Gold price struggles to capitalize on modest intraday gains to $3,250 area
- Gold price regained positive traction on Monday amid reviving safe-haven demand.
- A downgrade of the US credit rating and tariff threats weighs on investors’ sentiment.
- Fed rate cut bets keep the USD depressed and further lend support to the commodity.
Gold price (XAU/USD) attracts buyers during the Asian session on Monday as a surprise downgrade of the US government's credit rating tempers investors' appetite for riskier assets and boosts demand for traditional safe-haven assets. Furthermore, US Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent's reaffirmation of President Donald Trump's tariff threats lends additional support to the bullion. Meanwhile, bets that the Federal Reserve (Fed) will cut interest rates further this year keep the US Dollar (USD) depressed and turn out to be another factor lending some support to the non-yielding yellow metal.
However, the optimism over the US-China trade truce for 90 days and hopes for more US trade deals with other countries cap the upside for the Gold price near the $3,250-3,252 supply zone. This makes it prudent to wait for strong follow-through buying before confirming that the XAU/USD has formed a near-term bottom and positioning for an extension of last week's goodish recovery from the $3,120 area, or over a one-month low. In the absence of any relevant market-moving US macro data, speeches by influential FOMC members will drive the USD and provide some impetus to the commodity.
Daily Digest Market Movers: Gold price attracts safe-haven flows amid a softer USD; lacks bullish conviction
- Moody's downgraded America's top sovereign credit rating by one notch, to "Aa1" on Friday, citing concerns about the nation's growing debt pile. This comes as the House panel approved US President Donald Trump’s tax cut bill early Monday, which could add trillions to the US debt.
- Meanwhile, US Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent told CNN News on Sunday that President Donald Trump will impose tariffs at the rate he threatened last month on trading partners that do not negotiate in "good faith" on deals. This further underpins the safe-haven Gold price at the start of a new week.
- The US Consumer Price Index (CPI) and the Producer Price Index (PPI) released last week pointed to signs of easing inflationary pressures. Adding to this, the disappointing US Retail Sales data increased the likelihood that the US economy will experience several quarters of sluggish growth.
- Moreover, the University of Michigan's Surveys showed on Friday that the Consumer Sentiment Index deteriorated further in May and dropped from a final reading of 52.2 in April to 50.8 – the lowest level since June 2022. This reaffirmed bets for at least two 25-basis-point rate cuts by the Federal Reserve this year.
- The US Dollar continues with its struggle to attract any meaningful buyers in the wake of dovish Fed expectations, and turns out to be another factor that benefits the commodity. However, the trade optimism has eased concerns about a US recession and caps the upside for the XAU/USD pair.
- On the geopolitical front, Israel's Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu’s office said on Sunday that the military will let limited amounts of food into Gaza. However, sources said there had been no progress in a new round of indirect talks between Israel and the Palestinian militant group Hamas.
- Meanwhile, Ukraine on Sunday said Russia attacked with a record number of drones. This keeps geopolitical risks in play and should act as a tailwind for the precious metal in the absence of any relevant US economic releases and ahead of speeches by influential FOMC members later today.
Gold price needs to find acceptance above the 200-period SMA on the 4-hour timeframe for bulls to seize control
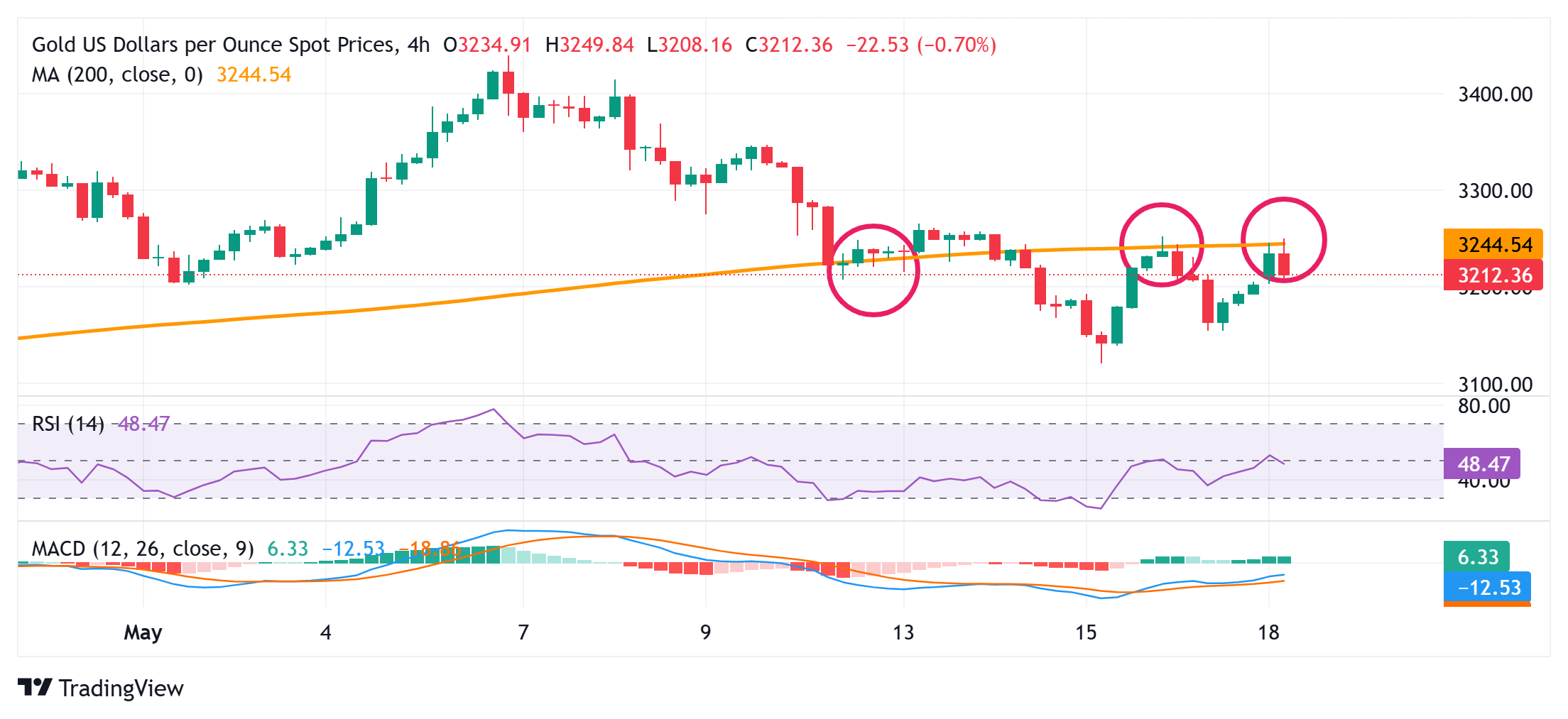
From a technical perspective, the Gold price seems to struggle to move back above the 200-period Simple Moving Average (SMA) support-turned-resistance on the 4-hour chart. Hence, it will be prudent to wait for some follow-through buying beyond the $3,250-3,252 supply zone before confirming that the Gold price has bottomed out and positioning for any further gains. The subsequent move up could lift the commodity above the $3.274-3,275 intermediate barrier, towards the $3,300 round figure. The latter should act as a pivotal point, which, if cleared decisively, could negate any near-term negative bias and shift the bias in favor of bullish traders, paving the way for further gains.
On the flip side, weakness back below the $3,200 mark might now find some support near the $3,178-3,177 area. Some follow-through selling could make the Gold price vulnerable to accelerating the slide towards last week's swing low, around the $3,120 area, or the lowest level since April 10, en route to the $3,100 mark. A convincing break below the latter would expose the next relevant support near the $3,060 region.
Risk sentiment FAQs
In the world of financial jargon the two widely used terms “risk-on” and “risk off'' refer to the level of risk that investors are willing to stomach during the period referenced. In a “risk-on” market, investors are optimistic about the future and more willing to buy risky assets. In a “risk-off” market investors start to ‘play it safe’ because they are worried about the future, and therefore buy less risky assets that are more certain of bringing a return, even if it is relatively modest.
Typically, during periods of “risk-on”, stock markets will rise, most commodities – except Gold – will also gain in value, since they benefit from a positive growth outlook. The currencies of nations that are heavy commodity exporters strengthen because of increased demand, and Cryptocurrencies rise. In a “risk-off” market, Bonds go up – especially major government Bonds – Gold shines, and safe-haven currencies such as the Japanese Yen, Swiss Franc and US Dollar all benefit.
The Australian Dollar (AUD), the Canadian Dollar (CAD), the New Zealand Dollar (NZD) and minor FX like the Ruble (RUB) and the South African Rand (ZAR), all tend to rise in markets that are “risk-on”. This is because the economies of these currencies are heavily reliant on commodity exports for growth, and commodities tend to rise in price during risk-on periods. This is because investors foresee greater demand for raw materials in the future due to heightened economic activity.
The major currencies that tend to rise during periods of “risk-off” are the US Dollar (USD), the Japanese Yen (JPY) and the Swiss Franc (CHF). The US Dollar, because it is the world’s reserve currency, and because in times of crisis investors buy US government debt, which is seen as safe because the largest economy in the world is unlikely to default. The Yen, from increased demand for Japanese government bonds, because a high proportion are held by domestic investors who are unlikely to dump them – even in a crisis. The Swiss Franc, because strict Swiss banking laws offer investors enhanced capital protection.

