EUR/USD faces pressure as US Dollar ticks higher, US-UK trade deal in focus
- EUR/USD edges down below 1.1300 as the US Dollar strengthens after the Fed said it is in no rush to cut interest rates.
- US President Trump is set to unveil a bilateral trade deal, reportedly with the UK, on Thursday.
- The EU prepares countermeasures against US tariffs to offset their costs.
EUR/USD ticks lower below 1.1300 during European trading hours on Thursday. The major currency pair edges down as the US Dollar (USD) trades slightly higher on signals from the Federal Reserve (Fed) that there is no rush to lower interest rates, which came on Wednesday just after the central bank left interest rates unchanged in the range of 4.25%-4.50% for the third time in a row.
The US Dollar Index (DXY), which gauges the Greenback’s value against six major currencies, ticks higher to near 100.00.
Fed Chair Jerome Powell stated that “uncertainty about the economic outlook has increased further" due to the fallout of tariffs announced by United States (US) President Donald Trump, which have skewed “risks to both inflation and unemployment on the upside”. Therefore, Powell advised that the right thing for the Fed now is to “await more clarity”.
According to the CME FedWatch tool, traders are confident that the Fed will also keep borrowing rates steady in the June policy meeting, but see around a 66% chance of interest rates being lower than current levels in July.
Meanwhile, investors await the announcement of the first bilateral trade deal by the White House under the leadership of US President Trump. On Wednesday, Trump declared through a post on Truth.Social that his team has closed a deal with one of his trading allies, which will be public on Thursday at 14:00 GMT. According to a report from The New York Times (NYT), the trading partner will be the United Kingdom (UK). This contradicts what Trump signaled last week on the NewsNation television network that India, South Korea, and Japan would be the first countries to close trade deals.
However, financial market participants are mainly focusing on trade discussions between the US and China, which are scheduled for Saturday in Switzerland. US Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent and Trade Representative Jamieson Greer confirmed that they will meet their Chinese counterparts, aiming to de-escalate the trade war.
Daily digest market movers: EUR/USD is marginally down as US Dollar ticks up
- EUR/USD is slightly down as the US Dollar moves higher. Though investors have underpinned the USD against the Euro (EUR), the latter is outperforming its peers. The major currency remains firm ahead of the release of countermeasures by the European Union (EU) commission against US tariffs on Thursday.
- On Wednesday, "Tomorrow we will announce next preparatory steps, both in the area of possible rebalancing measures, and also in the areas important for the further discussions," European Trade Commissioner Maros Sefcovic said, Reuters reported. Sefcovic clarified that the foremost priority of the continent is trade negotiations with the US, but not at any cost.
- A Bloomberg report showed on Tuesday that the EU plans to hit about 100 billion Euros worth of US goods with additional tariffs if trade talks fail to deliver a satisfactory result for the bloc.
- While the Euro manages to outperform its peers, its upside is expected to remain limited as the European Central Bank (ECB) is expected to continue the monetary expansion cycle further. Traders are increasingly confident that the ECB will reduce interest rates again in the June meeting.
- ECB officials have shown concerns over the Eurozone economic outlook, while remaining confident that inflation will sustainably return to the central bank’s target of 2% by the year-end.
Technical Analysis: EUR/USD holds key 20-day EMA
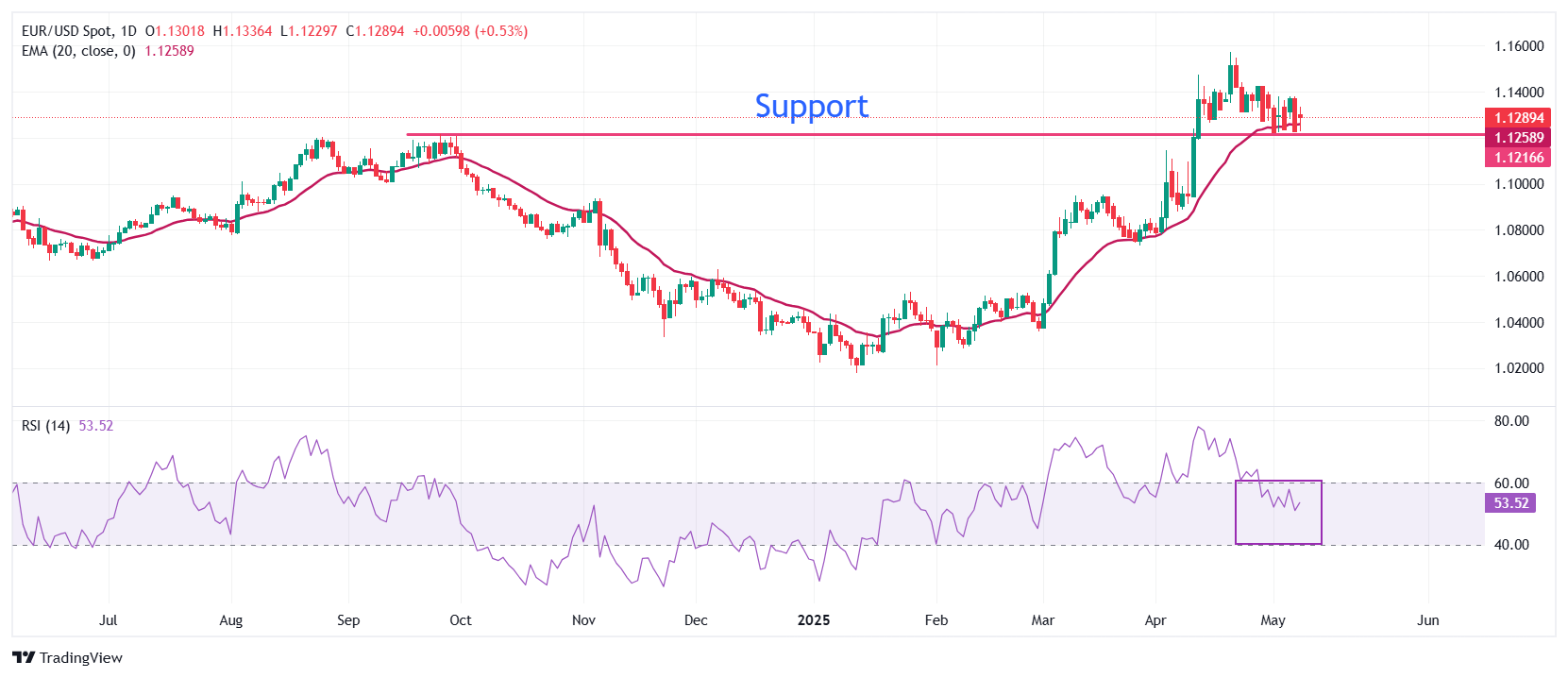
EUR/USD ticks lower below 1.1300 on Thursday. The pair continues to hold the 20-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA) around 1.1260.
The 14-day Relative Strength Index (RSI) falls inside the 40.00-60.00 range, indicating that the bullish momentum is concluded for now. However, the upside bias still prevails.
Looking up, the psychological level of 1.1500 will be the major resistance for the pair. Conversely, the September 25 high of 1.1214 will be a key support for the Euro bulls.
Euro FAQs
The Euro is the currency for the 19 European Union countries that belong to the Eurozone. It is the second most heavily traded currency in the world behind the US Dollar. In 2022, it accounted for 31% of all foreign exchange transactions, with an average daily turnover of over $2.2 trillion a day. EUR/USD is the most heavily traded currency pair in the world, accounting for an estimated 30% off all transactions, followed by EUR/JPY (4%), EUR/GBP (3%) and EUR/AUD (2%).
The European Central Bank (ECB) in Frankfurt, Germany, is the reserve bank for the Eurozone. The ECB sets interest rates and manages monetary policy. The ECB’s primary mandate is to maintain price stability, which means either controlling inflation or stimulating growth. Its primary tool is the raising or lowering of interest rates. Relatively high interest rates – or the expectation of higher rates – will usually benefit the Euro and vice versa. The ECB Governing Council makes monetary policy decisions at meetings held eight times a year. Decisions are made by heads of the Eurozone national banks and six permanent members, including the President of the ECB, Christine Lagarde.
Eurozone inflation data, measured by the Harmonized Index of Consumer Prices (HICP), is an important econometric for the Euro. If inflation rises more than expected, especially if above the ECB’s 2% target, it obliges the ECB to raise interest rates to bring it back under control. Relatively high interest rates compared to its counterparts will usually benefit the Euro, as it makes the region more attractive as a place for global investors to park their money.
Data releases gauge the health of the economy and can impact on the Euro. Indicators such as GDP, Manufacturing and Services PMIs, employment, and consumer sentiment surveys can all influence the direction of the single currency. A strong economy is good for the Euro. Not only does it attract more foreign investment but it may encourage the ECB to put up interest rates, which will directly strengthen the Euro. Otherwise, if economic data is weak, the Euro is likely to fall. Economic data for the four largest economies in the euro area (Germany, France, Italy and Spain) are especially significant, as they account for 75% of the Eurozone’s economy.
Another significant data release for the Euro is the Trade Balance. This indicator measures the difference between what a country earns from its exports and what it spends on imports over a given period. If a country produces highly sought after exports then its currency will gain in value purely from the extra demand created from foreign buyers seeking to purchase these goods. Therefore, a positive net Trade Balance strengthens a currency and vice versa for a negative balance.
This contradicts what Trump signaled last week on the NewsNation television network that India, South Korea, and Japan would be the first countries to close trade deals.

