Silver Price Forecast: XAG/USD bearish correction finds support at $34.00
- Silver corrects lower on Tuesday amid a stronger US Dollar.
- The broader trend remains positive, with bears limited above $34.00.
- XAG/USD faces significant resistance ahead of the $35.00 level.
Silver prices (XAG/USD) are trading lower on Tuesday’s European session, weighed by a somewhat firmer US Dollar, as the risk-off mood witnessed on Monday seems to have eased.
The precious metal hit fresh six-month highs on Monday, with the US Dollar hammered by renewed tariff concerns and downbeat US data. The US Manufacturing PMI confirmed the negative impact of tariffs on factory activity and pushed the US Dollar to fresh multi-month lows.
Technical analysis: Silver’s broader trend remains positive
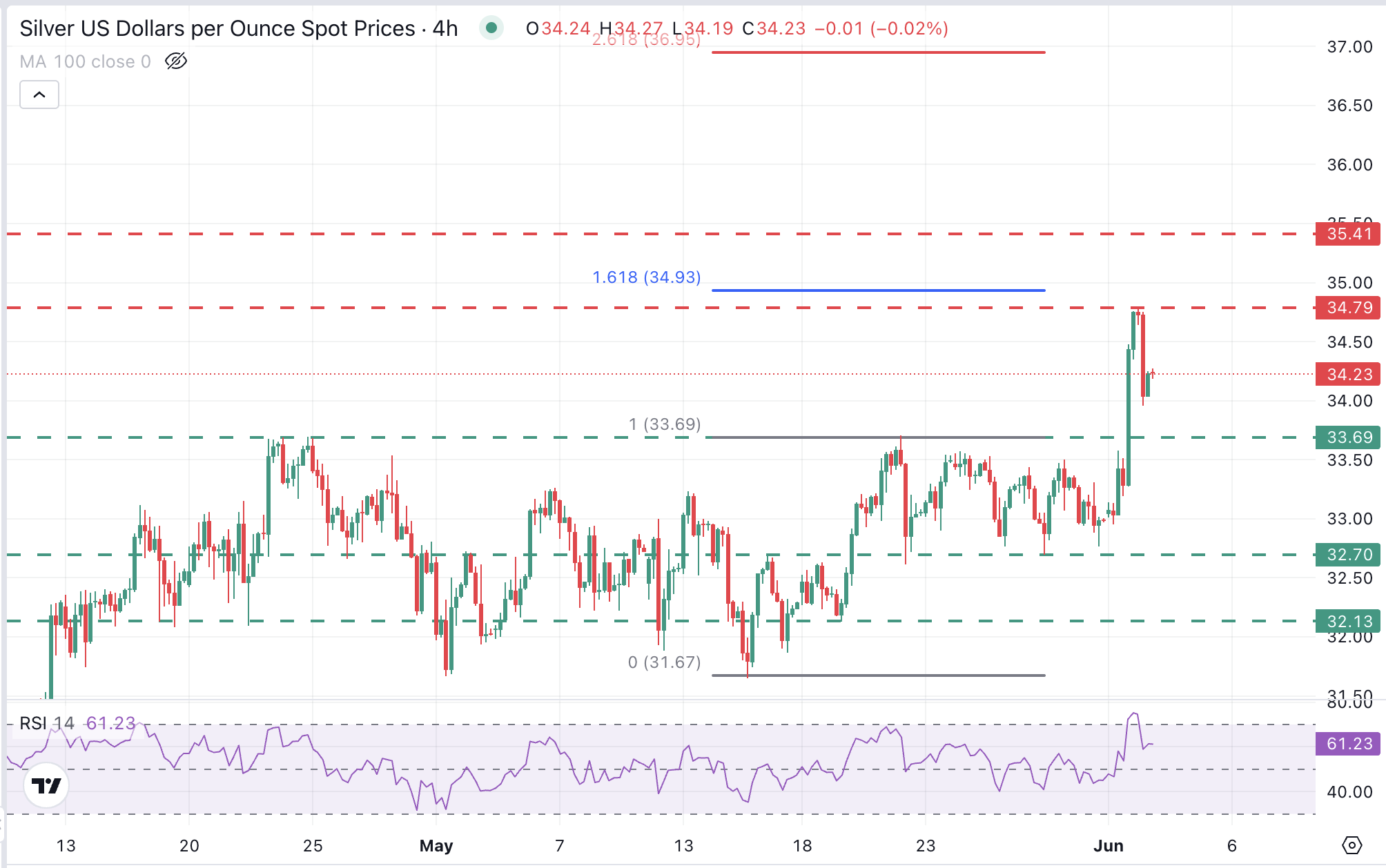
From a wider perspective, price action remains positive. The reversal from $34.75 has been contained at the 34.00 round level, above the previous resistance, now a potential support area, at $33.70.
On the upside, the area between $34.75 and $35.00 contains several resistance levels (October 23 and June 4 highs), and the 161.8% Fibonacci extension of the Mid may rally, and might be a tough nut to crack.
Above here, a late 2012 peak lies at $35.40. The 2611.8% Fiboinnacci retracement is at $37.00.
On the downside, immediate support is at the mentioned $33.70 and then at the $32.65-$32.75 zone.
XAG/USD 4-Hour Chart
Silver FAQs
Silver is a precious metal highly traded among investors. It has been historically used as a store of value and a medium of exchange. Although less popular than Gold, traders may turn to Silver to diversify their investment portfolio, for its intrinsic value or as a potential hedge during high-inflation periods. Investors can buy physical Silver, in coins or in bars, or trade it through vehicles such as Exchange Traded Funds, which track its price on international markets.
Silver prices can move due to a wide range of factors. Geopolitical instability or fears of a deep recession can make Silver price escalate due to its safe-haven status, although to a lesser extent than Gold's. As a yieldless asset, Silver tends to rise with lower interest rates. Its moves also depend on how the US Dollar (USD) behaves as the asset is priced in dollars (XAG/USD). A strong Dollar tends to keep the price of Silver at bay, whereas a weaker Dollar is likely to propel prices up. Other factors such as investment demand, mining supply – Silver is much more abundant than Gold – and recycling rates can also affect prices.
Silver is widely used in industry, particularly in sectors such as electronics or solar energy, as it has one of the highest electric conductivity of all metals – more than Copper and Gold. A surge in demand can increase prices, while a decline tends to lower them. Dynamics in the US, Chinese and Indian economies can also contribute to price swings: for the US and particularly China, their big industrial sectors use Silver in various processes; in India, consumers’ demand for the precious metal for jewellery also plays a key role in setting prices.
Silver prices tend to follow Gold's moves. When Gold prices rise, Silver typically follows suit, as their status as safe-haven assets is similar. The Gold/Silver ratio, which shows the number of ounces of Silver needed to equal the value of one ounce of Gold, may help to determine the relative valuation between both metals. Some investors may consider a high ratio as an indicator that Silver is undervalued, or Gold is overvalued. On the contrary, a low ratio might suggest that Gold is undervalued relative to Silver.

