Gold advances as shutdown looms, weak US data fuels rate cut bets
- XAU/USD trades near $3,846 as looming US government shutdown sparks investor flight into precious metals.
- JOLTS vacancies edge up, but Consumer Confidence drops, signaling weaker outlook for jobs and business conditions.
- Markets price in 96% chance of October Fed cut, reinforcing bullish momentum for the non-yielding, safe-haven asset.
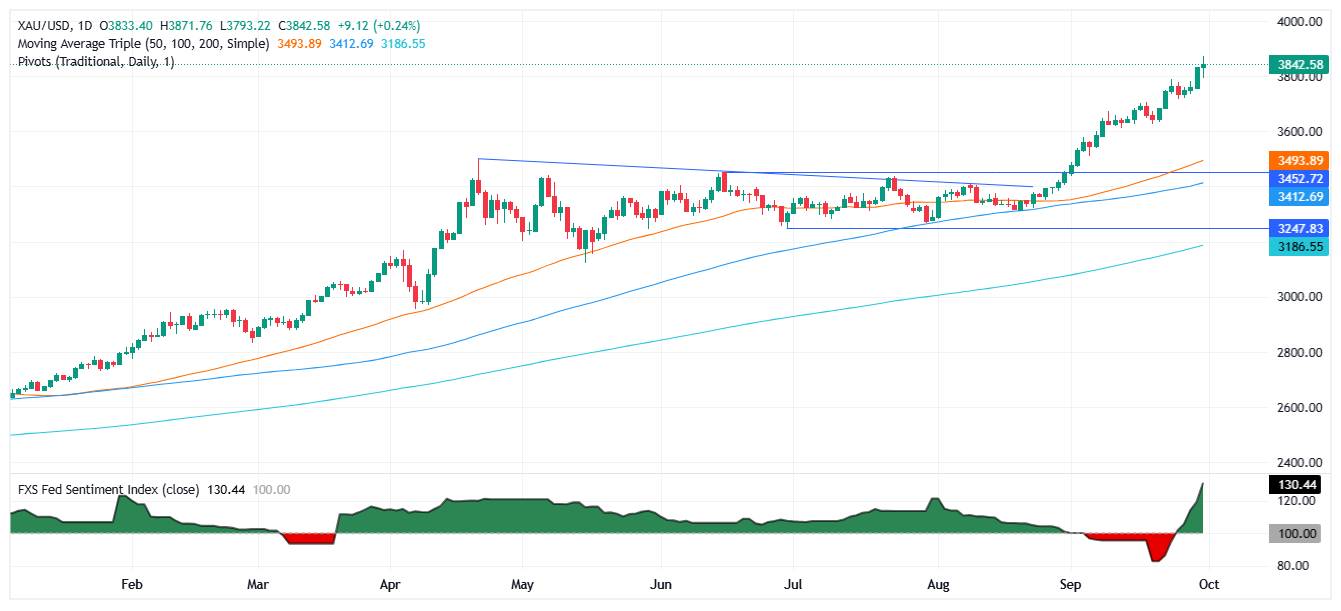
Gold climbs during the North American session on Tuesday yet remains below the record high hit in the Asian session of $3,871. Amid fears of a US government shutdown, jobs data reaffirmed expectations of rate cuts by the Federal Reserve (Fed). XAU/USD trades at $3,846, up 0.35%.
Bullion steadies as US Dollar weakness underpins safe-haven demand
The latest Job Openings and Labor Turnover Survey (JOLTS) revealed by the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) showed that US vacancies increased slightly but exceeded estimates. Meanwhile, the Conference Board's Consumer Confidence showed that Americans are growing pessimistic regarding current business and labor market conditions.
Bullion’s rally is being boosted by broad US Dollar weakness, amid a looming federal government shutdown. In the meantime, US President Donald Trump said that he had a good discussion with Democratic Congressional leaders Schumer and Jeffriesbut said to expect a government shutdown.
The US Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) revealed on Monday that a shutdown would delay the announcement of jobs data.
Expectations that the Fed would reduce rates at the October 29 meeting remain high, standing at 96% for a 25-basis-point rate cut and a 4% chance of holding rates unchanged.
Ahead the docket will feature a flurry of Fed speakers, US ADP National Employment Change, the ISM Manufacturing PMI, Initial Jobless Claims and Nonfarm Payrolls for September.
Daily market movers: Gold price uptrend to extend on weak US Dollar
- Bullion prices advance as the Greenback edges down as shown by the US Dollar Index (DXY). DXY, which tracks the buck’s value against a basket of six currencies, is down 0.17% at 97.78.
- US Treasury yields remain steady with the 10-year Treasury note unchanged at 4.146%. US real yields are also unchanged at 1.796%.
- Job Openings in the US showed the labor market is slowing, yet vacancies rose from 7.21 million to 7.23 million in August. Digging into the data, the hiring rate edged down to 3.2%, the lowest level since June 2024, while layoffs remained at a low level.
- Consumer Confidence in September missed estimates of 96.0, dipping from 97.6 in August to 94.2. “Consumer confidence weakened in September, declining to the lowest level since April 2025,” said Conference Board senior economist Stephanie Guichard.
- Fed Vice-Chair Philip Jefferson said that the labor market is softening and expects disinflation to resume after 2025.
- Boston Fed's Susan Collins said that it may be appropriate to cut rates gains if data supports easing. She favors a modestly restrictive policy due to inflation and added that inflation will be elevated going into 2026, and then it should ease. She added that gradual rate cuts are likely if the economy meets expectations but warned against aggressive cuts.
- Chicago Fed's Austan Goolsbee said that the US seems headed into a new wave of tariffs. He added the labor market remains “pretty steady,” and if inflation proves to be persistent, that would be a difficult scenario for the Fed.
Technical outlook: Gold price poised to challenge $3,900
Gold price uptrend remains in place, though set to end the day above $3,850 shy of the all-time high of $3,871. The Relative Strength Index (RSI), although overbought, remains stuck within the 70-80 level, an indication that bulls remain in charge.
If Gold clears $3,850, this clears the path to test the previous peak ahead of $3,900. A breach of the latter will expose $3,950 and the $4,000 mark.
On the other hand, if XAU/USD tumbles below $3,800, further downside is expected. The next support would be the $3,750 mark, followed by $3,700 and the 20-day Simple Moving Average (SMA) at $3,666.
Gold FAQs
Gold has played a key role in human’s history as it has been widely used as a store of value and medium of exchange. Currently, apart from its shine and usage for jewelry, the precious metal is widely seen as a safe-haven asset, meaning that it is considered a good investment during turbulent times. Gold is also widely seen as a hedge against inflation and against depreciating currencies as it doesn’t rely on any specific issuer or government.
Central banks are the biggest Gold holders. In their aim to support their currencies in turbulent times, central banks tend to diversify their reserves and buy Gold to improve the perceived strength of the economy and the currency. High Gold reserves can be a source of trust for a country’s solvency. Central banks added 1,136 tonnes of Gold worth around $70 billion to their reserves in 2022, according to data from the World Gold Council. This is the highest yearly purchase since records began. Central banks from emerging economies such as China, India and Turkey are quickly increasing their Gold reserves.
Gold has an inverse correlation with the US Dollar and US Treasuries, which are both major reserve and safe-haven assets. When the Dollar depreciates, Gold tends to rise, enabling investors and central banks to diversify their assets in turbulent times. Gold is also inversely correlated with risk assets. A rally in the stock market tends to weaken Gold price, while sell-offs in riskier markets tend to favor the precious metal.
The price can move due to a wide range of factors. Geopolitical instability or fears of a deep recession can quickly make Gold price escalate due to its safe-haven status. As a yield-less asset, Gold tends to rise with lower interest rates, while higher cost of money usually weighs down on the yellow metal. Still, most moves depend on how the US Dollar (USD) behaves as the asset is priced in dollars (XAU/USD). A strong Dollar tends to keep the price of Gold controlled, whereas a weaker Dollar is likely to push Gold prices up.

