Will there be a pause in interest rate hikes in June? How will the index trend?
- International Oil Prices Retreat Rapidly; G-7 to Discuss Emergency Oil Reserve Release
- Goldman Sachs Raises Oil Price Forecasts and Warns Oil May Break All-Time Highs if Strait of Hormuz Disruption Persists
- Crypto’s Great Recovery: Is the Post-Conflict Surge a Sustainable Rally or a Sophisticated Bull Trap?
- WTI recovers to near $86.50 as Strait of Hormuz remains closed
- Gold slumps to near $5,050 on oil-driven inflation fears, stronger US Dollar
- WTI climbs above $95.50 as Iran says the Strait of Hormuz must remain closed
Market Review
Last week, the US stock market performed well with the S&P 500 index rising by 1.8%, the Dow Jones index rising by 2.0%, and the Nasdaq 100 index rising by 1.7%. European stocks performed poorly, with the Europe Stoxx600 index barely rising by 0.2%.
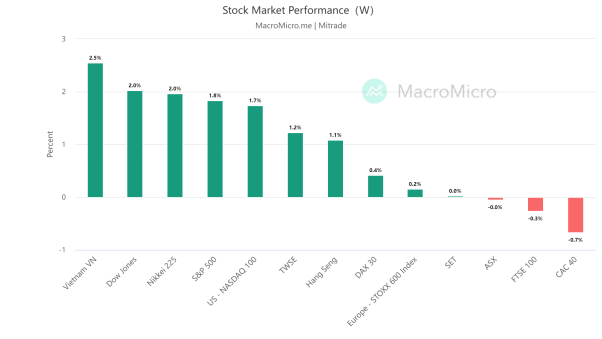
【Source: MacroMicro Date2023/5/29-2023/6/2】
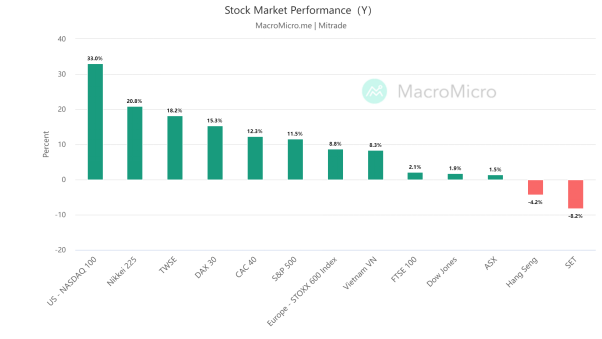
【Source: MacroMicro Date2023/1/1-2023/6/2】
1.Non-farm data brings mixed feelings, market bets on unchanged interest rates in June
The US non-farm payroll data was mixed on June 2nd. According to the data released by the US Department of Labor, the US added 339,000 non-farm jobs in May 2023, far higher than the market's expected 195,000. However, the unemployment rate rose significantly from 3.4% to 3.7%, higher than the market's expected 3.5%, reaching a new high since October 2022. Wage growth slowed in May with a month-on-month increase of 0.3%, which was in line with expectations, and a year-on-year increase of 4.3%, lower than the expected value of 4.4%.
The rising unemployment rate and slowing wage growth suggest that inflationary pressure may ease, but the strong addition of nonfarm payrolls increases the probability of the Federal Reserve continuing to raise interest rates.
After the data release, the market still bets on the Fed holding rates steady in June and raising them in July. According to CME FedWatch, the probability of the Fed not raising rates in June is 74.1%, and the probability of a 25 basis point rate hike in July is 54.0%.
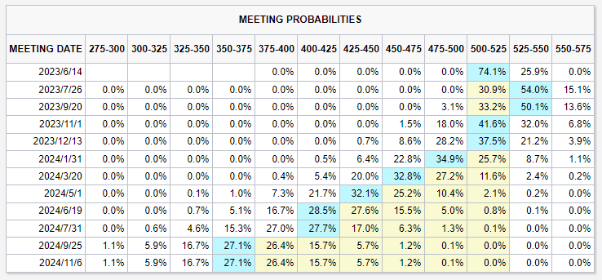
【Source: CME FedWatch as of June 5th, 2023】
Mitrade analyst:
As we anticipated previously, the Federal Reserve's interest rate hike process is not yet over. Pausing the rate hikes does not mean the end of rate hikes, and even if there is no rate hike at the June meeting, the probability of another rate hike in July remains high.
2.Debt ceiling agreement passed, will liquidity decrease?
On June 3rd, President Biden of the United States signed a bill to temporarily suspend the debt ceiling, avoiding a potential government default. The bill had previously been passed by both the House and Senate and will be effective until early 2025.
To bolster the TGA account, the Ministry of Finance is preparing to issue a large amount of bonds, with debt issuance potentially exceeding $1 trillion. Regardless of which institution decides to purchase US bonds, it is expected that funds will be freed up through bank deposits, meaning that liquidity in the banking industry will be significantly reduced.
In addition, a large issuance of US treasury bonds will have an impact on both stocks and bonds. Morgan Stanley's Nikolaos Panigirtzoglou estimates that debt issuance will intensify quantitative tightening, leading to a nearly 5% decline in stock performance. Citibank estimates that after such a significant reduction in liquidity, the median drop in the S&P 500 index over the next two months could reach 5.4%, and high-yield bond spreads could experience fluctuations of 37 basis points.
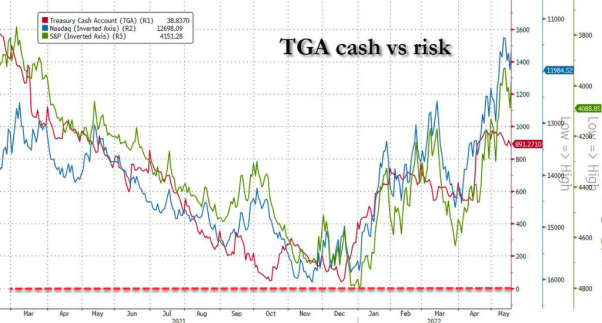
【Source:Bloomberg】
Mitrade analyst:
Issuing a large amount of bonds may cause market liquidity to shrink, but it is worth noting that the expectation of a Fed rate hike in June is weak, so the impact of this event may be limited.
3.Eurozone inflation falls, signaling dovish stance?
On June 1st, Eurostat released data showing that the harmonized CPI in the eurozone increased by 6.1% year-on-year in May, which was lower than the expected 6.3% and significantly lower than the previous month's 7%. The core harmonized CPI increased by 5.3% year-on-year, which was lower than expected and lower than the previous value of 5.6%.
ING notes that both overall and core inflation in the Eurozone have fallen more than expected. Many key inflation drivers have already improved, confirming the downward trend in inflation and sending a dovish signal to the ECB.
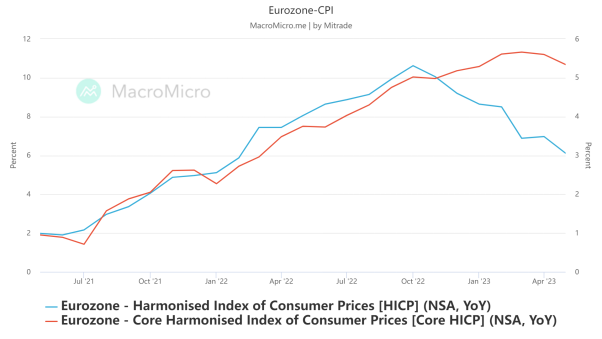
【Source: MacroMicro】
Mitrade analyst:
The main concern currently regarding inflation in Europe is the upward trend in wage growth. In the first quarter, negotiated wages increased by 4.3% compared to the same period last year, and in April, the unemployment rate dropped from 6.6% to 6.5%, indicating that wage pressure continues. This will lead to inflation falling back to 2% at a slower pace than expected, and we anticipate that the ECB will maintain a hawkish stance with subsequent interest rate hikes.
Read more
* The content presented above, whether from a third party or not, is considered as general advice only. This article should not be construed as containing investment advice, investment recommendations, an offer of or solicitation for any transactions in financial instruments.


