GBP/USD rebound challenged by downbeat UK labor data
- GBP/USD snapped a four-day win streak on Tuesday after UK labor data missed expectations.
- 1.3200 is forming into an immediate technical ceiling as bulls look to regather steam.
- UK job creation is proving more challenging than expected, and the US government shutdown remains ongoing.
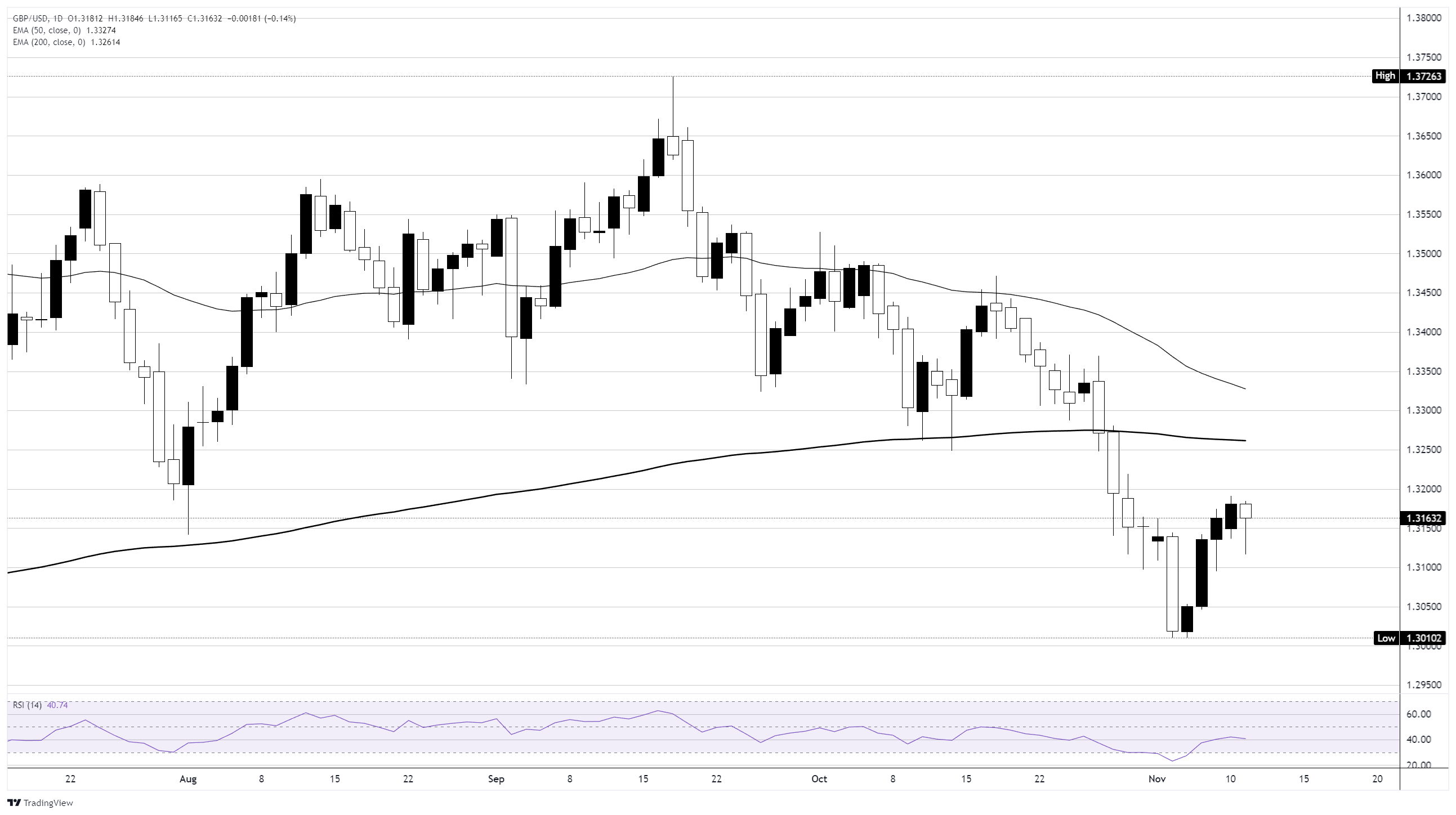
GBP/USD hit a fresh bearish challenge on Tuesday, hitting a snag and snapping a four-day winning streak. The pair remains hamstrung just south of the 1.3200 handle, and Cable traders will need a fresh shock to push Pound Sterling (GBP) bids back onto the high side.
UK employment figures broadly missed the mark on early Tuesday, with the ILO Unemployment Rate rising faster than expected, and more consumers seeking unemployment benefits than markets anticipated. Baseline wages info came in more or less as expected, but wages plus bonuses eased back more than expected, highlighting consumers’ difficulties in negotiating for higher employment remuneration amid rising unemployment.
A smattering of mid-tier Federal Reserve (Fed) policymaker speeches are due on Wednesday, and while the show of a widening array of opinions at the typically uniform Fed will be entertaining, little of note is likely to materialize.
UK datawatchers will be looking ahead to Thursday for another chance at an upbeat data push. UK Gross Domestic Product (GDP) growth figures for the third quarter are due, and are expected to come in more or less unchanged. US markets would have been getting their hands on the latest Consumer Price Index (CPI) inflation data, but the ongoing government shutdown has ended the flow of official data. A resolution is in the works after passing a vote in the US Senate, and now a short-term funding proposal needs to pass a lower house vote.
GBP/USD daily chart
Pound Sterling FAQs
The Pound Sterling (GBP) is the oldest currency in the world (886 AD) and the official currency of the United Kingdom. It is the fourth most traded unit for foreign exchange (FX) in the world, accounting for 12% of all transactions, averaging $630 billion a day, according to 2022 data. Its key trading pairs are GBP/USD, also known as ‘Cable’, which accounts for 11% of FX, GBP/JPY, or the ‘Dragon’ as it is known by traders (3%), and EUR/GBP (2%). The Pound Sterling is issued by the Bank of England (BoE).
The single most important factor influencing the value of the Pound Sterling is monetary policy decided by the Bank of England. The BoE bases its decisions on whether it has achieved its primary goal of “price stability” – a steady inflation rate of around 2%. Its primary tool for achieving this is the adjustment of interest rates. When inflation is too high, the BoE will try to rein it in by raising interest rates, making it more expensive for people and businesses to access credit. This is generally positive for GBP, as higher interest rates make the UK a more attractive place for global investors to park their money. When inflation falls too low it is a sign economic growth is slowing. In this scenario, the BoE will consider lowering interest rates to cheapen credit so businesses will borrow more to invest in growth-generating projects.
Data releases gauge the health of the economy and can impact the value of the Pound Sterling. Indicators such as GDP, Manufacturing and Services PMIs, and employment can all influence the direction of the GBP. A strong economy is good for Sterling. Not only does it attract more foreign investment but it may encourage the BoE to put up interest rates, which will directly strengthen GBP. Otherwise, if economic data is weak, the Pound Sterling is likely to fall.
Another significant data release for the Pound Sterling is the Trade Balance. This indicator measures the difference between what a country earns from its exports and what it spends on imports over a given period. If a country produces highly sought-after exports, its currency will benefit purely from the extra demand created from foreign buyers seeking to purchase these goods. Therefore, a positive net Trade Balance strengthens a currency and vice versa for a negative balance.

