Canadian Dollar soars as markets pull away from Greenback on Friday
- The Canadian Dollar gained a full percent against the US Dollar.
- The Loonie climbed to seven-month peaks against the USD as trade threats resume.
- Canadian economic data has been thin this week, leaving CAD to follow broad-market flows.
The Canadian Dollar (CAD) caught a huge boost from market-wide Greenback weakness on Friday. The Loonie climbed over a full percent against the waffling US Dollar (USD) following a fresh batch of eerily-familiar-looking tariff threats from United States (US) President Donald Trump.
Canadian economic data has been strictly mid-tier for most of this trading week, leaving the Loonie at the mercy of broader investment sentiment. Next week will also kick off with a notably thin note: US markets will be closed for an extended weekend, and there is little of note on either side of the data docket next week until Friday’s US Personal Consumption Expenditures Price Index (PCE) inflation print.
Daily digest market movers: Canadian Dollar traders take full advantage of Greenback weakness
- The Canadian Dollar tested into its highest bids against the US Dollar on Friday, pushing the USD/CAD pair into 1.3720.
- US President Donald Trump wants to tariff individual tech companies that don’t pivot their entire business model to producing their goods in the US, despite their entire production cycle being built around profit margins from importing goods from countries with lower wages.
- President Trump also returned to ‘recommending’ an across-the-board 50% tariff on goods imported from the European Union (EU) in a repeat of identical tariff threats that Trump had already backed down from in the first quarter.
- US markets will be shuttered on Monday for the Memorial Day long weekend, crimping market flows early next week.
- US PCE inflation will be the key print next week, but major inflation metrics are still missing possible fallout from tariffs.
Canadian Dollar price forecast
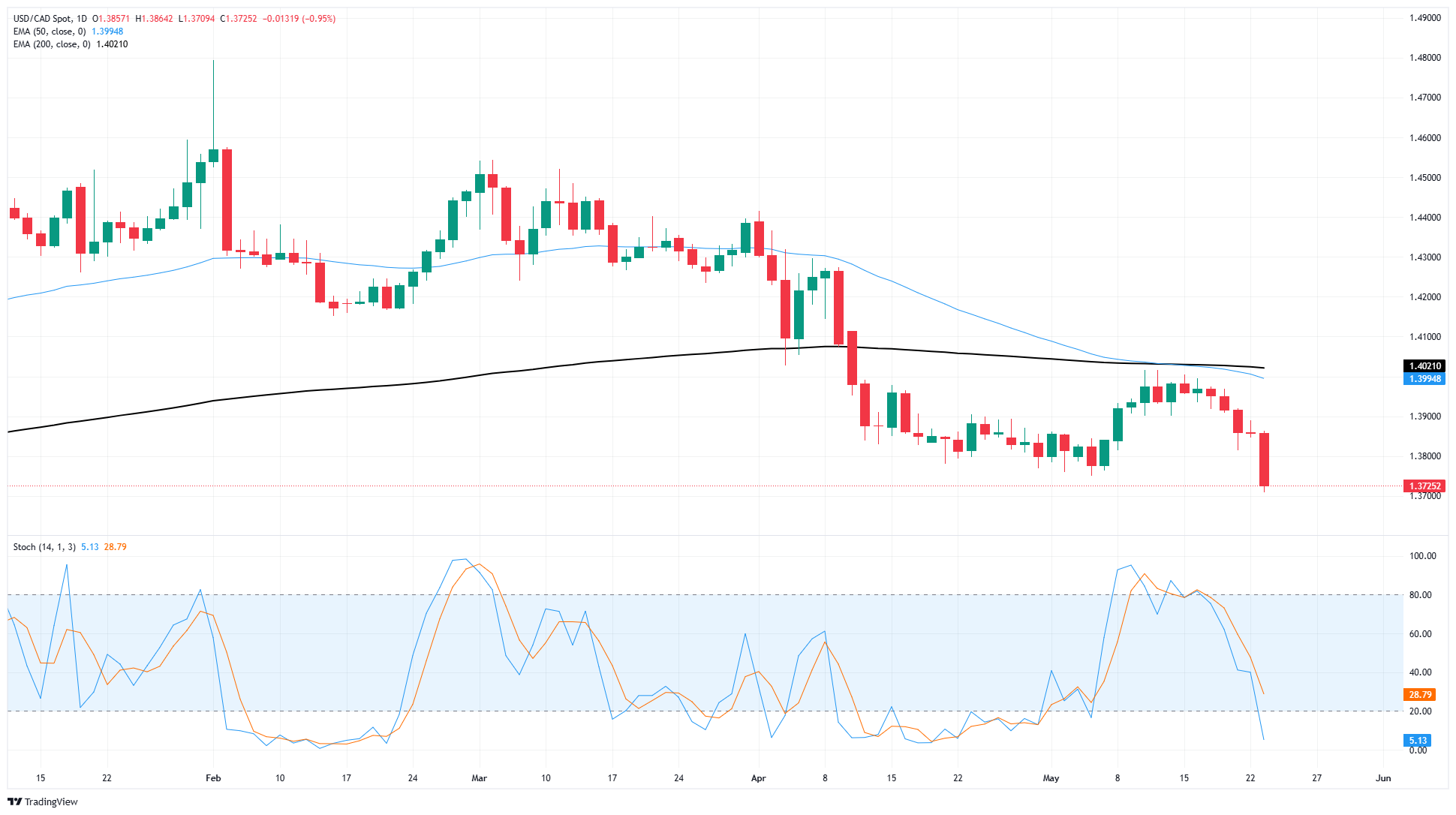
The Canadian Dollar is now testing into seven-month highs against the US Dollar, pushing into its best bids against the Greenback since last October. The Loonie is rushing to fill the void left by weakening US Dollar pressure, sending USD/CAD down toward the 1.3700 handle.
USD/CAD has declined for five consecutive trading sessions as Greenback selling picks up the pace. The pair is staring down a technical rejection of the 200-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA) near 1.4020, however too steep of a drop too quickly has snapped technical oscillators into oversold territory, implying a bounce could be on the cards.
USD/CAD daily chart
Canadian Dollar FAQs
The key factors driving the Canadian Dollar (CAD) are the level of interest rates set by the Bank of Canada (BoC), the price of Oil, Canada’s largest export, the health of its economy, inflation and the Trade Balance, which is the difference between the value of Canada’s exports versus its imports. Other factors include market sentiment – whether investors are taking on more risky assets (risk-on) or seeking safe-havens (risk-off) – with risk-on being CAD-positive. As its largest trading partner, the health of the US economy is also a key factor influencing the Canadian Dollar.
The Bank of Canada (BoC) has a significant influence on the Canadian Dollar by setting the level of interest rates that banks can lend to one another. This influences the level of interest rates for everyone. The main goal of the BoC is to maintain inflation at 1-3% by adjusting interest rates up or down. Relatively higher interest rates tend to be positive for the CAD. The Bank of Canada can also use quantitative easing and tightening to influence credit conditions, with the former CAD-negative and the latter CAD-positive.
The price of Oil is a key factor impacting the value of the Canadian Dollar. Petroleum is Canada’s biggest export, so Oil price tends to have an immediate impact on the CAD value. Generally, if Oil price rises CAD also goes up, as aggregate demand for the currency increases. The opposite is the case if the price of Oil falls. Higher Oil prices also tend to result in a greater likelihood of a positive Trade Balance, which is also supportive of the CAD.
While inflation had always traditionally been thought of as a negative factor for a currency since it lowers the value of money, the opposite has actually been the case in modern times with the relaxation of cross-border capital controls. Higher inflation tends to lead central banks to put up interest rates which attracts more capital inflows from global investors seeking a lucrative place to keep their money. This increases demand for the local currency, which in Canada’s case is the Canadian Dollar.
Macroeconomic data releases gauge the health of the economy and can have an impact on the Canadian Dollar. Indicators such as GDP, Manufacturing and Services PMIs, employment, and consumer sentiment surveys can all influence the direction of the CAD. A strong economy is good for the Canadian Dollar. Not only does it attract more foreign investment but it may encourage the Bank of Canada to put up interest rates, leading to a stronger currency. If economic data is weak, however, the CAD is likely to fall.

