USD/INR slips as RBI delivers surprise 50 bps interest-rate cut, markets cheer dovish pivot
- The Indian Rupee strengthens after the RBI delivers a surprise 50 basis points interest-rate cut, larger than expected.
- USD/INR retreats from 86.00 but holds above its key 100-day EMA near 85.63.
- The RBI lowers fiscal year 2026 inflation forecast to 3.7% and maintains GDP growth at 6.5%.
- All eyes are on May’s US Nonfarm Payrolls report, due later on Friday.
The Indian Rupee (INR) strengthens slightly against the United States Dollar (USD) on Friday, despite a surprise 50-basis-point (bps) interest-rate cut by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). The rate trim, which exceeded market expectations, briefly overshadowed a resilient Greenback ahead of the US Nonfarm Payrolls data.
At the time of writing, USD/INR trades around 85.73, down nearly 0.30% on the day, hovering near Thursday’s low after pulling back from the intraday high of 86.00.
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) surprised markets on Friday by cutting its benchmark repo rate by 50 basis points to 5.50%, opting for a stronger dose of monetary easing than the widely expected 25 bps move.
This is the third straight rate cut this year, signaling the central bank’s growing urgency to revive domestic demand and support the economy. Alongside the repo rate cut, the RBI also reduced the Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR) by 100 bps to 3%, injecting fresh liquidity into the banking system.
During the press briefing, RBI Governor Sanjay Malhotra emphasized that frontloading monetary easing is the best way to cushion the economy while inflation stays well within target.
The RBI’s updated projections showed a downward revision in inflation expectations, giving the central bank more flexibility to lower borrowing costs. Even with a shift from “accommodative” to a “neutral” stance, the overall tone suggested that the central bank is prepared to act again if needed.
Market Movers: RBI’s growth push, US data signals cooling labor market
- The Indian central bank maintained its GDP growth forecast for fiscal year 2026 at 6.5%, citing robust domestic demand and a favorable investment climate. Quarterly CPI projections suggest that inflation will gradually rise over the year, remaining within the 2-6% target range, at 2.9% in Q1, 3.4% in Q2, 3.9% in Q3, and 4.4% in Q4.
- In addition to the repo rate and CRR adjustments, the RBI reduced the Standing Deposit Facility (SDF) rate to 5.25%, and trimmed both the Marginal Standing Facility (MSF) rate and the Bank Rate to 5.75%, encouraging banks to reduce lending rates and improve credit flow in the economy.
- On the equity front, Indian stock markets surged following the announcement as investors cheered the central bank’s growth-supportive policy tone and liquidity boost. The BSE Sensex jumped 746 points to close at 82,188, while the Nifty 50 rallied 252 points to end above the 25,000 mark.
- Recent data from the United States (US) suggests the economy may be losing some momentum. The ISM Services PMI declined to 49.9 in May, indicating a slight contraction in the services sector. Meanwhile, weekly jobless claims rose to 247,000 — the highest reading since October — indicating early signs of strain in the labor market.
- The US Dollar Index (DXY) ticks higher, trading around 98.92 on Friday, as investors turn cautious ahead of the May Nonfarm Payrolls report. The mild strength in the Dollar reflects lingering uncertainty over the US economic outlook and a wait-and-see approach from market participants.
Technical analysis: USD/INR holds above trendline, 100-day EMA as market awaits NFP
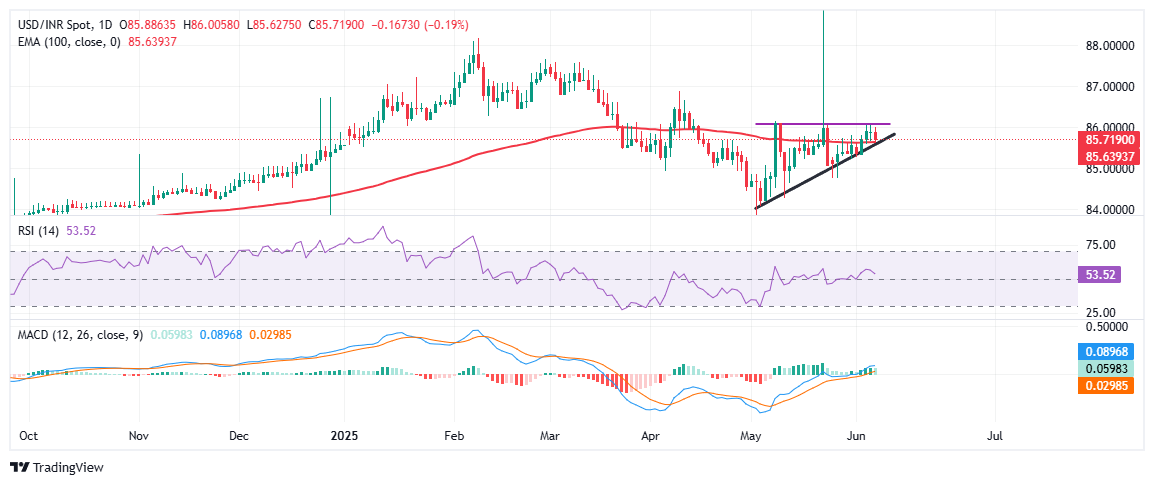
Following the Reserve Bank of India’s surprise 50-basis-point interest rate cut, USD/INR pulled back from the 86.00 mark and is now trading near 85.73.
The pair is trading just below the key resistance zone near 86.00 after multiple failed attempts to break higher. The pair remains supported by a short-term ascending trendline, which has been respected since early May, indicating persistent buying interest on dips. The 100-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA), currently at 85.63, is providing additional support. A daily close below this EMA could open the door for a deeper pullback toward 85.30 and possibly 85.00.
On the momentum side, the Relative Strength Index (RSI) holds steady around 53.5, suggesting that there is still room for either direction without signaling overbought or oversold conditions.
The Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) remains in bullish territory, with the MACD line above the signal line, hinting at underlying upward bias. A confirmed breakout above 86.00 could expose the April highs below 87.00, while a failure to hold above the rising trendline may shift the near-term bias back in favor of INR strength.
RBI FAQs
The role of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), in its own words, is "..to maintain price stability while keeping in mind the objective of growth.” This involves maintaining the inflation rate at a stable 4% level primarily using the tool of interest rates. The RBI also maintains the exchange rate at a level that will not cause excess volatility and problems for exporters and importers, since India’s economy is heavily reliant on foreign trade, especially Oil.
The RBI formally meets at six bi-monthly meetings a year to discuss its monetary policy and, if necessary, adjust interest rates. When inflation is too high (above its 4% target), the RBI will normally raise interest rates to deter borrowing and spending, which can support the Rupee (INR). If inflation falls too far below target, the RBI might cut rates to encourage more lending, which can be negative for INR.
Due to the importance of trade to the economy, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) actively intervenes in FX markets to maintain the exchange rate within a limited range. It does this to ensure Indian importers and exporters are not exposed to unnecessary currency risk during periods of FX volatility. The RBI buys and sells Rupees in the spot market at key levels, and uses derivatives to hedge its positions.



