Gold plunges below $3,300 as risk appetite surges on China trade deal, Middle East diplomacy
- XAU/USD falls over 1.5% as safe-haven demand wanes on global trade and geopolitical easing.
- US-China trade deal signed; more agreements expected before July 9, boosting sentiment.
- Iran signals diplomacy; Israel–Gaza war may end in two weeks, says Al Arabiya.
- Core PCE rose above forecasts; Fed’s Kashkari still expects two rate cuts in 2025.
Gold price tumbled over 1.50% on Friday amid an improvement in risk appetite, driven by several factors. The de-escalation of the Israel–Iran conflict, the trade agreement with China, and ongoing negotiations between the United States (US) and its peers to reach commercial deals were welcomed by investors, who had previously sought refuge in Bullion’s safe-haven demand.
The XAU/USD trades at $3,274 after hitting a daily high of $3,328. On Thursday, the White House announced that the US and China have formally signed a trade agreement, effectively ending the ongoing “trade war.” US Commerce Secretary, Howard Lutnick, said that additional deals are looming as the July 9 deadline approaches.
Regarding geopolitics, Iran has shown signs of flexibility, leaning toward diplomacy, as its representative in the UN said that Tehran is open to forming a regional nuclear consortium in the event of an agreement with Washington.
Adding to the upbeat mood is the possibility of the end of the Israel–Gaza war within two weeks, revealed Al Arabiya.
In the US, the Federal Reserve's (Fed) preferred inflation gauge, the core Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) Price Index, came in line with estimates in May but failed to show any progress toward disinflation.
Earlier, the Minneapolis Fed's Neel Kashkari commented that he still sees two rate cuts in 2025.
Daily digest market movers: Gold price set for correction amid steady US Dollar and US yields
- Gold price is losing its luster due to market participants becoming increasingly optimistic about the global economy. News of the trade deal with China, as well as those with other countries, including South Korea, Vietnam and the EU, was welcomed by investors.
- Howard Lutnick, the US Commerce Secretary, added that China is “going to deliver rare earths to us,” and once they do that, “we’ll take down our countermeasures,” Lutnick told Bloomberg News in an interview.
- Core PCE in May rose by 2.7% YoY, a tenth above estimates and April’s data. Headline inflation for the same period increased by 2.3% YoY as expected.
- The University of Michigan (UoM) revealed that Consumer Sentiment in June improved moderately. The Index rose from 60.5 to 60.7, while inflation expectations were downwardly revised, with households expecting prices to rise from 5.1% to 5% over the next year. For the next five years, inflation is projected to be around 4%, down from 4.1%.
- The US 10-year Treasury note is flat, yielding 4.242%. The US Dollar Index (DXY), which tracks the performance of the buck’s value against a basket of six peers, is virtually unchanged at 97.28.
- Minneapolis Fed President Neel Kashkari said an inflation boost is likely coming, but actual inflation indicates renewed progress toward the 2% target. More time is needed to determine whether the effects of the trade war are delayed or if they will be smaller than initially thought.
- Money markets suggest that traders are pricing in 63.5 basis points of easing toward the end of the year, according to Prime Market Terminal data.
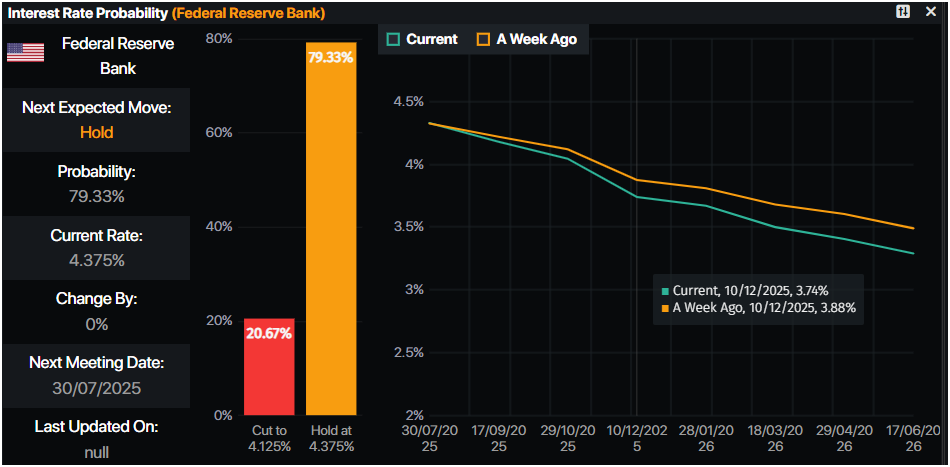
Source: Prime Market Terminal
XAU/USD technical outlook: Gold price set for a pullback to $3,200
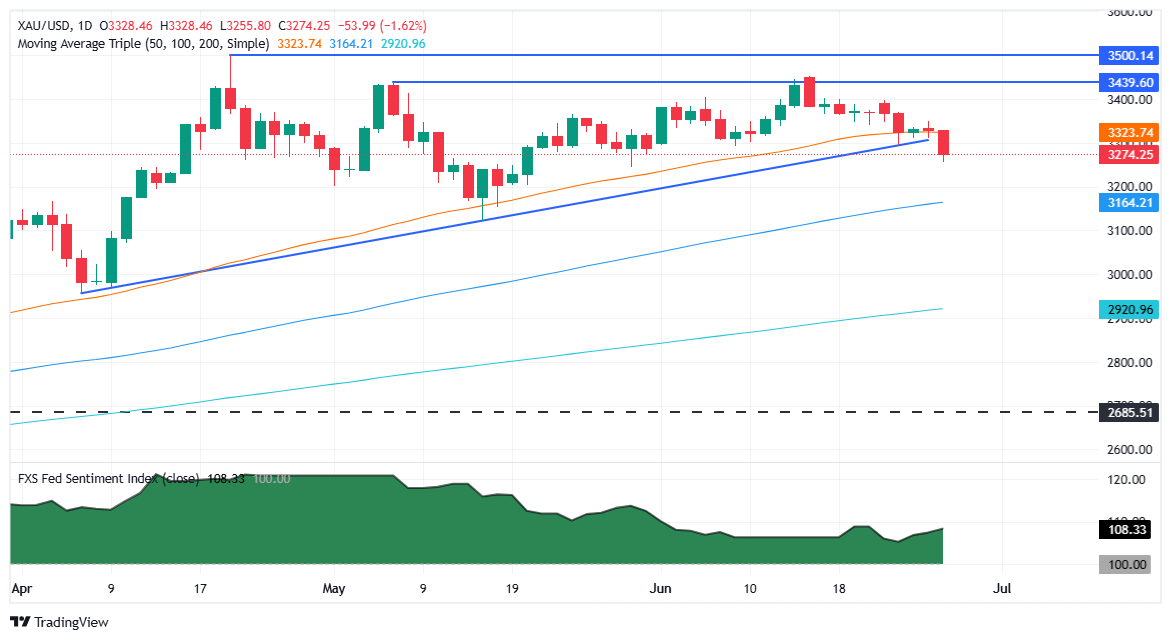
Gold price uptrend remains in place, but in the short term, it could drop further after breaking below the 50-day Simple Moving Average (SMA) at $3,323. The Relative Strength Index (RSI) indicates that momentum has turned bearish despite the price action achieving higher highs and higher lows.
For a bullish continuation, XAU/USD must climb past $3,300. The following key resistance would be the 50-day SMA at $3,323, followed by the June 26 peak of $3,350. If surpassed, up next is $3,400. On the flip side, if XAU/USD tumbles below $3,300, the May 29 low of $3,245 and $3,200 are up for grabs.
Gold FAQs
Gold has played a key role in human’s history as it has been widely used as a store of value and medium of exchange. Currently, apart from its shine and usage for jewelry, the precious metal is widely seen as a safe-haven asset, meaning that it is considered a good investment during turbulent times. Gold is also widely seen as a hedge against inflation and against depreciating currencies as it doesn’t rely on any specific issuer or government.
Central banks are the biggest Gold holders. In their aim to support their currencies in turbulent times, central banks tend to diversify their reserves and buy Gold to improve the perceived strength of the economy and the currency. High Gold reserves can be a source of trust for a country’s solvency. Central banks added 1,136 tonnes of Gold worth around $70 billion to their reserves in 2022, according to data from the World Gold Council. This is the highest yearly purchase since records began. Central banks from emerging economies such as China, India and Turkey are quickly increasing their Gold reserves.
Gold has an inverse correlation with the US Dollar and US Treasuries, which are both major reserve and safe-haven assets. When the Dollar depreciates, Gold tends to rise, enabling investors and central banks to diversify their assets in turbulent times. Gold is also inversely correlated with risk assets. A rally in the stock market tends to weaken Gold price, while sell-offs in riskier markets tend to favor the precious metal.
The price can move due to a wide range of factors. Geopolitical instability or fears of a deep recession can quickly make Gold price escalate due to its safe-haven status. As a yield-less asset, Gold tends to rise with lower interest rates, while higher cost of money usually weighs down on the yellow metal. Still, most moves depend on how the US Dollar (USD) behaves as the asset is priced in dollars (XAU/USD). A strong Dollar tends to keep the price of Gold controlled, whereas a weaker Dollar is likely to push Gold prices up.

