Canadian Dollar rebounds after losing ground for a week straight
- The Canadian Dollar showed signs of life on Monday, clawing back a scant 0.15% against the US Dollar.
- The Canadian side of the economic data docket this week remains thin.
- Key US data looms ahead, but a government shutdown could delay the figures.
The Canadian Dollar (CAD) showed a pulse on Monday, rebounding against the US Dollar (USD) after five straight sessions of declines. The Loonie caught a much-needed bullish boost to pump the brake’s against the Greenback’s broad-market decline, and investors are gearing up for a tense week of politics watching.
The latest US Nonfarm Payrolls (NFP) jobs data is technically due this Friday, but a looming government shutdown could see the national jobs figure delayed by the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) if the US government can’t figure out how to meet its funding obligations this week.
The latest Canadian Purchasing Managers Index (PMI) figures from September are due on Wednesday, followed by the Summary of Deliberations, or meeting minutes, from the Bank of Canada’s (BoC) latest interest rate decision.
Daily digest market movers: Canadian Dollar finally comes up for air on Monday
- The Canadian Dollar snapped a five-session losing streak against the US Dollar on Monday, pumping the brakes near the 1.3900 handle on the USD/CAD chart.
- The Canadian Dollar has lost ground against the US Dollar for all but one of the last eight consecutive market sessions, falling nearly 1.7% top-to-bottom against the Greenback in the process.
- The BoC’s latest meeting minutes, due on Wednesday, will draw some attention as CAD traders weigh odds of another interest rate cut from the cut-happy BoC.
- The market is beholden to political headlines this week: If the two sides of US Congress can’t find enough common ground to pass a basic budget spending bill, the US government could be heading into a budgetary shutdown.
- The Trump administration has overspent its budget limits every single month since Trump took office in January, rapidly depleting the federal government’s operations coffers.
Canadian Dollar price forecast
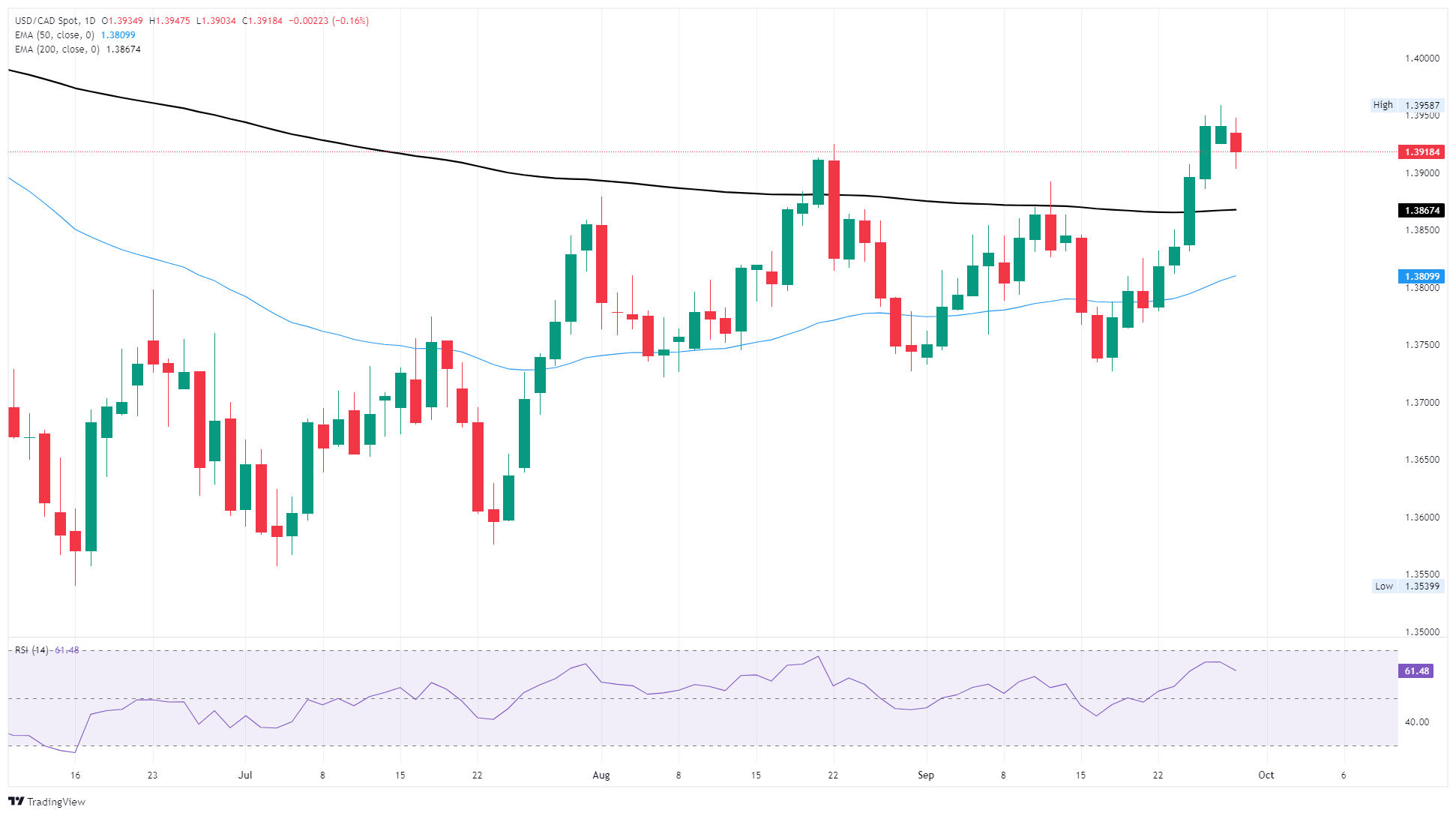
USD/CAD has transitioned from a choppy consolidation between 1.3600 and 1.3800 into a more decisive bullish move, confirmed by the break above the 200-day EMA. This is a classic bullish development, often seen as a longer-term trend reversal signal when combined with a rising 50-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA). The 1.4000 handle is the next key resistance area. Price has rejected this zone before, so bulls will need a clean daily close above 1.4015 to confirm further upside.
Immediate support sits at the 200-day EMA near 1.3870 and then at the 50-day EMA at 1.3810. These levels should act as a cushion if price pulls back. The Relative Strength Index (RSI) in the low 60s indicates bullish momentum is building, but not yet stretched. This suggests there’s room for continuation higher before conditions become overbought.
USD/CAD daily chart
Canadian Dollar FAQs
The key factors driving the Canadian Dollar (CAD) are the level of interest rates set by the Bank of Canada (BoC), the price of Oil, Canada’s largest export, the health of its economy, inflation and the Trade Balance, which is the difference between the value of Canada’s exports versus its imports. Other factors include market sentiment – whether investors are taking on more risky assets (risk-on) or seeking safe-havens (risk-off) – with risk-on being CAD-positive. As its largest trading partner, the health of the US economy is also a key factor influencing the Canadian Dollar.
The Bank of Canada (BoC) has a significant influence on the Canadian Dollar by setting the level of interest rates that banks can lend to one another. This influences the level of interest rates for everyone. The main goal of the BoC is to maintain inflation at 1-3% by adjusting interest rates up or down. Relatively higher interest rates tend to be positive for the CAD. The Bank of Canada can also use quantitative easing and tightening to influence credit conditions, with the former CAD-negative and the latter CAD-positive.
The price of Oil is a key factor impacting the value of the Canadian Dollar. Petroleum is Canada’s biggest export, so Oil price tends to have an immediate impact on the CAD value. Generally, if Oil price rises CAD also goes up, as aggregate demand for the currency increases. The opposite is the case if the price of Oil falls. Higher Oil prices also tend to result in a greater likelihood of a positive Trade Balance, which is also supportive of the CAD.
While inflation had always traditionally been thought of as a negative factor for a currency since it lowers the value of money, the opposite has actually been the case in modern times with the relaxation of cross-border capital controls. Higher inflation tends to lead central banks to put up interest rates which attracts more capital inflows from global investors seeking a lucrative place to keep their money. This increases demand for the local currency, which in Canada’s case is the Canadian Dollar.
Macroeconomic data releases gauge the health of the economy and can have an impact on the Canadian Dollar. Indicators such as GDP, Manufacturing and Services PMIs, employment, and consumer sentiment surveys can all influence the direction of the CAD. A strong economy is good for the Canadian Dollar. Not only does it attract more foreign investment but it may encourage the Bank of Canada to put up interest rates, leading to a stronger currency. If economic data is weak, however, the CAD is likely to fall.

