Silver Price Forecast: XAG/USD stumbles below $36.50 despite softer US CPI
- Silver retreats 0.87% as RSI signals overbought market conditions.
- US CPI miss boosts rate cut bets but fails to support metals.
- Key support lies at $36.00; upside targets remain near $37.50.
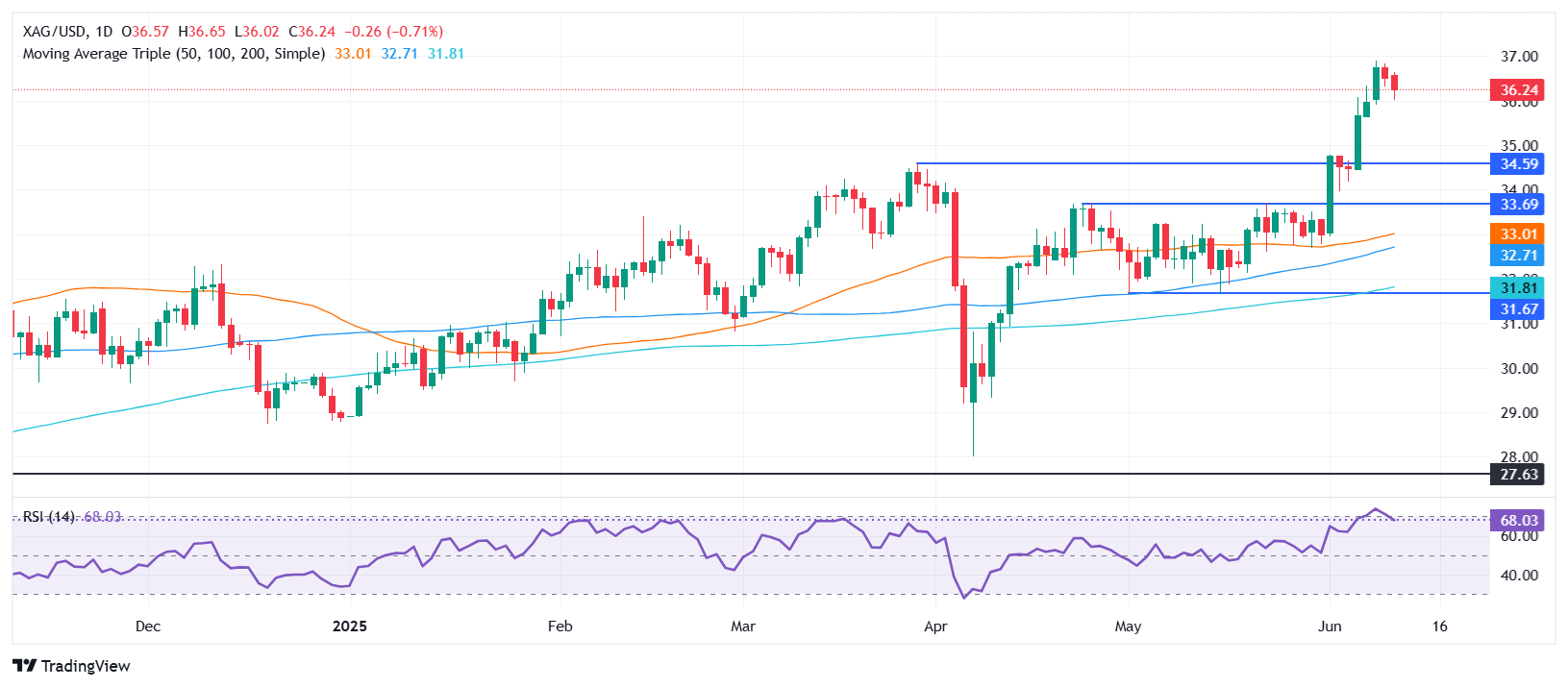
Silver price reverses course on Wednesday as the North American session ends, edging down 0.87%. Even though US inflation dipped in May, which would have warranted rate cuts by the Federal Reserve (Fed) and driven the US dollar lower, it failed to underpin the grey metal. XAG/USD trades at $36.21.
XAG/USD Price Forecast: Technical outlook
Despite retreating, XAG/USD remains poised to test higher prices. Momentum depicts that sellers had stepped in as the Relative Strength Index (RSI) reached overbought territory. This, along with traders' booking profits sent Silver prices below $36.50, which, once cleared, opened the door towards $36.00.
A breach of the latter will expose $35.40, a high from October 2012, which has since turned into support. Once surpassed, the next stop is $35.00, followed by the $34.00 and $33.00 figures,
On the other hand, XAG/USD reclaimed $36.50, and the next target is $37.00. On further strength, prices could reach 37.49, a 13-year high set on February 29.
XAG/USD Price Chart – Daily
Silver FAQs
Silver is a precious metal highly traded among investors. It has been historically used as a store of value and a medium of exchange. Although less popular than Gold, traders may turn to Silver to diversify their investment portfolio, for its intrinsic value or as a potential hedge during high-inflation periods. Investors can buy physical Silver, in coins or in bars, or trade it through vehicles such as Exchange Traded Funds, which track its price on international markets.
Silver prices can move due to a wide range of factors. Geopolitical instability or fears of a deep recession can make Silver price escalate due to its safe-haven status, although to a lesser extent than Gold's. As a yieldless asset, Silver tends to rise with lower interest rates. Its moves also depend on how the US Dollar (USD) behaves as the asset is priced in dollars (XAG/USD). A strong Dollar tends to keep the price of Silver at bay, whereas a weaker Dollar is likely to propel prices up. Other factors such as investment demand, mining supply – Silver is much more abundant than Gold – and recycling rates can also affect prices.
Silver is widely used in industry, particularly in sectors such as electronics or solar energy, as it has one of the highest electric conductivity of all metals – more than Copper and Gold. A surge in demand can increase prices, while a decline tends to lower them. Dynamics in the US, Chinese and Indian economies can also contribute to price swings: for the US and particularly China, their big industrial sectors use Silver in various processes; in India, consumers’ demand for the precious metal for jewellery also plays a key role in setting prices.
Silver prices tend to follow Gold's moves. When Gold prices rise, Silver typically follows suit, as their status as safe-haven assets is similar. The Gold/Silver ratio, which shows the number of ounces of Silver needed to equal the value of one ounce of Gold, may help to determine the relative valuation between both metals. Some investors may consider a high ratio as an indicator that Silver is undervalued, or Gold is overvalued. On the contrary, a low ratio might suggest that Gold is undervalued relative to Silver.

