Japanese Yen bounces off daily low, stays in the red amid domestic political uncertainty
- The Japanese Yen kicks off the new week on a weaker note in the wake of domestic political turmoil.
- Japanese PM Shigeru Ishiba’s resignation could temporarily hinder the BoJ’s policy normalization path.
- Rising Fed rate cut bets could weigh on the USD and keep a lid on any meaningful gains for USD/JPY.
The Japanese Yen (JPY) gaps lower at the start of a new week in reaction to news over the weekend that Japan's Prime Minister Shigeru Ishiba will step down. This overshadows the latest optimism over the recently signed US-Japan trade deal, which will entail lower trade tariffs on Japan and an upward revision of Japan's Q2 GDP growth figures. Adding to this, stronger-than-expected private spending data released on Friday could allow the Bank of Japan (BoJ) to hike interest rates in the coming months, though it does little to impress the JPY bulls.
Apart from this, the risk-on mood – as depicted by a generally positive tone around the equity markets – is seen as another factor undermining the JPY's safe-haven status. The US Dollar (USD), on the other hand, is seen moving away from its lowest level since July 28, touched in reaction to the disappointing US Nonfarm Payrolls (NFP) report on Friday, and further lends support to the USD/JPY pair. The JPY, however, manages to hold above a one-month low touched against its American counterpart last week, warranting some caution for bearish traders.
Japanese Yen drifts lower as political uncertainty overshadows upbeat GDP print and BoJ rate hike bets
- Prime Minister Shigeru Ishiba announced his resignation on Sunday and instructed his Liberal Democratic Party (LDP) to hold an emergency leadership race. This adds a layer of uncertainty, which may temporarily hinder the Bank of Japan from normalising policy and weighs heavily on the Japanese Yen at the start of a new week.
- On the economic data front, the Cabinet Office reported this Monday that Japan's economy expanded at an annualised 2.2% rate in the April-June period from the previous quarter, much faster than the initial reading of 1.0% growth. On a quarterly basis, GDP grew 0.5% compared to a median forecast and the estimate of a 0.3% rise.
- This comes on top of the upbeat data on Friday, which showed that real wages in Japan turned positive for the first time in seven months and a further rise in household spending. This keeps hopes alive for a BoJ rate hike by the end of this year, which might hold back the JPY bears from placing aggressive bets and help limit losses.
- From the US, the closely-watched Nonfarm Payrolls report showed on Friday that the economy added just 22K jobs in August and missed expectations by a big margin. Moreover, revisions to earlier prints revealed the economy lost 13K jobs in June, marking the first monthly decline since December 2020 and pointing to a softening US labor market.
- Additional details revealed that the US Unemployment Rate edged higher to 4.3% from 4.2% in July, as anticipated, while the Labor Force Participation Rate ticked up to 62.3% from 62.2%. Finally, annual wage inflation, as measured by the change in the Average Hourly Earnings, declined to the 3.7% YoY rate from the 3.9% previous.
- The data cemented bets for a rate cut by the Federal Reserve in September and also opened the door for more aggressive policy easing. In fact, traders are now pricing in a small possibility of a jumbo interest rate cut later this month and expect that the US central bank could lower borrowing costs three times by the end of this year.
- The speculations caused a slump in the US Treasury bond yields and favor the US Dollar bears, which should keep a lid on any further appreciating move for the USD/JPY pair. The focus now shifts to the US inflation figures – the Producer Price Index (PPI) and the Consumer Price Index (CPI) on Wednesday and Thursday, respectively.
USD/JPY needs to surpass the 200-day SMA barrier to back the case for any further appreciating move
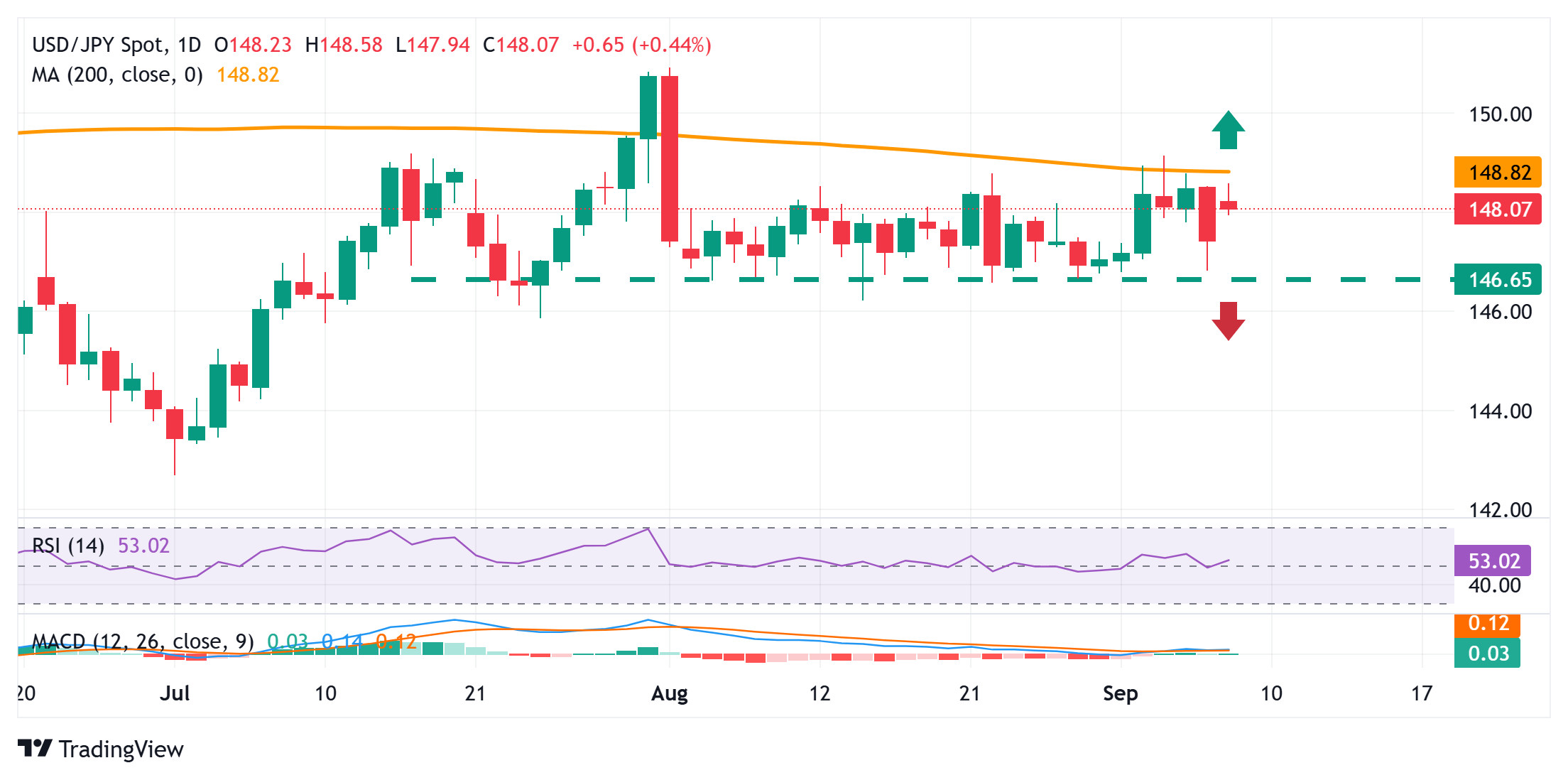
From a technical perspective, the intraday move higher stalls near the very important 200-day Simple Moving Average (SMA) barrier, currently pegged near the 148.75 region. This is closely followed by the 149.00 round figure and the 149.20 area, or a one-month high touched last week. The latter represents the 61.8% Fibonacci retracement level of the decline from the August swing high, which, if cleared decisively, would be seen as a fresh trigger for the USD/JPY bulls. Spot prices might then aim to reclaim the 150.00 psychological mark and extend the momentum further towards challenging the August monthly swing high, around the 151.00 neighborhood.
On the flip side, weakness below the 148.00 round figure could attract some dip-buyers near the 147.45-147.40 region. This should limit the downside for the USD/JPY pair near the 147.00 mark. Some follow-through selling below the 146.80-146.70 strong horizontal support would shift the near-term bias in favor of bearish traders and expose the August swing low, around the 146.20 region, before spot prices eventually drop to the 146.00 mark.
Japanese Yen FAQs
The Japanese Yen (JPY) is one of the world’s most traded currencies. Its value is broadly determined by the performance of the Japanese economy, but more specifically by the Bank of Japan’s policy, the differential between Japanese and US bond yields, or risk sentiment among traders, among other factors.
One of the Bank of Japan’s mandates is currency control, so its moves are key for the Yen. The BoJ has directly intervened in currency markets sometimes, generally to lower the value of the Yen, although it refrains from doing it often due to political concerns of its main trading partners. The BoJ ultra-loose monetary policy between 2013 and 2024 caused the Yen to depreciate against its main currency peers due to an increasing policy divergence between the Bank of Japan and other main central banks. More recently, the gradually unwinding of this ultra-loose policy has given some support to the Yen.
Over the last decade, the BoJ’s stance of sticking to ultra-loose monetary policy has led to a widening policy divergence with other central banks, particularly with the US Federal Reserve. This supported a widening of the differential between the 10-year US and Japanese bonds, which favored the US Dollar against the Japanese Yen. The BoJ decision in 2024 to gradually abandon the ultra-loose policy, coupled with interest-rate cuts in other major central banks, is narrowing this differential.
The Japanese Yen is often seen as a safe-haven investment. This means that in times of market stress, investors are more likely to put their money in the Japanese currency due to its supposed reliability and stability. Turbulent times are likely to strengthen the Yen’s value against other currencies seen as more risky to invest in.

