Why AI token Bittensor’s development activity surged 3,600% in June despite 22% price drop
- Bittensor accelerates its decline as broader crypto markets struggle to contain sell-side pressure.
- Bittensor was the biggest gainer in development activity, increasing by 3,600% in June.
- The crypto AI sector remains relatively subdued, with the largest token, TAO, posting negative returns in June.
Bittensor (TAO), the largest Artificial Intelligence (AI) token by market capitalization, upholds a bearish bias after facing rejection at $352 on Sunday. TAO is trading at $324, with intraday losses exceeding 3% on Tuesday.
Despite a significant drop in monthly returns, interest in the token remains relatively high, as indicated by the steady Bittensor futures Open Interest (OI), which currently stands at approximately $249 million, according to CoinGlass data.
Bittensor development activity up 36x in time
Santiment’s Development Activity metric, which tracks the level of “meaningful coding work being done on a cryptocurrency’s project over time,” increased by more than 3,600% in June.
According to Santiment, key attributes range from activities on GitHub, such as code updates and new feature development, to filtering out less important elements, including comments, forks, and issue tracking.
Bittensor led other protocols in this segment, with Celestia (TIA) seeing a 3,216% increase in development activity. Other notable improvements were recorded by other AI tokens, including Near Protocol (NEAR), whose activity surged by 3,100%, and Internet Computer (ICP), which saw a 2,779% increase.
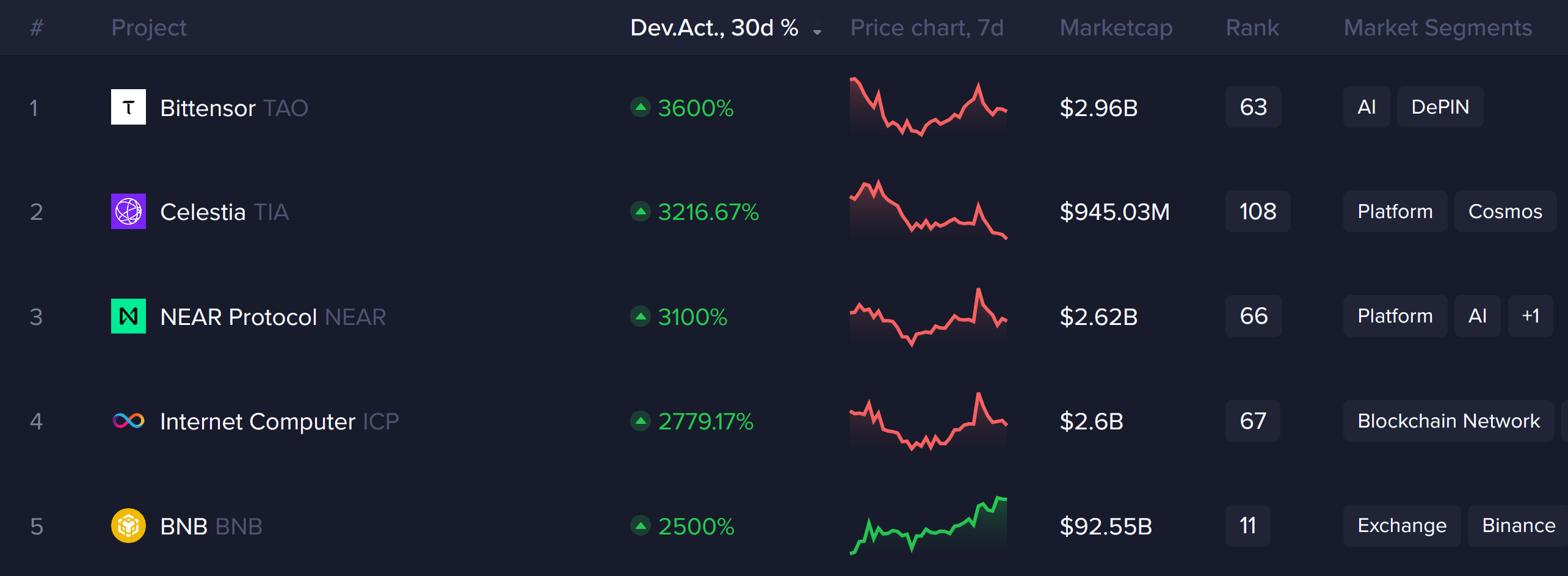
Blockchain development activity | Source Santiment
Despite the increase in Bittensor’s development activity, the price generally declined in June, with TAO recording a 22.2% decrease in monthly returns, as shown by CryptoRank data.
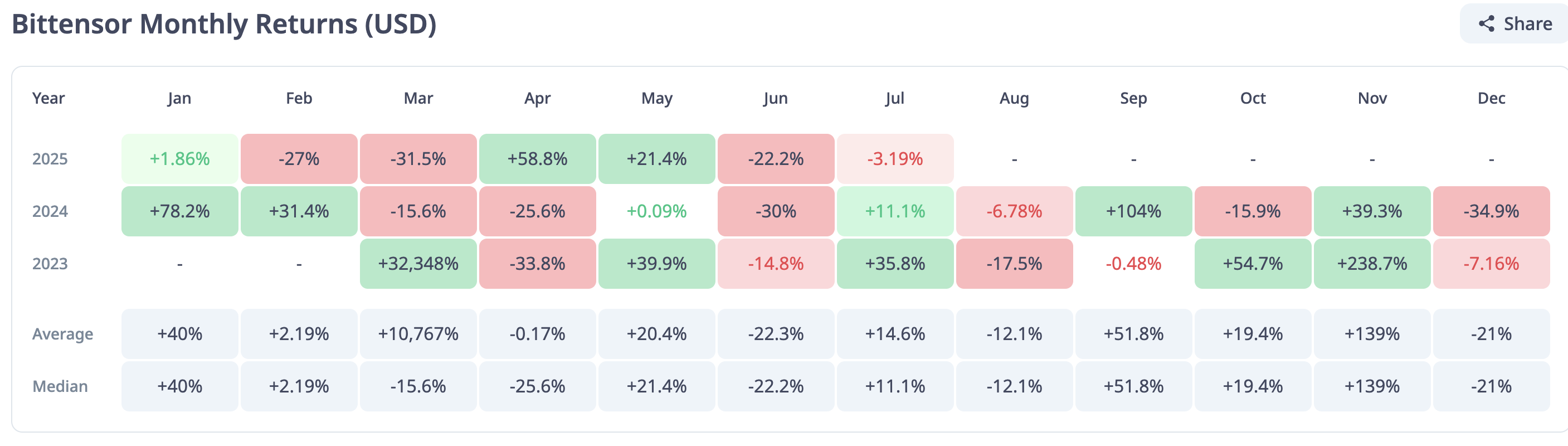
Bittensor monthly returns | Source: CryptoRank
The slump in returns broke a two-month bullish streak, during which Bittensor’s returns averaged 59% in May and leveled slightly above 21% in June. As for quarterly returns, TAO pared losses in the second quarter with a 50% increase in price compared to a 49% decline in the first quarter.
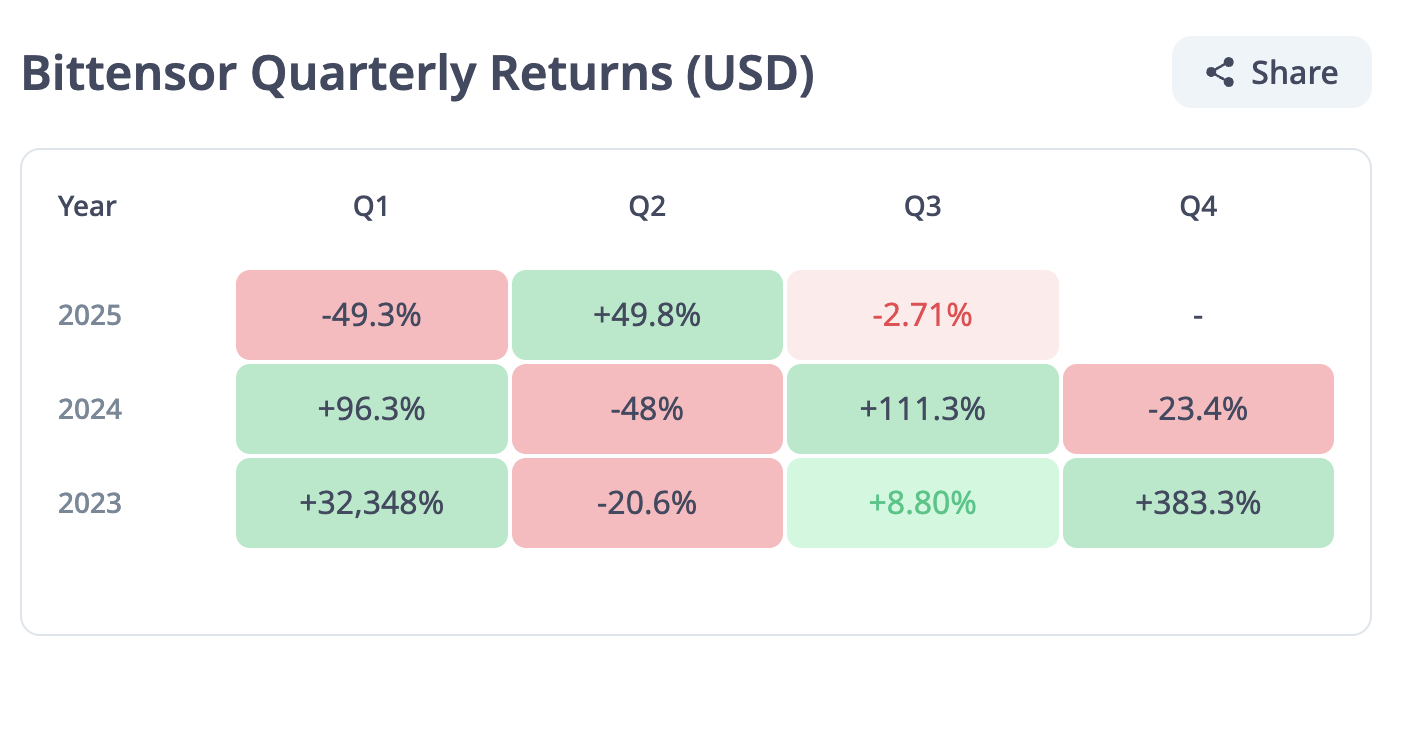
Bittensor monthly returns | Source: CryptoRank
Bittensor is the largest crypto AI token, with a market capitalization of nearly $2.9 billion. The protocol stands out for its role in the sector, developing a language for writing numerous decentralized commodity markets or subnets supported under a unified token system.
This allows subnets to interact via the Bittensor blockchain, creating a unified computing infrastructure. It is this unique infrastructure that attracts developers building decentralized applications that harness the power of AI, much like the role that Ethereum played in the early years of the crypto industry, with the support it provided for smart contracts.
Technical outlook: TAO stares at 12% potential drop
Bittensor offers bearish signals, underpinned by the Relative Strength Index (RSI), which has maintained a downtrend below the midline since reaching overbought territory in April and early May.
The AI token’s position below resistance at around $352, established when the 50-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA) and the 100-day EMA converged, significantly disadvantages the bulls, especially with the 200-day EMA highlighting another hurdle at $372.
If the lethargic market sentiment fails to improve and traders continue with de-risking activities, the path of least resistance could remain downward, thereby increasing the probability of Bittensor falling by almost 12% to the next key support at $287, as tested on June 22.
Still, traders may want to temper their bearish expectations, considering the Money Flow Index (RSI) is rising at 44, suggesting that risk-on sentiment is gaining momentum. If demand for TAO increases in upcoming sessions, a rebound above $352 near-term resistance could boost trader conviction in the uptrend and subsequently expand the token’s bullish scope above the $400 round-figure psychological resistance level.
Cryptocurrency metrics FAQs
The developer or creator of each cryptocurrency decides on the total number of tokens that can be minted or issued. Only a certain number of these assets can be minted by mining, staking or other mechanisms. This is defined by the algorithm of the underlying blockchain technology. On the other hand, circulating supply can also be decreased via actions such as burning tokens, or mistakenly sending assets to addresses of other incompatible blockchains.
Market capitalization is the result of multiplying the circulating supply of a certain asset by the asset’s current market value.
Trading volume refers to the total number of tokens for a specific asset that has been transacted or exchanged between buyers and sellers within set trading hours, for example, 24 hours. It is used to gauge market sentiment, this metric combines all volumes on centralized exchanges and decentralized exchanges. Increasing trading volume often denotes the demand for a certain asset as more people are buying and selling the cryptocurrency.
Funding rates are a concept designed to encourage traders to take positions and ensure perpetual contract prices match spot markets. It defines a mechanism by exchanges to ensure that future prices and index prices periodic payments regularly converge. When the funding rate is positive, the price of the perpetual contract is higher than the mark price. This means traders who are bullish and have opened long positions pay traders who are in short positions. On the other hand, a negative funding rate means perpetual prices are below the mark price, and hence traders with short positions pay traders who have opened long positions.



