USD/INR rises as RBI reduces Repo Rate by 25 bps to 5.25%, as expected
- The Indian Rupee falls against the US Dollar after the RBI’s dovish monetary policy announcement.
- The RBI cuts Repo Rate by 25 bps to 5.25%, and announces an OMO worth Rs. 1 lakh crore.
- Investors expect the Fed to cut interest rates by 25 bps to 3.50%-3.75% next week.
The Indian Rupee (INR) drops against the US Dollar (USD) on Friday, with the USD/INR pair edging higher to near 90.10, as the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) announces a dovish monetary policy. The RBI cuts its Repo Rate by 25 basis points (bps) to 5.25%, and announces to inject Rs. 1 lakh crore into the economy through Open Market Operations (OMO), a tool through which the Indian central bank purchases government securities and a three-year USD/INR swap of $5 billion in December.
The RBI has explained that members decided unanimously to lower borrowing rates amid cooling inflationary pressures. RBI Governor Sanjay Malhotra stated that the headline inflation has eased significantly and is likely to remain lower than projections.
The central bank has projected that both headline and core inflation will remain below 4% during the first half of 2026. For the current financial year, the RBI has revised inflation projections to 2.0% from 2.6% anticipated earlier. Taking strong cues from the Q3 Gross Domestic Product (GDP) data, the RBI has raised growth projections for the current fiscal year to 7.3% from 6.8%.
A dovish monetary policy announcement by the RBI is expected to exert pressure on the Indian Rupee going forward, which is already facing the burden of continuous outflow of overseas funds from the Indian stock market amid tariff issues with the United States (US).
Foreign Institutional Investors (FIIs) have turned out to be net sellers in all four trading days of December, and have offloaded shares worth Rs. 9,964.72 crores in this period. Overseas investors have also remained net sellers in all months since July.
Daily digest market movers: The Fed is expected to cut interest rates next week
- The Indian Rupee falls against the US Dollar, even as the US Dollar struggles to hold its immediate lows. At the press time, the US Dollar Index (DXY), which tracks the Greenback’s value against six major currencies, holds ground near the five-week low around 98.85 during late Asian trading hours, which it regained on Thursday.
- The outlook of the US Dollar remains weak as the Federal Reserve (Fed) is widely anticipated to cut interest rates in its monetary policy meeting next week. According to the November 28-December 4 Reuters poll, 82% of economists surveyed predicted that the Fed will reduce its key borrowing rates by 25 basis points (bps) to 3.50%-3.75% to support deteriorating job market conditions.
- Upbeat Fed dovish expectations are contrary to October’s Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) minutes, which showed that several members did not necessarily view a reduction in December as appropriate, while remaining confident that more rate cuts would be needed in the distant future.
- In the monetary policy meeting next week, investors would like to know how much the Fed will cut interest rates further if it decides to reduce the Federal Funds Rate by 25 bps. In addition, investors would also pay close attention to the Fed’s guidance on the labor market outlook.
- Meanwhile, labor demand has weakened significantly, partly driven by growing acceptance of Artificial Intelligence (AI) by firms. The US ADP reported on Thursday that the private sector shed 32K jobs in November, while it was expected to add 5K fresh workers.
- In Friday’s session, investors will focus on the US Personal Consumption Expenditure Price Index (PCE) data for September, which will be released on Friday.
Technical Analysis: USD/INR gains to near 90.20
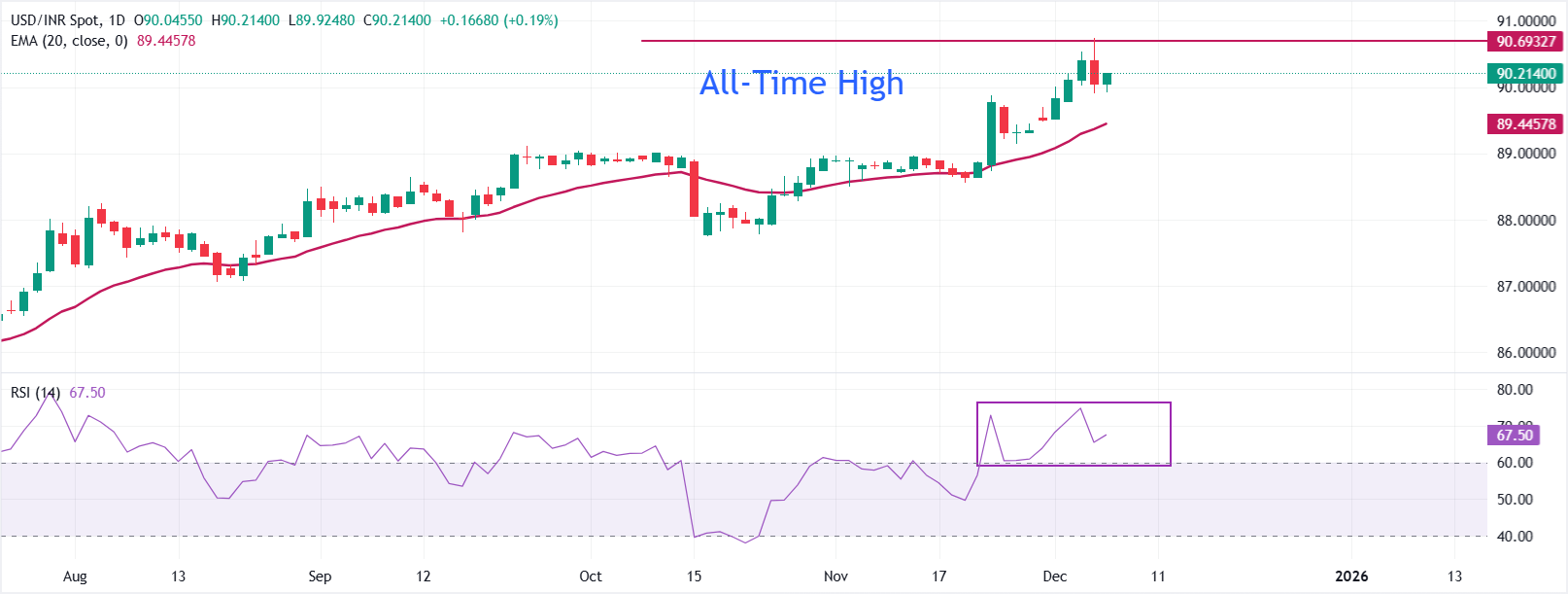
USD/INR rises to near 90.20 during the opening session on Friday. The pair corrected on Thursday after posting a fresh all-time high around 90.70.
The 14-day Relative Strength Index (RSI) retraces to near 67.50 after turning overbought around 76.14, flagging a cool down in stretched momentum.
Initial support is the 20-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA) near 89.44; above this gauge, the uptrend would stay in place. On the upside, the pair could extend its rally towards 91.00.
Indian Rupee FAQs
The Indian Rupee (INR) is one of the most sensitive currencies to external factors. The price of Crude Oil (the country is highly dependent on imported Oil), the value of the US Dollar – most trade is conducted in USD – and the level of foreign investment, are all influential. Direct intervention by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) in FX markets to keep the exchange rate stable, as well as the level of interest rates set by the RBI, are further major influencing factors on the Rupee.
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) actively intervenes in forex markets to maintain a stable exchange rate, to help facilitate trade. In addition, the RBI tries to maintain the inflation rate at its 4% target by adjusting interest rates. Higher interest rates usually strengthen the Rupee. This is due to the role of the ‘carry trade’ in which investors borrow in countries with lower interest rates so as to place their money in countries’ offering relatively higher interest rates and profit from the difference.
Macroeconomic factors that influence the value of the Rupee include inflation, interest rates, the economic growth rate (GDP), the balance of trade, and inflows from foreign investment. A higher growth rate can lead to more overseas investment, pushing up demand for the Rupee. A less negative balance of trade will eventually lead to a stronger Rupee. Higher interest rates, especially real rates (interest rates less inflation) are also positive for the Rupee. A risk-on environment can lead to greater inflows of Foreign Direct and Indirect Investment (FDI and FII), which also benefit the Rupee.
Higher inflation, particularly, if it is comparatively higher than India’s peers, is generally negative for the currency as it reflects devaluation through oversupply. Inflation also increases the cost of exports, leading to more Rupees being sold to purchase foreign imports, which is Rupee-negative. At the same time, higher inflation usually leads to the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) raising interest rates and this can be positive for the Rupee, due to increased demand from international investors. The opposite effect is true of lower inflation.



