Gold price falls as US-China tariff talks ease tensions, Fed in focus
- XAU/USD drops as risk appetite improves, traders await Powell's remarks.
- US-China trade talks set to begin in Switzerland, calming markets and lifting the US Dollar.
- Despite the pullback, Gold remains underpinned by global geopolitical risks and central bank buying.
- Fed expected to hold rates steady; Powell’s tone to guide next policy move.
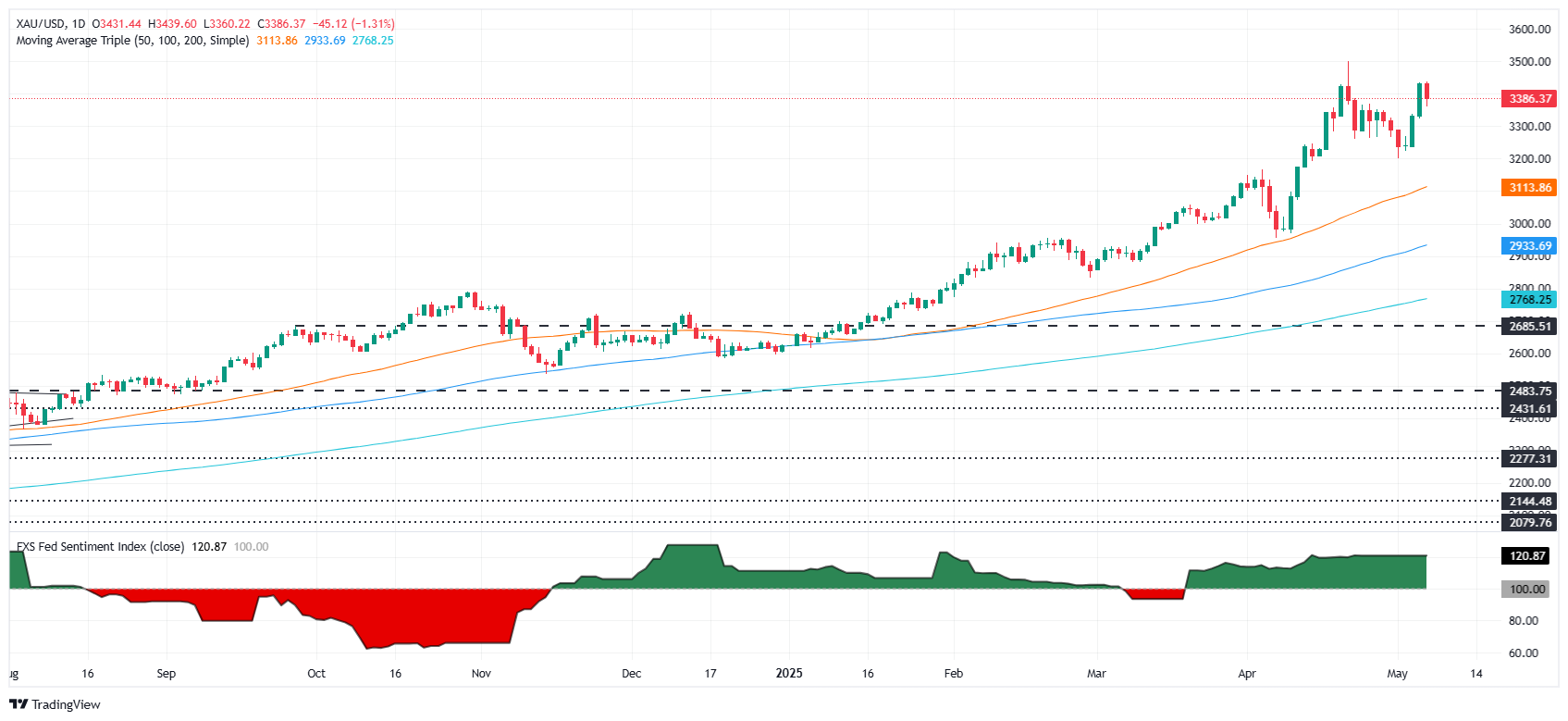
Gold prices retreated by more than 1.50% on Wednesday, driven by an improvement in risk appetite following the announcement of tariff talks between the United States (US) and China. Meanwhile, traders' focus is on the Federal Reserve’s (Fed) monetary policy meeting later in the day. XAU/USD trades at $3,384 after hitting a daily peak of $3,438.
On Tuesday, news that US Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent and China’s Vice Premier He Lifeng will meet in Switzerland calmed investors' fears about the trade war. Hence, the Greenback recovered some ground as traders booked profits and bought the US Dollar (USD) against its peers.
Despite this, Bullion prices are set to continue rallying amid the ongoing geopolitical conflicts between Russia and Ukraine, Israel and Hamas and India and Pakistan.
Central banks continued to add Gold to their reserves
The World Gold Council revealed that central banks from China, Poland and the Czech Republic increased their Bullion reserves in April.
Traders' eyes are on the Fed, which is expected to keep rates unchanged for the third time in 2025 at 18:00 GMT. Nevertheless, the spotlight will be on Fed Chair Jerome Powell's comments at the press conference at 18:30 GMT.
Before the meeting, policymakers expressed that the policy is appropriate to balance the central bank’s dual mandate.
Daily digest market movers: Gold rally halts as central banks continue to add Bullion to their reserves
- The Greenback’s recovery is a headwind for Bullion prices. The US Dollar Index (DXY), which tracks the buck’s value against a basket of six currencies, is up 0.13% at 99.52.
- Steady US Treasury yields have capped the Gold price rally. The US 10-year Treasury note yield is firm at 4.291%. Meanwhile, US real yields remain flat at 2.029%, as indicated by the US 10-year Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities yields.
- Data from the World Gold Council (WGC) revealed the People’s Bank of China (PBoC) added 2 tonnes to its Gold reserves in April – for the sixth consecutive month. Krishan Gopaul, Senior Analyst, EMEA, at the WGC, added, “Year-to-date net purchases now total 15 tonnes, helping to lift gold reserves to 2,294 tonnes.”
- The National Bank of Poland (NBP) increased 12 tonnes in April to 509 tonnes, while the Czech National Bank increased its reserves by 2.5 tonnes in April.
- Swap markets have so far priced in the Fed’s first 25 basis points (bps) rate cut for the July meeting, and they expect two additional reductions towards the end of the year.
XAU/USD technical outlook: Gold price trapped within the $3,350-$3,400 range
Gold price retreats below $3,400, but it remains bullish. Nevertheless, buyers must reclaim the latter so they can remain hopeful of reaching the $3,450 mark. If these levels are taken out, bulls could test $3,500 Bullion’s all-time high (ATH)
On the other hand, Gold prices falling below $3,350 could pave the path to test the May 1 cycle low of $3,202. A decline beneath and sellers could challenge the 50-day Simple Moving Average (SMA) at $3,113.
Gold FAQs
Gold has played a key role in human’s history as it has been widely used as a store of value and medium of exchange. Currently, apart from its shine and usage for jewelry, the precious metal is widely seen as a safe-haven asset, meaning that it is considered a good investment during turbulent times. Gold is also widely seen as a hedge against inflation and against depreciating currencies as it doesn’t rely on any specific issuer or government.
Central banks are the biggest Gold holders. In their aim to support their currencies in turbulent times, central banks tend to diversify their reserves and buy Gold to improve the perceived strength of the economy and the currency. High Gold reserves can be a source of trust for a country’s solvency. Central banks added 1,136 tonnes of Gold worth around $70 billion to their reserves in 2022, according to data from the World Gold Council. This is the highest yearly purchase since records began. Central banks from emerging economies such as China, India and Turkey are quickly increasing their Gold reserves.
Gold has an inverse correlation with the US Dollar and US Treasuries, which are both major reserve and safe-haven assets. When the Dollar depreciates, Gold tends to rise, enabling investors and central banks to diversify their assets in turbulent times. Gold is also inversely correlated with risk assets. A rally in the stock market tends to weaken Gold price, while sell-offs in riskier markets tend to favor the precious metal.
The price can move due to a wide range of factors. Geopolitical instability or fears of a deep recession can quickly make Gold price escalate due to its safe-haven status. As a yield-less asset, Gold tends to rise with lower interest rates, while higher cost of money usually weighs down on the yellow metal. Still, most moves depend on how the US Dollar (USD) behaves as the asset is priced in dollars (XAU/USD). A strong Dollar tends to keep the price of Gold controlled, whereas a weaker Dollar is likely to push Gold prices up.

