USD/INR corrects as RBI intervenes to support Indian Rupee
- The Indian Rupee bounces back from its record lows against the US Dollar, following the RBI’s intervention.
- FIIs have remained net sellers in seven months so far this year.
- The Fed is expected to hold interest rates steady in the January 2026 meeting.
The Indian Rupee (INR) gains sharply against the US Dollar (USD) in the opening session on Wednesday. The USD/INR pair plunges over 1% to near 90.00 from its all-time high of 91.56 due to the Reserve Bank of India’s (RBI) intervention in the spot and Non-deliverable Forward (NDF) markets.
State-run banks were spotted offering US dollars aggressively, most likely on behalf of the RBI, three traders told Reuters.
The RBI was expected to intervene to support the domestic currency, which has remained the worst-performing Asian currency against the US Dollar, and is down almost 6.45% so far this year.
The continuous outflow of foreign funds from the Indian stock market is due to the absence of a trade announcement between the United States (US) and India. The ongoing US-Indian trade stalemate has also increased demand for US Dollars by Indian importers, resulting in weakness in the Indian Rupee.
So far this year, Foreign Institutional Investors (FIIs) have remained net sellers in seven out of 11 months. In December, FIIs have offloaded stake in the Indian equity market worth Rs. 23,455.75 crore.
On the monetary policy front, RBI Governor Sanjay Malhotra has stated in an interview with Financial Times (FT) that interest rates will “remain low for a longer period”. Malhotra added that the recent headline Gross Domestic Product (GDP) figure "was surprising", which led the central bank to "improve its forecasting". He further added that the impact of the US-India trade deal could be as much as 0.5% on the overall GDP.
Daily digest market movers: US Dollar bounces back after release of key domestic data
- The US Dollar extends its Tuesday’s recovery move during Wednesday’s Asian trading hours, even as weak US data has escalated concerns over the economic outlook. At the time of writing, the US Dollar Index (DXY), which tracks the Greenback’s value against six major currencies, trades 0.17% higher to near 98.40. The USD Index rebounded on Tuesday after posting a fresh eight-week low near 98.00.
- On Wednesday, the combined Nonfarm Payrolls (NFP) report for October and November showed that the Unemployment Rate rose to 4.6% lately, the highest figure seen since September 2021. The report also showed that the economy shed 105K jobs in October before creating 64K fresh in November.
- Apart from the labour market data, Retail Sales data for October and preliminary S&P Global Purchasing Managers’ Index (PMI) data for December remained weak. Month-on-month Retail Sales turned out flat, while they were expected to grow steadily by 0.1%. Meanwhile, flash private sector activity data grew at a moderate pace. The Composite PMI landed at 53.0, sharply lower than 54.2 in November.
- While the US data has prompted economic concerns, market experts believe that it is unlikely to impact the Federal Reserve’s (Fed) monetary policy expectations, as the data was distorted by the government shutdown.
- Currently, the CME FedWatch tool shows that the Fed is unlikely to cut interest rates in the January 2026 policy meeting.
- Going forward, investors will focus on the US Consumer Price Index (CPI) data for November, which will be released on Thursday.
Technical Analysis: USD/INR finds cushion near 20-day EMA
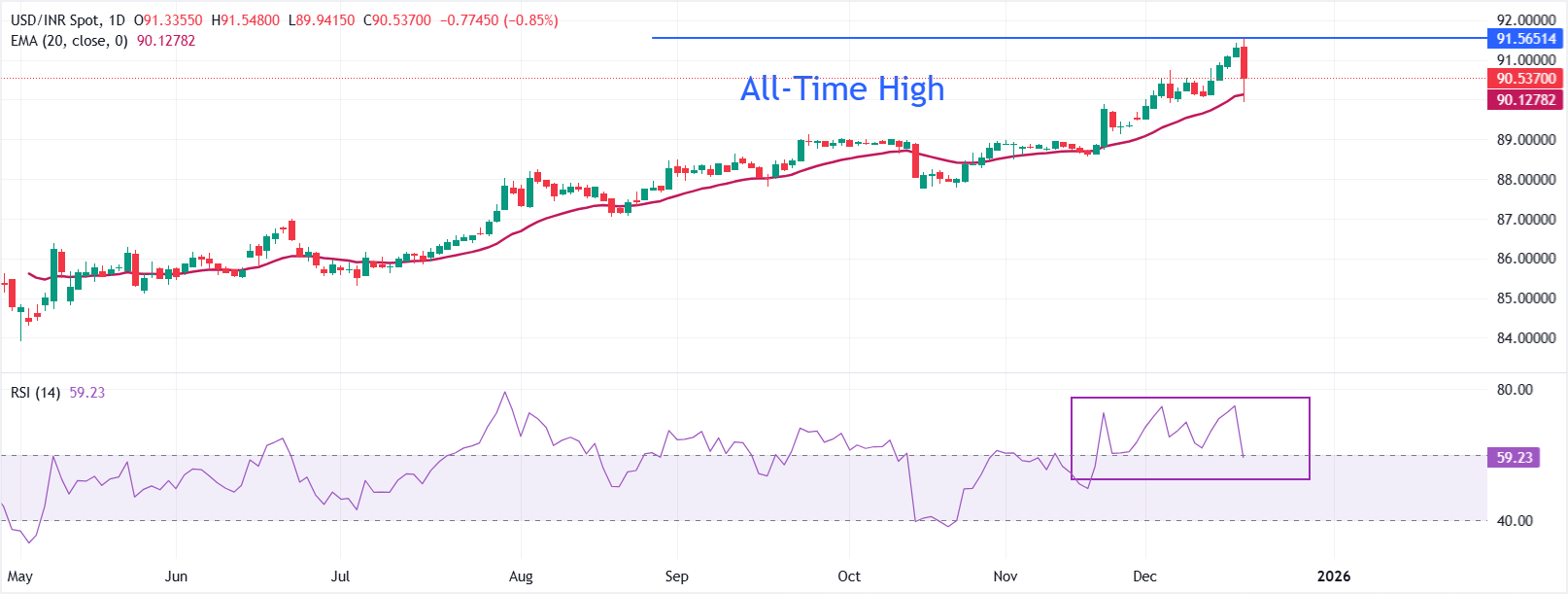
In the daily chart, USD/INR trades at 90.5370. Price holds above the rising 20-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA), preserving a bullish bias. The average continues to ascend and now stands at 90.1278.
The RSI at 59.23, above the 50 midline, confirms positive momentum after unwinding from recent overbought readings. Initial support is at the 20-EMA at 90.1278; sustained trade above this gauge keeps the topside favored.
Trend conditions remain firm, though momentum has moderated as the RSI pulled back from the 70s to 59.23. Pullbacks would remain in check while USD/INR defends the moving-average base, with a support zone across the 20-EMA cluster at 89.9556–89.8364. A daily close below that area would tilt the bias toward consolidation, whereas maintaining bids above it would leave scope for an extension higher.
(The technical analysis of this story was written with the help of an AI tool)
Indian Rupee FAQs
The Indian Rupee (INR) is one of the most sensitive currencies to external factors. The price of Crude Oil (the country is highly dependent on imported Oil), the value of the US Dollar – most trade is conducted in USD – and the level of foreign investment, are all influential. Direct intervention by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) in FX markets to keep the exchange rate stable, as well as the level of interest rates set by the RBI, are further major influencing factors on the Rupee.
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) actively intervenes in forex markets to maintain a stable exchange rate, to help facilitate trade. In addition, the RBI tries to maintain the inflation rate at its 4% target by adjusting interest rates. Higher interest rates usually strengthen the Rupee. This is due to the role of the ‘carry trade’ in which investors borrow in countries with lower interest rates so as to place their money in countries’ offering relatively higher interest rates and profit from the difference.
Macroeconomic factors that influence the value of the Rupee include inflation, interest rates, the economic growth rate (GDP), the balance of trade, and inflows from foreign investment. A higher growth rate can lead to more overseas investment, pushing up demand for the Rupee. A less negative balance of trade will eventually lead to a stronger Rupee. Higher interest rates, especially real rates (interest rates less inflation) are also positive for the Rupee. A risk-on environment can lead to greater inflows of Foreign Direct and Indirect Investment (FDI and FII), which also benefit the Rupee.
Higher inflation, particularly, if it is comparatively higher than India’s peers, is generally negative for the currency as it reflects devaluation through oversupply. Inflation also increases the cost of exports, leading to more Rupees being sold to purchase foreign imports, which is Rupee-negative. At the same time, higher inflation usually leads to the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) raising interest rates and this can be positive for the Rupee, due to increased demand from international investors. The opposite effect is true of lower inflation.



