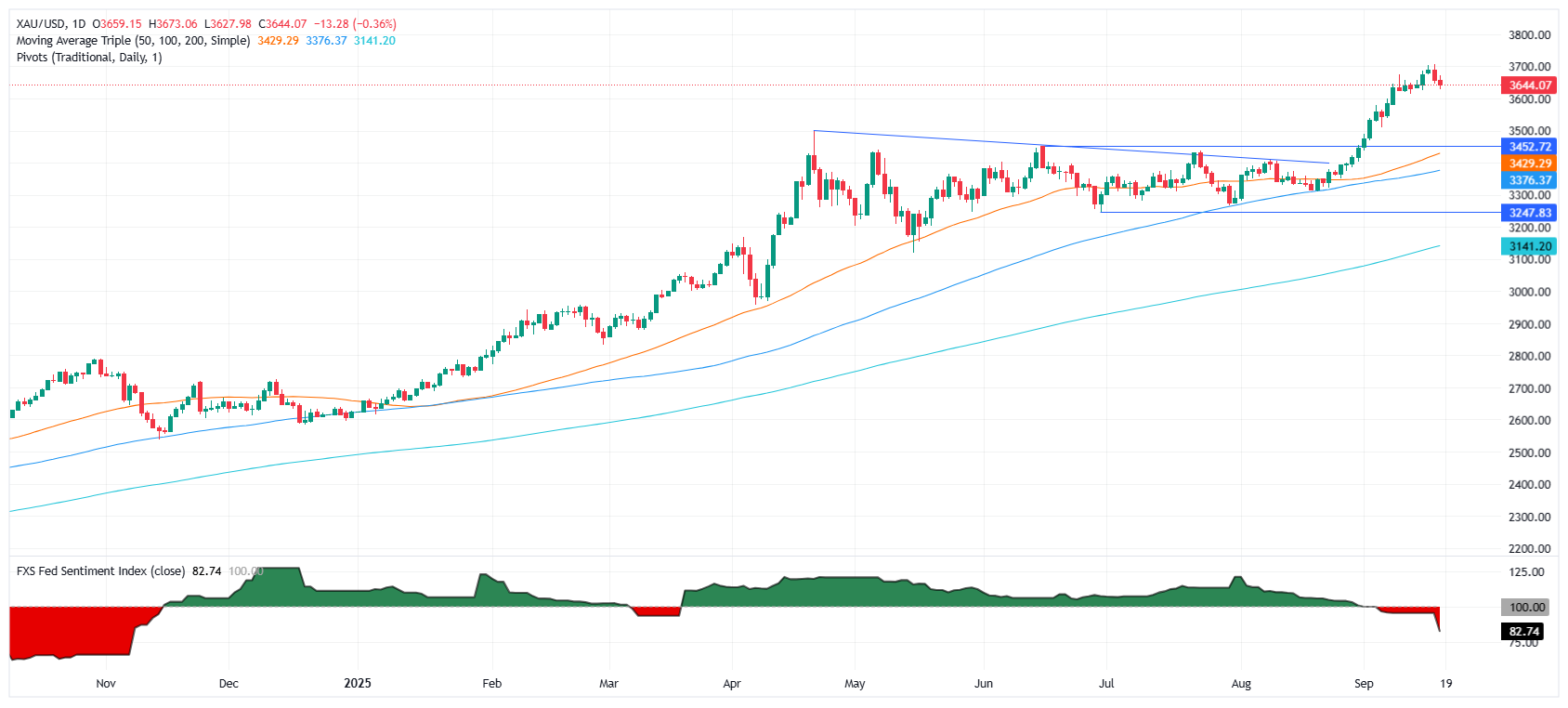
Gold Price retreats during the North American session and is down 0.39% in the aftermath of the Federal Reserve’s (Fed) rate cut decision on Wednesday and better than expected Initial Jobs Claims data. At the time of writing, XAU/USD trades at $3,643 after hitting a daily high of $3,673.
Bullion falls after Jobless Claims, strong Philly Fed Survey offsets Fed cut
The yellow metal remains pressured as traders book profits following the release of upbeat labor market data, which contradicts some of Fed Chair Jerome Powell’s comments during his press conference on Wednesday. The Philadelphia Fed Manufacturing Index for September crushed forecasts, improving compared to August’s print.
On Wednesday, the Fed cut rates by 25 basis points, though the decision was not unanimous, with Stephen Miran voting for 50 bps as widely expected. This cemented the case for subsequent easing for the last two meetings of the year. Although Powell said that every meeting is “live” and that they would be data-dependent, worries about deterioration in the labor market set aside the mandate of price stability.
Consequently, Gold’s outlook looks promising as the non-yielding metal tends to perform well amid easing cycles by the Fed. Also, data showed that Gold exports from Switzerland to China rose by 254%, according to Reuters.
Daily market movers: Gold remains heavy as US Dollar strengthens
- US Initial Jobless Claims for the week ending September 13 came in at 231K, below forecasts of 240K and the previous week's upwardly revised 264K. Continuing Claims dipped from 1.939 million to 1.92 million
- The Philadelphia Fed Manufacturing Index in September reached 23.2 from August’s -0.3 contraction, exceeding forecasts for a 2.3 improvement. The Philadelphia Fed survey revealed that “Almost 40 percent of the firms reported increases in general activity this month, while 17 percent reported decreases; 43 percent reported no change. The new orders index rose 14 points to 12.4 this month, and the shipments index rose 22 points to 26.1.”
- Regarding inflation, the central bank said that it has moved up, remaining “somewhat elevated.” The Fed noted that economic growth has moderated over the first half of 2025.
- Meanwhile, the Summary of Economic Projections (SEP) revealed that 50 bps of cuts are expected toward the year’s end as the median estimate for the fed funds rate was 3.60%.
- Fed Chair Jerome Powell said that labor demand “has softened,” and that inflation remained “somewhat elevated.” He added that the balance of risks “shifted,” that policy is well-positioned to respond in a timely manner and that the labor market is not solid. When asked about discussions about a 50 bps cut, he said “No widespread support for 50 bps cut today,” adding that they are not in a rush to ease policy.
- The US Dollar Index (DXY), which tracks the buck’s performance against a basket of six currencies, is up 0.32% at 97.31.
- US Treasury yields are rising steadily with the 10-year Treasury note up one-and-a-half bps at 4.102%. US real yields surged almost two bps to 1.722% at the time of writing.
Technical outlook: Gold price retreats below $3,650 but remains bullish
Gold price remains upwardly biased despite retreating below Wednesday’s close of $3,646. Bullion is set to extend its gains if it remains above $3,600. Although the Relative Strength Index (RSI) pushed below the 70 level, sparking Wednesday’s sell-off, price action remains constructive.
If Gold regains $3,650, the next resistance would be the record high of $3,703. If surpassed, the next area of interest would be $3,750 and $3,800. Conversely, if XAU/USD drops below the September 11 low at $3,613, expect a challenge of the $3,600 figure.
Gold FAQs
Gold has played a key role in human’s history as it has been widely used as a store of value and medium of exchange. Currently, apart from its shine and usage for jewelry, the precious metal is widely seen as a safe-haven asset, meaning that it is considered a good investment during turbulent times. Gold is also widely seen as a hedge against inflation and against depreciating currencies as it doesn’t rely on any specific issuer or government.
Central banks are the biggest Gold holders. In their aim to support their currencies in turbulent times, central banks tend to diversify their reserves and buy Gold to improve the perceived strength of the economy and the currency. High Gold reserves can be a source of trust for a country’s solvency. Central banks added 1,136 tonnes of Gold worth around $70 billion to their reserves in 2022, according to data from the World Gold Council. This is the highest yearly purchase since records began. Central banks from emerging economies such as China, India and Turkey are quickly increasing their Gold reserves.
Gold has an inverse correlation with the US Dollar and US Treasuries, which are both major reserve and safe-haven assets. When the Dollar depreciates, Gold tends to rise, enabling investors and central banks to diversify their assets in turbulent times. Gold is also inversely correlated with risk assets. A rally in the stock market tends to weaken Gold price, while sell-offs in riskier markets tend to favor the precious metal.
The price can move due to a wide range of factors. Geopolitical instability or fears of a deep recession can quickly make Gold price escalate due to its safe-haven status. As a yield-less asset, Gold tends to rise with lower interest rates, while higher cost of money usually weighs down on the yellow metal. Still, most moves depend on how the US Dollar (USD) behaves as the asset is priced in dollars (XAU/USD). A strong Dollar tends to keep the price of Gold controlled, whereas a weaker Dollar is likely to push Gold prices up.

