EUR/USD recovers 1.1700 as US CPI and jobless claims weigh on US Dollar
- EUR/USD is boosted by softer-than-expected US CPI and highest jobless claims in nearly four years.
- Dollar weakness offsets steady Eurozone policy, with ECB confirming data-dependent and meeting-by-meeting rate stance.
- Markets see Fed easing path intact, keeping EUR/USD supported above key 1.1700 level in North American session.
EUR/USD advances during the North American session after the European Central Bank decided to hold rates unchanged, while the Greenback weakened after the Consumer Price Index (CPI) report was aligned with estimates. At the time of writing, the pair trades at 1.1733 up by 0.34%.
Euro gains 0.34% after ECB holds rates steady, weak US labor data boosts Fed cut bets
The latest inflation print in the US revealed that prices on the consumer front increased but were aligned with estimates, maintained the status quo. Initial Jobless Claims data showed that the number of Americans filling for unemployment benefits exceeded forecasts, hitting its highest level in nearly four years.
On the Euro front, the ECB maintained the Deposit Rate at 2% and noted that monetary policy decisions adjustments would be made in a meeting-by-meeting and data-dependent approach. The Governing Council revealed that they are not on a pre-committed path on rates.
Daily market movers: EUR/USD rises after US CPI figures
- US Consumer Price Index (CPI) accelerated to 2.9% YoY in August from 2.7%, in line with expectations. Core CPI held steady at 3.1% YoY, matching projections and unchanged from July’s level. Market reaction was subdued, with Fed rate-cut bets largely unaffected.
- Separately, Initial Jobless Claims for the week ending September 6 jumped to 267K, well above consensus of 235K and higher than the prior 237K, underscoring renewed weakness in the labor market.
- ECB’s President Christine Lagarde said that the disinflationary process is over, added that policy is in a good place and that today’s decision was unanimous. Furthermore, she commented that trade uncertainty has diminished and that risks to economic growth are tilted to the downside.
- The US Dollar Index (DXY), which measures the greenback against a basket of six peers, is down 0.28% at 97.53.
- Fitch Ratings Agency expects two 25 basis rate cuts, each in September and December, with three more reductions penciled in 2026. Conversely, the ratings agency does not project any rate cuts by the European Central Bank (ECB) again.
- After the data, traders had priced in a 90% chance of the Fed easing policy by 25 basis points (bps) and a 10% chance for a 50-bps cut, according to Prime Market Terminal interest rate probability tool. The ECB is likely to keep rates unchanged, with a 93% probability, and only a 7% chance of a 25-bps cut.
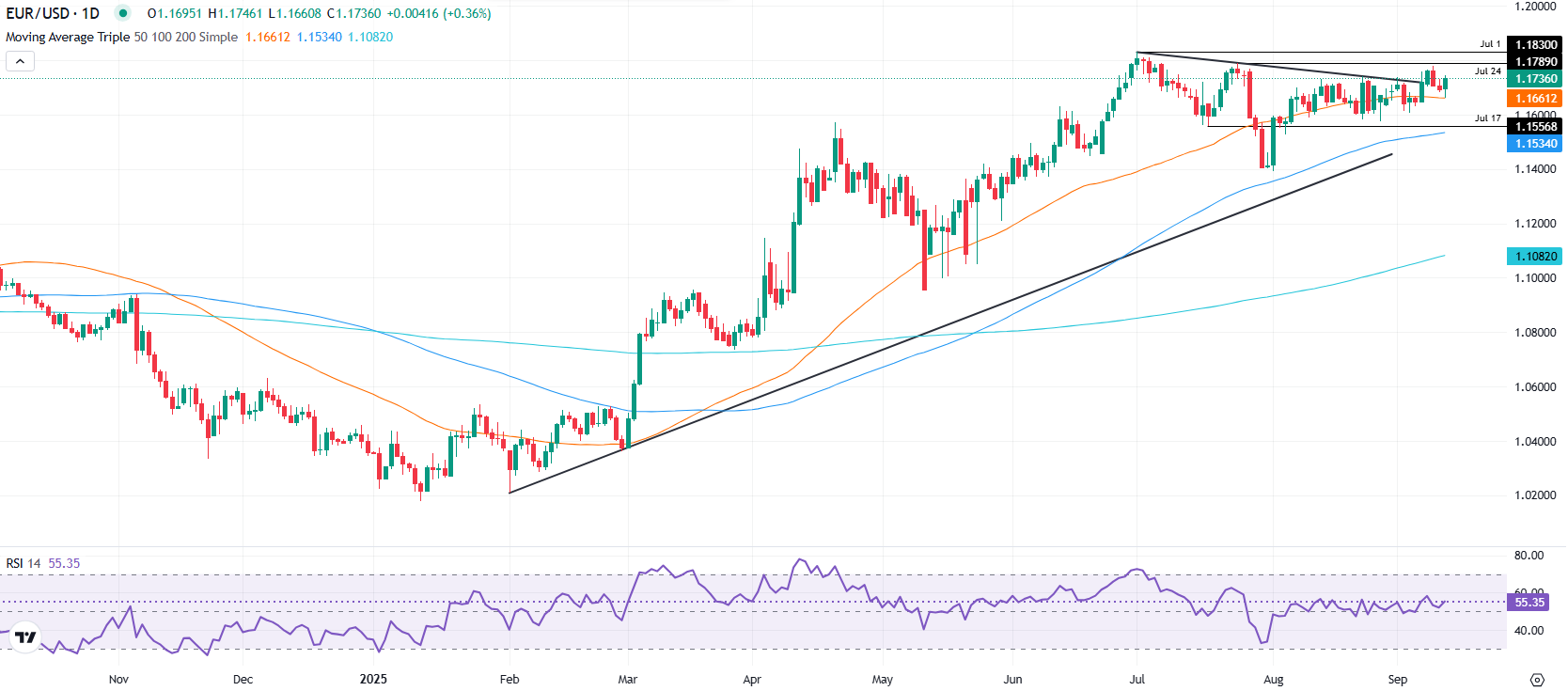
Technical outlook: EUR/USD clears 1.1700 as bulls eye 1.1800
EUR/USD resumed its uptrend on Thursday as it forms a ‘bullish engulfing’ chart pattern, a two-candlestick formation that suggests that further upside is seen. Also, momentum has improved as depicted by the Relative Strength Index (RSI), which, despite retreating, it aims higher above Wednesday’s 52 at 56.
If EUR/USD clears 1.1750, the next key resistance levels would be 1.1800 and the year-to-date high at 1.1829. Otherwise, if the pair slumps below 1.1700, the first support would be the 20-day SMA at 1.1677 and the 50-day SMA at 1.1658.
Euro FAQs
The Euro is the currency for the 19 European Union countries that belong to the Eurozone. It is the second most heavily traded currency in the world behind the US Dollar. In 2022, it accounted for 31% of all foreign exchange transactions, with an average daily turnover of over $2.2 trillion a day. EUR/USD is the most heavily traded currency pair in the world, accounting for an estimated 30% off all transactions, followed by EUR/JPY (4%), EUR/GBP (3%) and EUR/AUD (2%).
The European Central Bank (ECB) in Frankfurt, Germany, is the reserve bank for the Eurozone. The ECB sets interest rates and manages monetary policy. The ECB’s primary mandate is to maintain price stability, which means either controlling inflation or stimulating growth. Its primary tool is the raising or lowering of interest rates. Relatively high interest rates – or the expectation of higher rates – will usually benefit the Euro and vice versa. The ECB Governing Council makes monetary policy decisions at meetings held eight times a year. Decisions are made by heads of the Eurozone national banks and six permanent members, including the President of the ECB, Christine Lagarde.
Eurozone inflation data, measured by the Harmonized Index of Consumer Prices (HICP), is an important econometric for the Euro. If inflation rises more than expected, especially if above the ECB’s 2% target, it obliges the ECB to raise interest rates to bring it back under control. Relatively high interest rates compared to its counterparts will usually benefit the Euro, as it makes the region more attractive as a place for global investors to park their money.
Data releases gauge the health of the economy and can impact on the Euro. Indicators such as GDP, Manufacturing and Services PMIs, employment, and consumer sentiment surveys can all influence the direction of the single currency. A strong economy is good for the Euro. Not only does it attract more foreign investment but it may encourage the ECB to put up interest rates, which will directly strengthen the Euro. Otherwise, if economic data is weak, the Euro is likely to fall. Economic data for the four largest economies in the euro area (Germany, France, Italy and Spain) are especially significant, as they account for 75% of the Eurozone’s economy.
Another significant data release for the Euro is the Trade Balance. This indicator measures the difference between what a country earns from its exports and what it spends on imports over a given period. If a country produces highly sought after exports then its currency will gain in value purely from the extra demand created from foreign buyers seeking to purchase these goods. Therefore, a positive net Trade Balance strengthens a currency and vice versa for a negative balance.

