USD/INR strengthens toward two-month high as Oil rally and Iran-Israel tensions weigh on Rupee
- USD/INR trades near 86.36, touching its highest level since April amid persistent geopolitical tensions.
- Escalating Iran-Israel conflict and Trump’s evacuation call lift safe-haven demand, pressuring emerging market currencies.
- Firm WTI Crude and weak Indian equities raise concerns about wider FII outflows, adding to the Rupee’s downside.
- Traders are eyeing US Retail Sales and the Fed's decision for fresh cues on the US Dollar's direction.
The Indian Rupee (INR) weakens against the US Dollar (USD) on Tuesday, giving up Monday’s modest rebound as heightened geopolitical tensions in the Middle East, stronger Crude Oil prices, and a resilient Greenback dampen sentiment ahead of the Federal Reserve’s (Fed) key interest rate decision.
The USD/INR pair climbed to an intraday high of 86.46 — a level last seen on April 11 — and was trading around 86.41 at the time of writing, up nearly 0.38% on the day. However, the US Dollar eased slightly after US Retail Sales missed market expectations, dampening buying interest in the Greenback.
Tensions between Iran and Israel flared further on Tuesday after Israel reportedly assassinated Iran’s wartime chief of staff, Ali Shadmani — the second senior commander killed within days. In response, Iran launched a new wave of missile and drone attacks targeting Tel Aviv and Herzliya, triggering air-raid sirens and chaos in Tehran. Adding to the sense of urgency, former US President Donald Trump called for an immediate civilian evacuation of Tehran and insisted he wants a “real end” to the conflict rather than a temporary ceasefire. The heightened geopolitical risk has fuelled risk-off flows across global markets.
Market Movers: Risk-off flows, steady US Dollar, and FII outflows pressure the Rupee
- The Rupee has now dropped to its weakest level in over two months, reflecting a steady downtrend so far this month. It has depreciated about 0.77% in June, widening its year-to-date decline to roughly 0.73% as persistent oil strength and global market jitters continue to weigh on the currency.
- According to Jateen Trivedi, Vice President and Research Analyst for Commodities and Currencies at LKP Securities, the Rupee remains vulnerable amid the escalating Middle East conflict. “Weakness in capital markets signals potential FII outflows, adding to Rupee pressure,” he noted in a report published by Business Standard.
- Equity markets mirrored the cautious mood. Broad-based selling dragged the BSE Sensex lower by 212.85 points to settle at 81,583.30, while the NSE Nifty shed 93.10 points to close at 24,853.40. Foreign institutional investors (FIIs) were net sellers on Monday, pulling out ₹2,539.42 crore worth of equities, according to exchange data.
- In commodities, US West Texas Intermediate (WTI) crude rose by about 2.22% to around $71.69 per barrel on Tuesday, underpinned by concerns about potential supply disruptions amid the Iran-Israel standoff. Higher oil prices typically add to India’s import bill, putting additional pressure on the Rupee and the current account balance.
- Meanwhile, the US Dollar Index (DXY), which tracks the Greenback against a basket of six major currencies, remains firm above the 98.00 mark after slipping to 97.68 on Monday on the back of weaker-than-expected factory data. The Empire State Manufacturing Index tumbled to -16.0 in June, down from -9.2 in May, falling well short of market forecasts and indicating a deeper contraction in regional factory activity.
- Market focus turned to fresh US Retail Sales data for May, which showed a sharper-than-expected decline of 0.9% MoM — the biggest drop in four months — following a 0.1% dip in April. The figure came in weaker than the market forecast of a 0.7% fall, suggesting that consumers pulled back on spending ahead of anticipated tariffs. Meanwhile, the Fed is still expected to keep rates unchanged at its policy meeting on Wednesday, with updated projections and Chair Jerome Powell’s remarks likely to draw attention for any hints on the outlook.
Technical Outlook: Breakout targets 87.00 as momentum builds
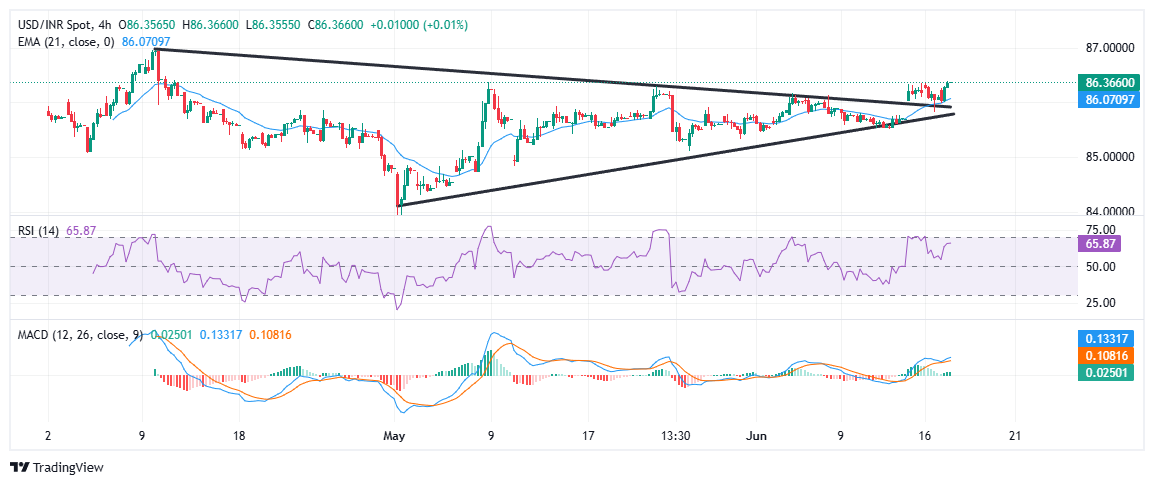
On the technical front, USD/INR has broken above a symmetrical triangle formation on the 4-hour chart, hinting at a continuation of the recent bullish momentum. The pair holds well above the 21-period EMA near 86.07, supporting the near-term positive bias. Momentum indicators remain encouraging, with the RSI hovering near 66 — below overbought territory — and the MACD histogram and signal lines building further upside traction. Sustained trade above the 86.20–86.30 zone could clear the path for a move toward the psychological 87.00 handle.
Indian economy FAQs
The Indian economy has averaged a growth rate of 6.13% between 2006 and 2023, which makes it one of the fastest growing in the world. India’s high growth has attracted a lot of foreign investment. This includes Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) into physical projects and Foreign Indirect Investment (FII) by foreign funds into Indian financial markets. The greater the level of investment, the higher the demand for the Rupee (INR). Fluctuations in Dollar-demand from Indian importers also impact INR.
India has to import a great deal of its Oil and gasoline so the price of Oil can have a direct impact on the Rupee. Oil is mostly traded in US Dollars (USD) on international markets so if the price of Oil rises, aggregate demand for USD increases and Indian importers have to sell more Rupees to meet that demand, which is depreciative for the Rupee.
Inflation has a complex effect on the Rupee. Ultimately it indicates an increase in money supply which reduces the Rupee’s overall value. Yet if it rises above the Reserve Bank of India’s (RBI) 4% target, the RBI will raise interest rates to bring it down by reducing credit. Higher interest rates, especially real rates (the difference between interest rates and inflation) strengthen the Rupee. They make India a more profitable place for international investors to park their money. A fall in inflation can be supportive of the Rupee. At the same time lower interest rates can have a depreciatory effect on the Rupee.
India has run a trade deficit for most of its recent history, indicating its imports outweigh its exports. Since the majority of international trade takes place in US Dollars, there are times – due to seasonal demand or order glut – where the high volume of imports leads to significant US Dollar- demand. During these periods the Rupee can weaken as it is heavily sold to meet the demand for Dollars. When markets experience increased volatility, the demand for US Dollars can also shoot up with a similarly negative effect on the Rupee.