Dow Jones Industrial Average wobbles near record highs
- The Dow Jones opened on a cautious note despite opening near all-time highs.
- Fed rate cuts remain the key point of focus for equities.
- Investors continue to shrug off the ongoing government shutdown, at least for now.
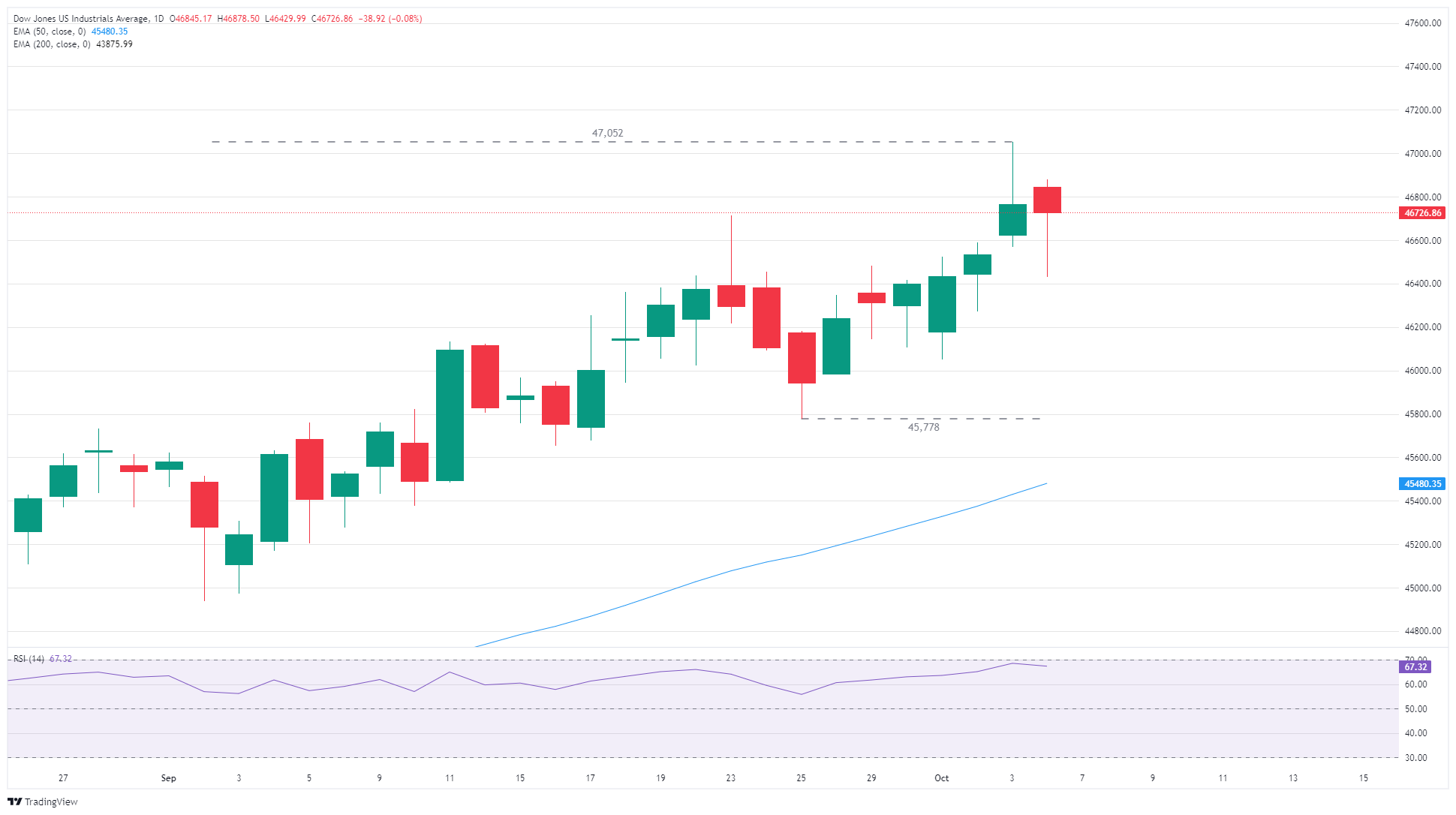
The Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) struggled to keep its footing on Monday, kicking off the new trading week opening at record highs above 46,800. The Dow slipped early on Monday after investors briefly showed frayed nerves, but general market sentiment continues to drift into the high side.
The Federal Reserve (Fed) is still firmly on pace to deliver a follow-up interest rate cut on October 29, keeping equity markets well bid as interest rate cuts remain a key point of focus for stock traders. Key economic datapoints have been suspended or delayed as a result of the US government’s ongoing shutdown, which has extended into a second week. Lacking the latest Nonfarm Payrolls (NFP) jobs report, investors are running on the assumption that the Fed will be forced to make interest rate decisions on currently available data, which tilts in favor of more rate cuts.
It's a rate cut market, and we're all just trading in it
According to the CME’s FedWatch Tool, rate markets are pricing in around 95% odds that the Fed will trim interest rates by 25 basis points on October 29, the closest to a sure thing that rate futures can provide. Rate traders are also pricing in over 80% odds of a third consecutive interest rate cut on December 10, but the long end of the tail has continued to extend, and rate odds currently place a fourth cut way out in April of 2026.
The economic data docket remains relatively mid-tier this week. The Federal Open Market Committee’s (FOMC) latest Meeting Minutes will be released on Wednesday and will give investors a closer look at the Fed’s internal dialogue from its last interest rate decision. Fed Chair Jerome Powell’s avatar will also be making a public appearance on Thursday, when a pre-recorded message by the Fed head will be released during the Community Bank Conference in Washington, DC.
Dow Jones daily chart
Dow Jones FAQs
The Dow Jones Industrial Average, one of the oldest stock market indices in the world, is compiled of the 30 most traded stocks in the US. The index is price-weighted rather than weighted by capitalization. It is calculated by summing the prices of the constituent stocks and dividing them by a factor, currently 0.152. The index was founded by Charles Dow, who also founded the Wall Street Journal. In later years it has been criticized for not being broadly representative enough because it only tracks 30 conglomerates, unlike broader indices such as the S&P 500.
Many different factors drive the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA). The aggregate performance of the component companies revealed in quarterly company earnings reports is the main one. US and global macroeconomic data also contributes as it impacts on investor sentiment. The level of interest rates, set by the Federal Reserve (Fed), also influences the DJIA as it affects the cost of credit, on which many corporations are heavily reliant. Therefore, inflation can be a major driver as well as other metrics which impact the Fed decisions.
Dow Theory is a method for identifying the primary trend of the stock market developed by Charles Dow. A key step is to compare the direction of the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) and the Dow Jones Transportation Average (DJTA) and only follow trends where both are moving in the same direction. Volume is a confirmatory criteria. The theory uses elements of peak and trough analysis. Dow’s theory posits three trend phases: accumulation, when smart money starts buying or selling; public participation, when the wider public joins in; and distribution, when the smart money exits.
There are a number of ways to trade the DJIA. One is to use ETFs which allow investors to trade the DJIA as a single security, rather than having to buy shares in all 30 constituent companies. A leading example is the SPDR Dow Jones Industrial Average ETF (DIA). DJIA futures contracts enable traders to speculate on the future value of the index and Options provide the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell the index at a predetermined price in the future. Mutual funds enable investors to buy a share of a diversified portfolio of DJIA stocks thus providing exposure to the overall index.




