Pound Sterling strengthens against US Dollar on strong UK Retail Sales data
- The Pound Sterling performs strongly against the US Dollar on robust UK Retail Sales data for April.
- Month-on-month, UK Retail Sales grew strongly by 1.2%.
- US President Trump’s new bill moves to the Senate after passing in the House of Representatives.
The Pound Sterling (GBP) revisits the three-year high against the US Dollar (USD), which it posted earlier this week around 1.3470, in European trading hours on Friday. The British currency strengthens after the release of stronger-than-projected United Kingdom (UK) Retail Sales data for April.
The Office for National Statistics (ONS) reported that Retail Sales, a key measure of consumer spending, rose at a robust pace of 1.2% on the month, compared to estimates of 0.2% and the 0.1% growth seen in March, revised lower from 0.4%. On year, the consumer spending measure grew by 5%, faster than expectations of 4.5% and the prior release of 2.6%.
According to the Retail Sales report, Food stores, Departmental stores, and Household goods stores saw a substantial increase in sales receipts.
Signs of robust household spending are expected to further add to expectations that the Bank of England (BoE) officials will not lower interest rates in the June meeting. This week, hotter-than-expected UK Consumer Price Index (CPI) data for April also forced traders to pare BoE dovish bets.
Meanwhile, flash UK S&P Global Purchasing Managers’ Index (PMI) data for May came in better-than-expected. Still, overall business activity remained contracting as the Composite PMI improved to 49.4, against estimates of 49.3 and from 48.5 in April. Overall business activity declined at a slower pace due to a robust increase in the service sector output. The Services PMI came in at 50.2, higher than expectations of 50.0 and the prior release of 49.0. Meanwhile, the Manufacturing PMI declined at a faster pace to 45.1 from 45.4 in April, below the 46 expected.
Daily digest market movers: Pound Sterling trades higher against US Dollar
- The Pound Sterling outperforms the US Dollar on Friday on the back of upbeat UK Retail Sales data. While growing concerns over the United States (US) fiscal imbalances have also kept the US Dollar on the backfoot. The US Dollar Index (DXY), which tracks the Greenback’s value against six major currencies, declines to near 99.65.
- Financial market participants are worried that US President Donald Trump’s new bill, which comprises tax cuts, increased spending on defense and border enforcement, cuts in the Medicaid program, and subsidies on green energy, is expected to worsen the already overstretched fiscal deficit.
- According to the nonpartisan Congressional Budget Office, Trump’s new bill would increase the US debt by $3.8 trillion over the decade, which is currently $36.2 trillion. Such a scenario would further damage the US Sovereign credit rating, which was already downgraded by Moody’s to Aa1 from Aaa last week.
- President Trump’s new bill has been approved by the Republican-controlled House of Representatives and is advanced to the Senate, where it is expected to face significant objections. "I expect there will be considerable changes in the Senate," Republican Senator Ted Cruz of Texas said, Reuters reported.
- On the monetary policy front, Federal Reserve (Fed) officials are expected to continue arguing in favor of keeping interest rates in their current range of 4.25%-4.50% for a longer time, as Trump’s tax bill could be another trigger for high inflation in the economy. Policymakers have already acknowledged that patience is required amid unusually high uncertainty in the wake of new economic policies announced by US President Trump.
Technical Analysis: Pound Sterling trades firmly near three-year high of 1.3470
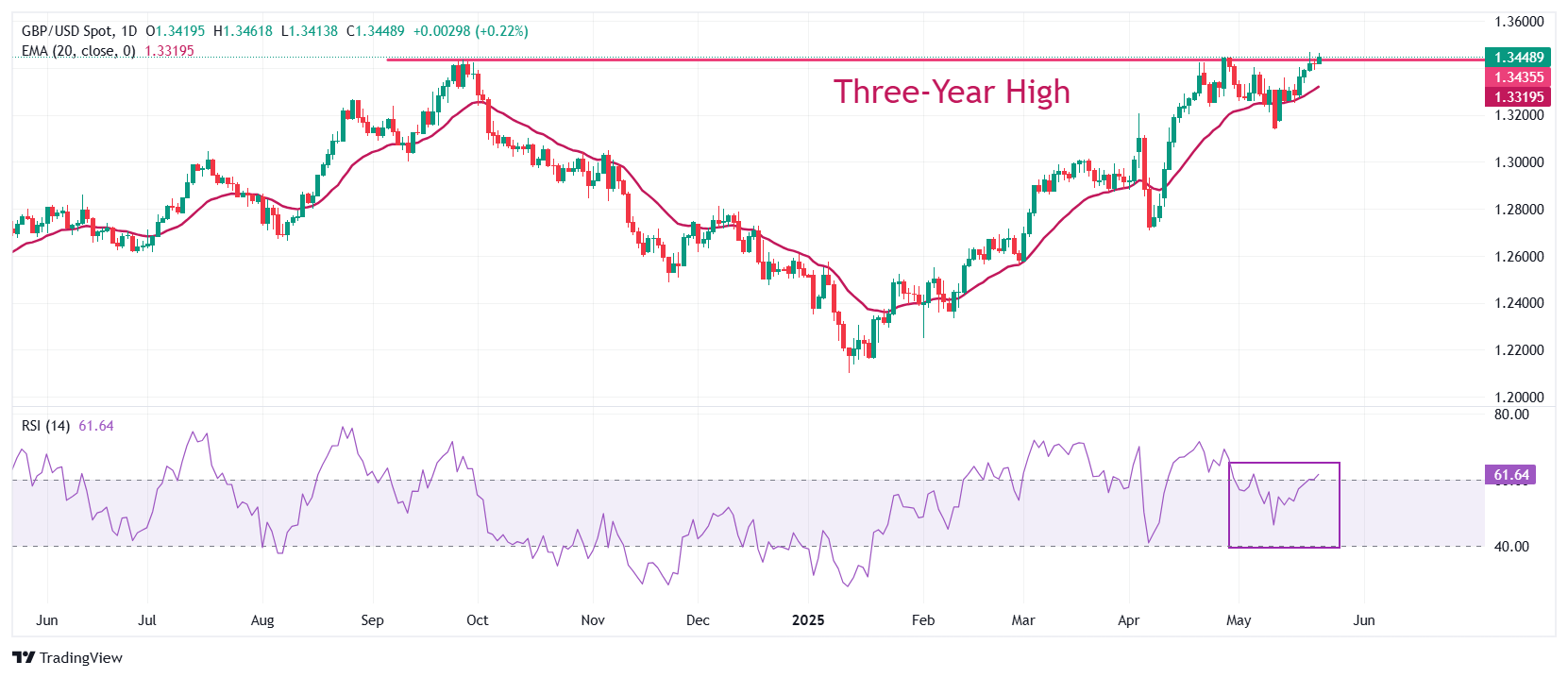
The Pound Sterling trades close to the three-year high of 1.3470 against the US Dollar on Friday. The near-term trend of the GBP/USD pair remains bullish as the 20-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA) is sloping higher around 1.3320.
The 14-day Relative Strength Index (RSI) breaks above 60.00. Should the RSI hold above that level, a fresh bullish momentum would be triggered.
On the upside, the 13 January 2022 high of 1.3750 will be a key hurdle for the pair. Looking down, the 20-day EMA near 1.3320 will act as a major support area.
Pound Sterling FAQs
The Pound Sterling (GBP) is the oldest currency in the world (886 AD) and the official currency of the United Kingdom. It is the fourth most traded unit for foreign exchange (FX) in the world, accounting for 12% of all transactions, averaging $630 billion a day, according to 2022 data. Its key trading pairs are GBP/USD, also known as ‘Cable’, which accounts for 11% of FX, GBP/JPY, or the ‘Dragon’ as it is known by traders (3%), and EUR/GBP (2%). The Pound Sterling is issued by the Bank of England (BoE).
The single most important factor influencing the value of the Pound Sterling is monetary policy decided by the Bank of England. The BoE bases its decisions on whether it has achieved its primary goal of “price stability” – a steady inflation rate of around 2%. Its primary tool for achieving this is the adjustment of interest rates. When inflation is too high, the BoE will try to rein it in by raising interest rates, making it more expensive for people and businesses to access credit. This is generally positive for GBP, as higher interest rates make the UK a more attractive place for global investors to park their money. When inflation falls too low it is a sign economic growth is slowing. In this scenario, the BoE will consider lowering interest rates to cheapen credit so businesses will borrow more to invest in growth-generating projects.
Data releases gauge the health of the economy and can impact the value of the Pound Sterling. Indicators such as GDP, Manufacturing and Services PMIs, and employment can all influence the direction of the GBP. A strong economy is good for Sterling. Not only does it attract more foreign investment but it may encourage the BoE to put up interest rates, which will directly strengthen GBP. Otherwise, if economic data is weak, the Pound Sterling is likely to fall.
Another significant data release for the Pound Sterling is the Trade Balance. This indicator measures the difference between what a country earns from its exports and what it spends on imports over a given period. If a country produces highly sought-after exports, its currency will benefit purely from the extra demand created from foreign buyers seeking to purchase these goods. Therefore, a positive net Trade Balance strengthens a currency and vice versa for a negative balance.

