Commodities are essential goods that serve as the building blocks of the economy, encompassing raw materials and primary agricultural products. Key examples include precious metals like gold and energy sources such as crude oil.
For investors and consumers alike, grasping the importance of commodities is key, as they wield significant influence over global markets. In this article, we delve into the diverse world of commodities, uncovering their vital roles, their impact, and the intricacies of trading them
1. What are commodities and commodity trading?
Commodities refer to raw materials that are extensively used in industry or agriculture, and are purchased and sold on a wholesale rather than retail basis. Commodities trading is the buying and selling of these raw materials. Sometimes it involves the physical trading of goods. But more often it happens through futures contracts, where you agree to buy or sell a commodity for a certain price at a specified date.
2. Type of commodities and Where are they traded?
Commodities are categorized into either soft or hard commodities. Hard commodities, which are defined as natural resources that must be mined or extracted such as gold or oil. Soft commodities are agricultural products or livestock such as corn, wheat, sugar and meat.
Some examples of commodities include;
Energy (Hard) – including crude oil, natural gas, etc.
Basic raw materials (Hard) – including gold, silver, copper, aluminum, etc.
Agricultural products (Soft) – including sugar, corn, coffee, etc.
Livestock (Soft) – cattle, milk, beef
3. How to trade commodities online?
Trading commodities on exchange platforms involves speculating on the price movements of raw materials like gold, oil, or agricultural products. Platforms like Mitrade make this process accessible through Contracts for Difference (CFDs), where traders can profit from price fluctuations without owning the physical asset. The following steps to trade commodities online:
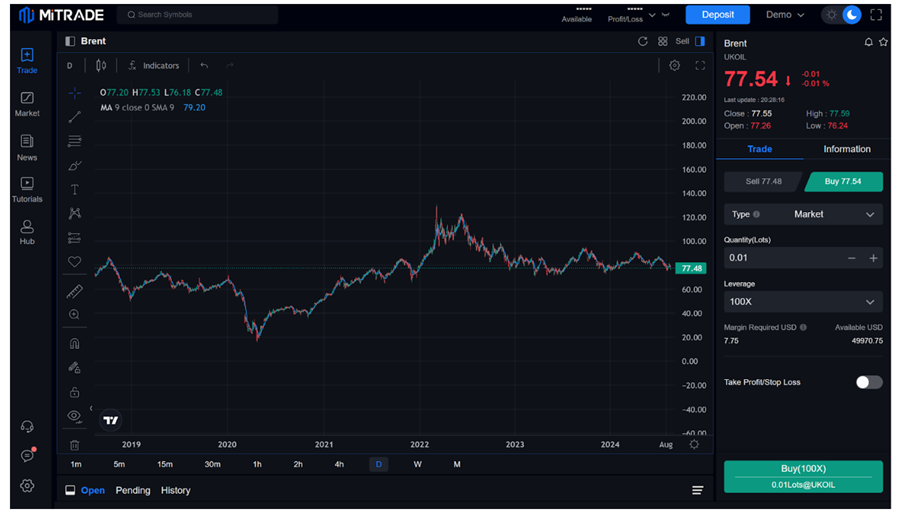
Create an Account: Start by signing up on Mitrade or another platform. Complete the registration and verify your identity as required.
Deposit Funds: Add money to your trading account using available payment methods like bank transfers or credit cards.
Choose a Commodity: Browse available commodities such as gold, oil, or agricultural products. Use the platform’s analysis tools to study price trends and market conditions.
Select Trade Type: On Mitrade, you can trade commodities using CFDs, where you speculate on price movements. Decide whether you want to go long (buy) if you expect prices to rise or short (sell) if you expect them to fall.
Set Trade Parameters: Determine the size of your trade, set leverage (if applicable), and apply risk management tools like stop-loss or take-profit orders.
Place the Trade: Confirm your trade after reviewing all settings. The platform will execute it in real time.
Monitor and Manage: Track your trade using Mitrade’s real-time charts and tools. You can adjust stop-loss levels, add more units, or close the trade at any time.
Close Your Position: Once your target is reached or market conditions change, you can close the trade. Profits or losses are calculated based on the price difference from your entry to exit.
Withdraw Funds: If your trade is successful, you can withdraw your profits using the platform’s withdrawal options.
 0 commission, low spreads
0 commission, low spreads Diverse risk management tools
Diverse risk management tools Flexible leverages and instant analysis
Flexible leverages and instant analysis Practice with $50,000 risk-free virtual money
Practice with $50,000 risk-free virtual money 
4. Summary
Commodities are basic goods used in commerce, categorized into two main types: hard commodities (natural resources like oil and gold) and soft commodities (agricultural products like wheat and coffee).
Commodity trading involves buying and selling these goods, often through futures contracts, which are agreements to purchase or sell at a predetermined price in the future. The article highlights the role of commodity markets in price discovery, speculation, and risk management, emphasizing their significance in the global economy.
5. FAQs
#What factors influence commodity prices?
Commodity prices are influenced by supply and demand, geopolitical events, weather conditions, currency fluctuations, and economic indicators.
#What are the risks of commodity trading?
Commodity trading involves risks such as price volatility, market fluctuations, and potential losses, making it essential for traders to have a solid risk management strategy.
#Who participates in commodity trading?
Participants in commodity trading include producers, consumers, traders, speculators, and investors, each engaging in the market for various reasons such as hedging, speculation, or fulfilling business needs.
* The content presented above, whether from a third party or not, is considered as general advice only. This article should not be construed as containing investment advice, investment recommendations, an offer of or solicitation for any transactions in financial instruments.